Microsoft Word - no15.docx
|
|
|
- かおり あきます
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ex33.c /* */ #define IDLENGTH 7 /* */ #define MAX 100 /* */ /* */ struct student char idnumber[idlength + 1]; /* */ int math; /* () */ int english; /* () */ int japanese; /* () */ double average; /* */ ; /* */ void printstudent(struct student x); int main(void) struct student student[30]; /* */ int numstudent = 0; /* */ int i, j; while((numstudent < 1) (numstudent > MAX)) printf("(1-%d): ", MAX); scanf("%d", &numstudent); /* */ for(i = 0; i < numstudent; i++) printf("%d :\n : ", i + 1); scanf("%7s", student[i].idnumber); printf(": "); scanf("%d", &(student[i].math)); printf(": "); scanf("%d", &(student[i].english)); printf(": "); scanf("%d", &(student[i].japanese)); student[i].average = (double)(student[i].math + student[i].english + student[i].japanese) / 3;
2 /* */ printf("\n\n :\n"); for(i = 0; i < numstudent; i++) printstudent(student[i]); return (0); /* */ void printstudent(struct student x) printf("%10s: %3d %3d %3d %6.2f\n", x.idnumber, x.math, x.english, x.japanese, x.average); student (infomation) ex34.c /* */ /* */ struct fraction int sgn; /* sign */ int num; /* numerator */ int den; /* denominator */ ; /* */ struct fraction input_fraction(void); void print_fraction(struct fraction); struct fraction reduce_fraction(struct fraction); struct fraction add_fraction(struct fraction, struct fraction); int gcd(int, int); int main(void) struct fraction x, y, z; printf(" n"); x = input_fraction(); printf(" n"); y = input_fraction(); z = add_fraction(x, y); printf(" n"); print_fraction(z);
3 return(0); /* */ struct fraction input_fraction(void) struct fraction a; a.sgn = 1; printf(":"); scanf("%d", &(a.num)); if(a.num < 0) a.sgn = -a.sgn; a.num = -a.num; printf(":"); scanf("%d", &(a.den)); if(a.den < 0) a.sgn = -a.sgn; a.den = -a.den; return(a); /* */ void print_fraction(struct fraction a) if(a.den > 1) printf("%13d n", a.num); if(a.sgn < 0) printf("- "); /* */ else printf(" "); /* */ printf(" n"); /* */ printf("%13d n", a.den); else printf("%d n", a.sgn * a.num); /* */ struct fraction add_fraction(struct fraction x, struct fraction y) struct fraction z; z.sgn = 1; z.den = x.den * y.den; z.num = x.sgn * x.num * y.den + y.sgn * y.num * x.den; if(z.num < 0) z.sgn = -z.sgn; z.num = -z.num; return(reduce_fraction(z));
4 /* */ struct fraction reduce_fraction(struct fraction a) int m = gcd(a.num, a.den); a.num /= m; a.den /= m; return(a); /* */ int gcd(int p, int q) /* */ int r; for(r = p % q; r > 0; r = p % q) p = q; q = r; return (q);
5 : 12ff80 12ff81 int 5 12ff82 12ff83 12ff84 12ff85 12ff86 12ff87 double ff88 12ff89 12ff8A 12ff8B 12ff8C short int 5 12ff8D 12ff8E char 'x' :
6 ex35.c /* */ int main(void) int i; /* i int */ int *j; /* j int */ i = 5; /* i 5 */ j = &i; /* j i */ *j = 8; /* j 8 */ printf("i = %d\n", i); /* i */ printf("&i = %d\n", &i); /* i */ printf("&i = %x\n", &i); /* i (16 ) */ printf("sizeof(i)= %d\n", sizeof(i)); /* i */ printf("j = %d\n", j); /* j */ printf("*j = %d\n", *j); /* j */ printf("&j = %x\n", &j); /* j (16 ) */ printf("sizeof(j)= %d\n", sizeof(j)); /* j */ return(0); "&" "*" "*" "*" & j i
7 /* */ int main(void) int *j; /* j int */ *j = 8; /* j 8 printf("j = %d\n", j); /* j */ printf("*j = %d\n", *j); /* j */ return(0); j 8 j *; ex36.c /* */ /* */ void exchange (int *x, int *y); int main(void) int m = 5, n = 10; printf(": m = %d, n = %d\n", m, n);
8 printf("exchange(&m, &n)\n"); exchange(&m, &n); /* & */ printf(": m = %d, n = %d\n", m, n); return(0); void exchange (int *x, int *y) /* */ /* x *x */ /* y *y */ int t; /* */ t = *x; *x = *y; *y = t; /* x y */ *x, *y * &** & scanf '&' scanf & scanf : m 5 n 10 : x y t : scanf("", &,...); scanf("",,...);
Microsoft Word - no13.docx
 4. 構造体 4.1 構造体とは たとえば 分数をそのまま扱うときを考えてみましょう 分数は分子と分母の 2 つの部分からな っていることから 2 つの変数を用いて表すことが必要です ここでは約分も行うこととします ex34.c /* 分数の計算 */ int gcd(int m, int n); int a_num, a_den; /* 分数 a */ int b_num, b_den; /* 分数
4. 構造体 4.1 構造体とは たとえば 分数をそのまま扱うときを考えてみましょう 分数は分子と分母の 2 つの部分からな っていることから 2 つの変数を用いて表すことが必要です ここでは約分も行うこととします ex34.c /* 分数の計算 */ int gcd(int m, int n); int a_num, a_den; /* 分数 a */ int b_num, b_den; /* 分数
Microsoft Word - no12.doc
 7.5 ポインタと構造体 構造体もメモリのどこかに値が格納されているのですから 構造体へのポインタ も存在します また ポインタも変数ですから 構造体のメンバに含めることができます まずは 構造体へのポインタをあつかってみます ex53.c /* 成績表 */ #define IDLENGTH 7 /* 学籍番号の長さ */ #define MAX 100 /* 最大人数 */ /* 成績管理用の構造体の定義
7.5 ポインタと構造体 構造体もメモリのどこかに値が格納されているのですから 構造体へのポインタ も存在します また ポインタも変数ですから 構造体のメンバに含めることができます まずは 構造体へのポインタをあつかってみます ex53.c /* 成績表 */ #define IDLENGTH 7 /* 学籍番号の長さ */ #define MAX 100 /* 最大人数 */ /* 成績管理用の構造体の定義
17 1. strucr Potter ( ) Harry Potter and the Philosopher s Stone 1997 English Title : Harry Potter and the Philosopher s Stone : : 1997 #include<stdio
 17 1. strucr Potter ( ) Harry Potter and the Philosopher s Stone 1997 English Title : Harry Potter and the Philosopher s Stone : : 1997 #include typedef struct Potter{ Potter; int main(void){
17 1. strucr Potter ( ) Harry Potter and the Philosopher s Stone 1997 English Title : Harry Potter and the Philosopher s Stone : : 1997 #include typedef struct Potter{ Potter; int main(void){
main
 14 1. 12 5 main 1.23 3 1.230000 3 1.860867 1 2. 1988 1925 1911 1867 void JPcalendar(int x) 1987 1 64 1 1 1 while(1) Ctrl C void JPcalendar(int x){ if (x > 1988) printf(" %d %d \n", x, x-1988); else if(x
14 1. 12 5 main 1.23 3 1.230000 3 1.860867 1 2. 1988 1925 1911 1867 void JPcalendar(int x) 1987 1 64 1 1 1 while(1) Ctrl C void JPcalendar(int x){ if (x > 1988) printf(" %d %d \n", x, x-1988); else if(x
Microsoft Word - no14.docx
 ex26.c #define MAX 20 int max(int n, int x[]); int num[max]; int i, x; printf(" "); scanf("%d", &x); if(x > MAX) printf("%d %d \n", MAX, MAX); x = MAX; for(i = 0; i < x; i++) printf("%3d : ", i + 1); scanf("%d",
ex26.c #define MAX 20 int max(int n, int x[]); int num[max]; int i, x; printf(" "); scanf("%d", &x); if(x > MAX) printf("%d %d \n", MAX, MAX); x = MAX; for(i = 0; i < x; i++) printf("%3d : ", i + 1); scanf("%d",
PowerPoint Presentation
 p.130 p.198 p.208 2 double weight[num]; double min, max; min = max = weight[0]; for( i= 1; i i < NUM; i++ ) ) if if ( weight[i] > max ) max = weight[i]: if if ( weight[i] < min ) min = weight[i]: weight
p.130 p.198 p.208 2 double weight[num]; double min, max; min = max = weight[0]; for( i= 1; i i < NUM; i++ ) ) if if ( weight[i] > max ) max = weight[i]: if if ( weight[i] < min ) min = weight[i]: weight
P02.ppt
 int If 2 1 ,,, 3 a + b ab a - b ab a * b ab a / b ab a % b ab a + b 4 2 list0201.c /, % /*/ int vx, vy; puts(""); printf("vx"); scanf("%d", &vx); printf("vy"); scanf("%d", &vy); printf("vx + vy = %d\n",
int If 2 1 ,,, 3 a + b ab a - b ab a * b ab a / b ab a % b ab a + b 4 2 list0201.c /, % /*/ int vx, vy; puts(""); printf("vx"); scanf("%d", &vx); printf("vy"); scanf("%d", &vy); printf("vx + vy = %d\n",
 C V C 6 1 6.1.............................. 1 6.......................... 3 6.3..................... 5 6.4 NULL............................. 8 6.5......................... 9 6.6..............................
C V C 6 1 6.1.............................. 1 6.......................... 3 6.3..................... 5 6.4 NULL............................. 8 6.5......................... 9 6.6..............................
Microsoft Word - no15.docx
 7. ファイルいままでは プログラムを実行したとき その結果を画面で確認していました 簡単なものならそれでもいいのですか 複雑な結果は画面で見るだけでなく ファイルに保存できればよいでしょう ここでは このファイルについて説明します 使う関数のプロトタイプは次のとおりです FILE *fopen(const char *filename, const char *mode); ファイルを読み書きできるようにする
7. ファイルいままでは プログラムを実行したとき その結果を画面で確認していました 簡単なものならそれでもいいのですか 複雑な結果は画面で見るだけでなく ファイルに保存できればよいでしょう ここでは このファイルについて説明します 使う関数のプロトタイプは次のとおりです FILE *fopen(const char *filename, const char *mode); ファイルを読み書きできるようにする
演算増幅器
 構造体 ここまでに char int doulbe などの基本的なデータ型に加えて 同じデータ型が連続している 配列についてのデータ構造について習った これ以外にも もっと複雑なデータ型をユーザが定義 することが可能である それが構造体と呼ばれるもので 異なる型のデータをひとかたまりのデー タとして扱うことができる 異なるデータをまとめて扱いたい時とはどんな場合だろうか 例えば 住民データを管理したい
構造体 ここまでに char int doulbe などの基本的なデータ型に加えて 同じデータ型が連続している 配列についてのデータ構造について習った これ以外にも もっと複雑なデータ型をユーザが定義 することが可能である それが構造体と呼ばれるもので 異なる型のデータをひとかたまりのデー タとして扱うことができる 異なるデータをまとめて扱いたい時とはどんな場合だろうか 例えば 住民データを管理したい
Microsoft Word - no202.docx
 1.4 ポインタと配列 ポインタ変数は前回説明したように 値の入っているアドレスを示す変数です では 配列はどの ようにメモリ上に格納されるか調べてみましょう ex07.c /* ポインタと配列の関係 */ int a[3]={1, 2, 3; /* int 型の大きさ 3 の配列として宣言 */ int *i; /* int 型へのポインタとして宣言 */ double x[3] = {1.0,
1.4 ポインタと配列 ポインタ変数は前回説明したように 値の入っているアドレスを示す変数です では 配列はどの ようにメモリ上に格納されるか調べてみましょう ex07.c /* ポインタと配列の関係 */ int a[3]={1, 2, 3; /* int 型の大きさ 3 の配列として宣言 */ int *i; /* int 型へのポインタとして宣言 */ double x[3] = {1.0,
C言語7
 C 言語 7 ポインタ アドレスを出力 int a; a=5; printf(" 変数 aの値は %dです n", a); printf(" 変数 aのアドレスは %pです n", &a); 実行結果 変数 a の値は 5 です 変数 a のアドレスは 0038FAC4 です 変数 a の値は 15 です 変数 a のアドレスは 0038FAC4 です 注 アドレスの値は実行環境やプログラムの実行状況により異なります
C 言語 7 ポインタ アドレスを出力 int a; a=5; printf(" 変数 aの値は %dです n", a); printf(" 変数 aのアドレスは %pです n", &a); 実行結果 変数 a の値は 5 です 変数 a のアドレスは 0038FAC4 です 変数 a の値は 15 です 変数 a のアドレスは 0038FAC4 です 注 アドレスの値は実行環境やプログラムの実行状況により異なります
‚æ4›ñ
 ( ) ( ) ( ) A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 (OUS) 9 26 1 / 28 ( ) ( ) ( ) A B C D Z a b c d z 0 1 2 9 (OUS) 9
( ) ( ) ( ) A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 (OUS) 9 26 1 / 28 ( ) ( ) ( ) A B C D Z a b c d z 0 1 2 9 (OUS) 9
£Ã¥×¥í¥°¥é¥ß¥ó¥°ÆþÌç (2018) - Â裶²ó ¨¡ À©¸æ¹½Â¤¡§·«¤êÊÖ¤· ¨¡
 (2018) 2018 5 24 ( ) while ( ) do while ( ); for ( ; ; ) while int i = 0; while (i < 100) { printf("i = %3d\n", i); i++; while int i = 0; i while (i < 100) { printf("i = %3d\n", i); i++; while int i =
(2018) 2018 5 24 ( ) while ( ) do while ( ); for ( ; ; ) while int i = 0; while (i < 100) { printf("i = %3d\n", i); i++; while int i = 0; i while (i < 100) { printf("i = %3d\n", i); i++; while int i =
P06.ppt
 p.130 p.198 p.208 2 1 double weight[num]; double min, max; min = max = weight[0]; for( i= 1; i < NUM; i++ ) if ( weight[i] > max ) max = weight[i]: if ( weight[i] < min ) min = weight[i]: weight 3 maxof(a,
p.130 p.198 p.208 2 1 double weight[num]; double min, max; min = max = weight[0]; for( i= 1; i < NUM; i++ ) if ( weight[i] > max ) max = weight[i]: if ( weight[i] < min ) min = weight[i]: weight 3 maxof(a,
A/B (2010/10/08) Ver kurino/2010/soft/soft.html A/B
 A/B (2010/10/08) Ver. 1.0 kurino@math.cst.nihon-u.ac.jp http://edu-gw2.math.cst.nihon-u.ac.jp/ kurino/2010/soft/soft.html 2010 10 8 A/B 1 2010 10 8 2 1 1 1.1 OHP.................................... 1 1.2.......................................
A/B (2010/10/08) Ver. 1.0 kurino@math.cst.nihon-u.ac.jp http://edu-gw2.math.cst.nihon-u.ac.jp/ kurino/2010/soft/soft.html 2010 10 8 A/B 1 2010 10 8 2 1 1 1.1 OHP.................................... 1 1.2.......................................
Microsoft Word - no204.docx
 2. ファイル処理 2.1 ファイル処理の基本いままでは プログラムを実行したとき 入力はキーボードから入れていました また その結果を画面で確認していました 簡単なものならそれでもいいのですが 複雑な入力はファイルから読み込んだり 結果は画面で見るだけでなくファイルに保存できればよいでしょう ここでは ファイル処理について説明します 使う関数のプロトタイプは次のとおりです FILE *fopen(const
2. ファイル処理 2.1 ファイル処理の基本いままでは プログラムを実行したとき 入力はキーボードから入れていました また その結果を画面で確認していました 簡単なものならそれでもいいのですが 複雑な入力はファイルから読み込んだり 結果は画面で見るだけでなくファイルに保存できればよいでしょう ここでは ファイル処理について説明します 使う関数のプロトタイプは次のとおりです FILE *fopen(const
/* do-while */ #include <stdio.h> #include <math.h> int main(void) double val1, val2, arith_mean, geo_mean; printf( \n ); do printf( ); scanf( %lf, &v
 1 http://www7.bpe.es.osaka-u.ac.jp/~kota/classes/jse.html kota@fbs.osaka-u.ac.jp /* do-while */ #include #include int main(void) double val1, val2, arith_mean, geo_mean; printf( \n );
1 http://www7.bpe.es.osaka-u.ac.jp/~kota/classes/jse.html kota@fbs.osaka-u.ac.jp /* do-while */ #include #include int main(void) double val1, val2, arith_mean, geo_mean; printf( \n );
‚æ2›ñ C„¾„ê‡Ìš|
 I 8 10 10 I ( 6 ) 10 10 1 / 23 1 C ( ) getchar(), gets(), scanf() ( ) putchar(), puts(), printf() 1 getchar(), putchar() 1 I ( 6 ) 10 10 2 / 23 1 (getchar 1 1) 1 #include 2 void main(void){ 3 int
I 8 10 10 I ( 6 ) 10 10 1 / 23 1 C ( ) getchar(), gets(), scanf() ( ) putchar(), puts(), printf() 1 getchar(), putchar() 1 I ( 6 ) 10 10 2 / 23 1 (getchar 1 1) 1 #include 2 void main(void){ 3 int
ex14.dvi
 1,, 0, b (b b 2 b ) n k n = n j b j, (0 n j b 1), n =(n k n k 1...n 1 n 0 ) b, n j j j +1, 0,...,b 1 (digit). b b, n b 1 ñ, ñ = k (b 1 n j )b j b N, n b n, n = b N n, n =ñ+1 b N, n m n + m (mod b N ),
1,, 0, b (b b 2 b ) n k n = n j b j, (0 n j b 1), n =(n k n k 1...n 1 n 0 ) b, n j j j +1, 0,...,b 1 (digit). b b, n b 1 ñ, ñ = k (b 1 n j )b j b N, n b n, n = b N n, n =ñ+1 b N, n m n + m (mod b N ),
Microsoft Word - no103.docx
 次は 数える例です ex19.c /* Zeller の公式によって 1 日の曜日の分布を求めるプログラム */ int year, month, c, y, m, wnumber, count[7] = {0, i; for(year = 2001; year
次は 数える例です ex19.c /* Zeller の公式によって 1 日の曜日の分布を求めるプログラム */ int year, month, c, y, m, wnumber, count[7] = {0, i; for(year = 2001; year
C言語によるアルゴリズムとデータ構造
 Algorithms and Data Structures in C 4 algorithm List - /* */ #include List - int main(void) { int a, b, c; int max; /* */ Ÿ 3Ÿ 2Ÿ 3 printf(""); printf(""); printf(""); scanf("%d", &a); scanf("%d",
Algorithms and Data Structures in C 4 algorithm List - /* */ #include List - int main(void) { int a, b, c; int max; /* */ Ÿ 3Ÿ 2Ÿ 3 printf(""); printf(""); printf(""); scanf("%d", &a); scanf("%d",
C¥×¥í¥°¥é¥ß¥ó¥° ÆþÌç
 C (3) if else switch AND && OR (NOT)! 1 BMI BMI BMI = 10 4 [kg]) ( [cm]) 2 bmi1.c Input your height[cm]: 173.2 Enter Input your weight[kg]: 60.3 Enter Your BMI is 20.1. 10 4 = 10000.0 1 BMI BMI BMI = 10
C (3) if else switch AND && OR (NOT)! 1 BMI BMI BMI = 10 4 [kg]) ( [cm]) 2 bmi1.c Input your height[cm]: 173.2 Enter Input your weight[kg]: 60.3 Enter Your BMI is 20.1. 10 4 = 10000.0 1 BMI BMI BMI = 10
Microsoft Word - no206.docx
 3.2 双方向リスト 今までのリストは 前から順にたどることしかできませんでした 今度は逆にもたどることができる 双方向リストを扱います この場合は 構造体には次を表すポインタの他に前を表すポインタを持つ ことになります 今回は最初と最後をポインタを使うと取り扱いが面倒になるので 最初 (start) と最後 (end) を どちらとも構造体 ( 値は意味を持たない ) を使うことにします こうすることによって
3.2 双方向リスト 今までのリストは 前から順にたどることしかできませんでした 今度は逆にもたどることができる 双方向リストを扱います この場合は 構造体には次を表すポインタの他に前を表すポインタを持つ ことになります 今回は最初と最後をポインタを使うと取り扱いが面倒になるので 最初 (start) と最後 (end) を どちらとも構造体 ( 値は意味を持たない ) を使うことにします こうすることによって
[1] #include<stdio.h> main() { printf("hello, world."); return 0; } (G1) int long int float ± ±
![[1] #include<stdio.h> main() { printf(hello, world.); return 0; } (G1) int long int float ± ± [1] #include<stdio.h> main() { printf(hello, world.); return 0; } (G1) int long int float ± ±](/thumbs/99/143405735.jpg) [1] #include printf("hello, world."); (G1) int -32768 32767 long int -2147483648 2147483647 float ±3.4 10 38 ±3.4 10 38 double ±1.7 10 308 ±1.7 10 308 char [2] #include int a, b, c, d,
[1] #include printf("hello, world."); (G1) int -32768 32767 long int -2147483648 2147483647 float ±3.4 10 38 ±3.4 10 38 double ±1.7 10 308 ±1.7 10 308 char [2] #include int a, b, c, d,
DVIOUT
 2005 年度プログラミング演習 II レポート 7 学生用 学籍番号 : 氏名 : 下記の注意事項を守り 次ページ以降の問いに答え レポートを完成させなさい 提出期限 : 2005 年 12 月 13 日 ( 火 ) 13:15 まで提出場所 : 理学部棟正面玄関内に設置のレポートボックス 注意事項 : (1) このページを印刷し 必要事項を記入の上 ( 学籍番号欄と氏名欄は 2 箇所あるので忘れずに記入すること
2005 年度プログラミング演習 II レポート 7 学生用 学籍番号 : 氏名 : 下記の注意事項を守り 次ページ以降の問いに答え レポートを完成させなさい 提出期限 : 2005 年 12 月 13 日 ( 火 ) 13:15 まで提出場所 : 理学部棟正面玄関内に設置のレポートボックス 注意事項 : (1) このページを印刷し 必要事項を記入の上 ( 学籍番号欄と氏名欄は 2 箇所あるので忘れずに記入すること
新・明解C言語 ポインタ完全攻略
 2 1-1 1-1 /* 1-1 */ 1 int n = 100; int *p = &n; printf(" n %d\n", n); /* n int */ printf("*&n %d\n", *&n); /* *&n int */ printf(" p %p\n", p); /* p int * */ printf("&*p %p\n", &*p); /* &*p int * */ printf("sizeof(n)
2 1-1 1-1 /* 1-1 */ 1 int n = 100; int *p = &n; printf(" n %d\n", n); /* n int */ printf("*&n %d\n", *&n); /* *&n int */ printf(" p %p\n", p); /* p int * */ printf("&*p %p\n", &*p); /* &*p int * */ printf("sizeof(n)
Cプログラミング - 第8回 構造体と再帰
 C 8 ( ) C 1 / 30 n! a n+2 = a n+1 + a n ( ) C 2 / 30 #include struct student{ char name[20]; int math; int phys; ; int main(void){ struct student a, b; struct student c={"frank", 90; ( ) C 3 /
C 8 ( ) C 1 / 30 n! a n+2 = a n+1 + a n ( ) C 2 / 30 #include struct student{ char name[20]; int math; int phys; ; int main(void){ struct student a, b; struct student c={"frank", 90; ( ) C 3 /
Microsoft Word - no11.docx
 3. 関数 3.1 関数関数は数学の関数と同じようなイメージを持つと良いでしょう 例えば三角関数の様に一つの実数値 ( 角度 ) から値を求めますし 対数関数の様に二つの値から一つの値を出すものもあるでしょう これをイメージしてもらえば結構です つまり 何らかの値を渡し それをもとに何かの作業や計算を行い その結果を返すのが関数です C 言語の関数も基本は同じです 0 cos 1 cos(0) =
3. 関数 3.1 関数関数は数学の関数と同じようなイメージを持つと良いでしょう 例えば三角関数の様に一つの実数値 ( 角度 ) から値を求めますし 対数関数の様に二つの値から一つの値を出すものもあるでしょう これをイメージしてもらえば結構です つまり 何らかの値を渡し それをもとに何かの作業や計算を行い その結果を返すのが関数です C 言語の関数も基本は同じです 0 cos 1 cos(0) =
新版明解C言語入門編
 175cm 60kg ( ) 175cm 175.3cm 175.869758 cm 175cm 60kg p.177 18-1 vx - vy vx vy List -1 List -1 int vx, vy; puts(""); printf(" vx "); scanf("%d", &vx); printf(" vy "); scanf("%d", &vy); printf("vx + vy
175cm 60kg ( ) 175cm 175.3cm 175.869758 cm 175cm 60kg p.177 18-1 vx - vy vx vy List -1 List -1 int vx, vy; puts(""); printf(" vx "); scanf("%d", &vx); printf(" vy "); scanf("%d", &vy); printf("vx + vy
tuat1.dvi
 ( 1 ) http://ist.ksc.kwansei.ac.jp/ tutimura/ 2012 6 23 ( 1 ) 1 / 58 C ( 1 ) 2 / 58 2008 9 2002 2005 T E X ptetex3, ptexlive pt E X UTF-8 xdvi-jp 3 ( 1 ) 3 / 58 ( 1 ) 4 / 58 C,... ( 1 ) 5 / 58 6/23( )
( 1 ) http://ist.ksc.kwansei.ac.jp/ tutimura/ 2012 6 23 ( 1 ) 1 / 58 C ( 1 ) 2 / 58 2008 9 2002 2005 T E X ptetex3, ptexlive pt E X UTF-8 xdvi-jp 3 ( 1 ) 3 / 58 ( 1 ) 4 / 58 C,... ( 1 ) 5 / 58 6/23( )
Microsoft Word - no205.docx
 3 応用 3.1 連結リスト 前回 先頭に追加する例を扱いました しかし start が指す node を変更することから 関数 の戻り値として作成しました 今回は ポインタ変数 start の値を関数で変更できるように ポイ ンタ変数へのポインタを利用します 先頭を削除するものと 最後を削除する関数を追加します ex25.c /* リストの追加と削除 */ typedef struct node
3 応用 3.1 連結リスト 前回 先頭に追加する例を扱いました しかし start が指す node を変更することから 関数 の戻り値として作成しました 今回は ポインタ変数 start の値を関数で変更できるように ポイ ンタ変数へのポインタを利用します 先頭を削除するものと 最後を削除する関数を追加します ex25.c /* リストの追加と削除 */ typedef struct node
1 4 2 EP) (EP) (EP)
 2003 2004 2 27 1 1 4 2 EP) 5 3 6 3.1.............................. 6 3.2.............................. 6 3.3 (EP)............... 7 4 8 4.1 (EP).................... 8 4.1.1.................... 18 5 (EP)
2003 2004 2 27 1 1 4 2 EP) 5 3 6 3.1.............................. 6 3.2.............................. 6 3.3 (EP)............... 7 4 8 4.1 (EP).................... 8 4.1.1.................... 18 5 (EP)
gengo1-11
 関数の再帰定義 自然数 n の階乗 n! を計算する関数を定義してみる 引数は整数 返却値も整数 n! = 1*2*3*... * (n 1)*n である ただし 0! = 1 とする int factorial(int n) int i, tmp=1; if( n>0 ) for(i=1; i
関数の再帰定義 自然数 n の階乗 n! を計算する関数を定義してみる 引数は整数 返却値も整数 n! = 1*2*3*... * (n 1)*n である ただし 0! = 1 とする int factorial(int n) int i, tmp=1; if( n>0 ) for(i=1; i
I ASCII ( ) NUL 16 DLE SP P p 1 SOH 17 DC1! 1 A Q a q STX 2 18 DC2 " 2 B R b
 I 4 003 4 30 1 ASCII ( ) 0 17 0 NUL 16 DLE SP 0 @ P 3 48 64 80 96 11 p 1 SOH 17 DC1! 1 A Q a 33 49 65 81 97 113 q STX 18 DC " B R b 34 50 66 8 98 114 r 3 ETX 19 DC3 # 3 C S c 35 51 67 83 99 115 s 4 EOT
I 4 003 4 30 1 ASCII ( ) 0 17 0 NUL 16 DLE SP 0 @ P 3 48 64 80 96 11 p 1 SOH 17 DC1! 1 A Q a 33 49 65 81 97 113 q STX 18 DC " B R b 34 50 66 8 98 114 r 3 ETX 19 DC3 # 3 C S c 35 51 67 83 99 115 s 4 EOT
void hash1_init(int *array) int i; for (i = 0; i < HASHSIZE; i++) array[i] = EMPTY; /* i EMPTY */ void hash1_insert(int *array, int n) if (n < 0 n >=
![void hash1_init(int *array) int i; for (i = 0; i < HASHSIZE; i++) array[i] = EMPTY; /* i EMPTY */ void hash1_insert(int *array, int n) if (n < 0 n >= void hash1_init(int *array) int i; for (i = 0; i < HASHSIZE; i++) array[i] = EMPTY; /* i EMPTY */ void hash1_insert(int *array, int n) if (n < 0 n >=](/thumbs/89/97513163.jpg) II 14 2018 7 26 : : proen@mm.ics.saitama-u.ac.jp 14,, 8 2 12:00 1 O(1) n O(n) O(log n) O(1) 32 : 1G int 4 250 M 2.5 int 21 2 0 100 0 100 #include #define HASHSIZE 100 /* */ #define NOTFOUND 0
II 14 2018 7 26 : : proen@mm.ics.saitama-u.ac.jp 14,, 8 2 12:00 1 O(1) n O(n) O(log n) O(1) 32 : 1G int 4 250 M 2.5 int 21 2 0 100 0 100 #include #define HASHSIZE 100 /* */ #define NOTFOUND 0
解きながら学ぶC言語
 printf 2-5 37 52 537 52 printf("%d\n", 5 + 37); 5370 source program source file.c ex00.c 0 comment %d d 0 decimal -2 -p.6 3-2 5 37 5 37-22 537 537-22 printf("537%d\n", 5-37); function function call ( )argument,
printf 2-5 37 52 537 52 printf("%d\n", 5 + 37); 5370 source program source file.c ex00.c 0 comment %d d 0 decimal -2 -p.6 3-2 5 37 5 37-22 537 537-22 printf("537%d\n", 5-37); function function call ( )argument,
Prog1_15th
 2012 年 7 月 26 日 ( 木 ) 実施構造体と typedef typedef 宣言によって,struct 構造体タグ名という表記を再定義し, データ型名のように扱うことができる 構文は typedef struct 構造体タグ名 再定義名 ; となり, この場合の構造体変数の宣言は, 再定義名を用いて行うことができる なお, ここでは 構造体タグ名は省略可能である 構造体を指すポインタ
2012 年 7 月 26 日 ( 木 ) 実施構造体と typedef typedef 宣言によって,struct 構造体タグ名という表記を再定義し, データ型名のように扱うことができる 構文は typedef struct 構造体タグ名 再定義名 ; となり, この場合の構造体変数の宣言は, 再定義名を用いて行うことができる なお, ここでは 構造体タグ名は省略可能である 構造体を指すポインタ
プログラミング方法論 II 第 14,15 回 ( 担当 : 鈴木伸夫 ) 問題 17. x 座標と y 座標をメンバに持つ構造体 Point を作成せよ 但し座標 は double 型とする typedef struct{ (a) x; (b) y; } Point; 問題 18. 問題 17 の
 プログラミング方法論 II 第 14,15 回 ( 担当 : 鈴木伸夫 ) 問題 17. x 座標と y 座標をメンバに持つ構造体 Point を作成せよ 但し座標 は double 型とする typedef struct{ (a) x; (b) y; Point; 問題 18. 問題 17 の Point を用いて 2 点の座標を入力するとその 2 点間の距 離を表示するプログラムを作成せよ 平方根は
プログラミング方法論 II 第 14,15 回 ( 担当 : 鈴木伸夫 ) 問題 17. x 座標と y 座標をメンバに持つ構造体 Point を作成せよ 但し座標 は double 型とする typedef struct{ (a) x; (b) y; Point; 問題 18. 問題 17 の Point を用いて 2 点の座標を入力するとその 2 点間の距 離を表示するプログラムを作成せよ 平方根は
PC Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows NT, Windows 2000, MS-DOS, UNIX CPU
 1. 1.1. 1.2. 1 PC Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows NT, Windows 2000, MS-DOS, UNIX CPU 2. 2.1. 2 1 2 C a b N: PC BC c 3C ac b 3 4 a F7 b Y c 6 5 a ctrl+f5) 4 2.2. main 2.3. main 2.4. 3 4 5 6 7 printf printf
1. 1.1. 1.2. 1 PC Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows NT, Windows 2000, MS-DOS, UNIX CPU 2. 2.1. 2 1 2 C a b N: PC BC c 3C ac b 3 4 a F7 b Y c 6 5 a ctrl+f5) 4 2.2. main 2.3. main 2.4. 3 4 5 6 7 printf printf
PowerPoint Presentation
 ファイルの入出力 芝浦工業大学情報工学科 青木義満 今回の講義内容 ファイル入出力 ファイルからのデータ読込み ファイルと配列 2 1 ファイルへのデータ書き込み ( 復習 ) ソースファイル名 :fileio1.c データをファイルに書き込み #include int main(void) { ファイルポインタ宣言 int student_id = 100; char name[
ファイルの入出力 芝浦工業大学情報工学科 青木義満 今回の講義内容 ファイル入出力 ファイルからのデータ読込み ファイルと配列 2 1 ファイルへのデータ書き込み ( 復習 ) ソースファイル名 :fileio1.c データをファイルに書き込み #include int main(void) { ファイルポインタ宣言 int student_id = 100; char name[
初歩のC言語ターミナル_2014_May.pages
 C Mac OS X ( Vi Mi) Xcode CD >cd C:\Users\\Desktop gcc first.c C:\Users\\Desktop>gcc -o first first.c gcc first.c C:\Users\\Desktop>first Windows OS VisualStudio VisualStudio VS2012 CD C:\ >cd C:\Users\
C Mac OS X ( Vi Mi) Xcode CD >cd C:\Users\\Desktop gcc first.c C:\Users\\Desktop>gcc -o first first.c gcc first.c C:\Users\\Desktop>first Windows OS VisualStudio VisualStudio VS2012 CD C:\ >cd C:\Users\
[ 1] 1 Hello World!! 1 #include <s t d i o. h> 2 3 int main ( ) { 4 5 p r i n t f ( H e l l o World!! \ n ) ; 6 7 return 0 ; 8 } 1:
![[ 1] 1 Hello World!! 1 #include <s t d i o. h> 2 3 int main ( ) { 4 5 p r i n t f ( H e l l o World!! \ n ) ; 6 7 return 0 ; 8 } 1: [ 1] 1 Hello World!! 1 #include <s t d i o. h> 2 3 int main ( ) { 4 5 p r i n t f ( H e l l o World!! \ n ) ; 6 7 return 0 ; 8 } 1:](/thumbs/97/132863283.jpg) 005 9 7 1 1.1 1 Hello World!! 5 p r i n t f ( H e l l o World!! \ n ) ; 7 return 0 ; 8 } 1: 1 [ ] Hello World!! from Akita National College of Technology. 1 : 5 p r i n t f ( H e l l o World!! \ n ) ;
005 9 7 1 1.1 1 Hello World!! 5 p r i n t f ( H e l l o World!! \ n ) ; 7 return 0 ; 8 } 1: 1 [ ] Hello World!! from Akita National College of Technology. 1 : 5 p r i n t f ( H e l l o World!! \ n ) ;
新・明解C言語で学ぶアルゴリズムとデータ構造
 第 1 章 基本的 1 n 141 1-1 三値 最大値 algorithm List 1-1 a, b, c max /* */ #include int main(void) { int a, b, c; int max; /* */ List 1-1 printf("\n"); printf("a"); scanf("%d", &a); printf("b"); scanf("%d",
第 1 章 基本的 1 n 141 1-1 三値 最大値 algorithm List 1-1 a, b, c max /* */ #include int main(void) { int a, b, c; int max; /* */ List 1-1 printf("\n"); printf("a"); scanf("%d", &a); printf("b"); scanf("%d",
演習課題No12
 演習課題 No.12 ( 課題は 3 題ある ) 課題 12-1 時間内提出 従来の C 言語には複素数を直接扱うデータ型はないので (*), 構造体で複素数 ( 英語で complex) を表すことにする. 複素数を表す構造体を以下のように定義する. struct complex float r; // 実部 ( 英語で real) float i; // 虚部 ( 英語で imaginary)
演習課題 No.12 ( 課題は 3 題ある ) 課題 12-1 時間内提出 従来の C 言語には複素数を直接扱うデータ型はないので (*), 構造体で複素数 ( 英語で complex) を表すことにする. 複素数を表す構造体を以下のように定義する. struct complex float r; // 実部 ( 英語で real) float i; // 虚部 ( 英語で imaginary)
( ) ( ) 30 ( ) 27 [1] p LIFO(last in first out, ) (push) (pup) 1
![( ) ( ) 30 ( ) 27 [1] p LIFO(last in first out, ) (push) (pup) 1 ( ) ( ) 30 ( ) 27 [1] p LIFO(last in first out, ) (push) (pup) 1](/thumbs/96/128219471.jpg) () 2006 2 27 1 10 23 () 30 () 27 [1] p.97252 7 2 2.1 2.1.1 1 LIFO(last in first out, ) (push) (pup) 1 1: 2.1.2 1 List 4-1(p.100) stack[] stack top 1 2 (push) (pop) 1 2 void stack push(double val) val stack
() 2006 2 27 1 10 23 () 30 () 27 [1] p.97252 7 2 2.1 2.1.1 1 LIFO(last in first out, ) (push) (pup) 1 1: 2.1.2 1 List 4-1(p.100) stack[] stack top 1 2 (push) (pop) 1 2 void stack push(double val) val stack
C C UNIX C ( ) 4 1 HTML 1
 C 2007 4 18 C UNIX 1 2 1 1.1 C ( ) 4 1 HTML 1 はじめ mkdir work 作業用ディレクトリーの作成 emacs hoge.c& エディターによりソースプログラム作成 gcc -o fuga hoge.c コンパイルにより機械語に変換 コンパイルエラー./fuga 実行 実行時エラー 完成 1: work hooge.c fuga 1 4 4 1 1.
C 2007 4 18 C UNIX 1 2 1 1.1 C ( ) 4 1 HTML 1 はじめ mkdir work 作業用ディレクトリーの作成 emacs hoge.c& エディターによりソースプログラム作成 gcc -o fuga hoge.c コンパイルにより機械語に変換 コンパイルエラー./fuga 実行 実行時エラー 完成 1: work hooge.c fuga 1 4 4 1 1.
P03.ppt
 (2) Switch case 5 1 1 2 1 list0317.c if /*/ intnum; printf(""); scanf("%d", &num); 2 if (num % 3 == 0) puts( 0"); else if (num % 3 == 1) puts(" 1"); else puts( 32"); 3 if list0318.c /*/ intnum; printf("");
(2) Switch case 5 1 1 2 1 list0317.c if /*/ intnum; printf(""); scanf("%d", &num); 2 if (num % 3 == 0) puts( 0"); else if (num % 3 == 1) puts(" 1"); else puts( 32"); 3 if list0318.c /*/ intnum; printf("");
<4D F736F F D20438CBE8CEA8D758DC03389F0939A82C282AB2E646F63>
 C 言語講座第 3 回 キャスト ( 型変換 ) 強制的に式の型を変換する ( 変換したい型名 ) 変換元で記述する int num_a = 10, num_b = 3; float result1, result2; // 結果格納用 // 計算用 result1 = num_a / num_b; // 通常のint/int 割り算 result2 = (float)num_a / num_b;//
C 言語講座第 3 回 キャスト ( 型変換 ) 強制的に式の型を変換する ( 変換したい型名 ) 変換元で記述する int num_a = 10, num_b = 3; float result1, result2; // 結果格納用 // 計算用 result1 = num_a / num_b; // 通常のint/int 割り算 result2 = (float)num_a / num_b;//
18 C ( ) hello world.c 1 #include <stdio.h> 2 3 main() 4 { 5 printf("hello World\n"); 6 } [ ] [ ] #include <stdio.h> % cc hello_world.c %./a.o
![18 C ( ) hello world.c 1 #include <stdio.h> 2 3 main() 4 { 5 printf(hello World\n); 6 } [ ] [ ] #include <stdio.h> % cc hello_world.c %./a.o 18 C ( ) hello world.c 1 #include <stdio.h> 2 3 main() 4 { 5 printf(hello World\n); 6 } [ ] [ ] #include <stdio.h> % cc hello_world.c %./a.o](/thumbs/95/124976715.jpg) 18 C ( ) 1 1 1.1 hello world.c 5 printf("hello World\n"); 6 } [ ] [ ] #include % cc hello_world.c %./a.out Hello World [a.out ] % cc hello_world.c -o hello_world [ ( ) ] (K&R 4.1.1) #include
18 C ( ) 1 1 1.1 hello world.c 5 printf("hello World\n"); 6 } [ ] [ ] #include % cc hello_world.c %./a.out Hello World [a.out ] % cc hello_world.c -o hello_world [ ( ) ] (K&R 4.1.1) #include
char int float double の変数型はそれぞれ 文字あるいは小さな整数 整数 実数 より精度の高い ( 数値のより大きい より小さい ) 実数 を扱う時に用いる 備考 : 基本型の説明に示した 浮動小数点 とは数値を指数表現で表す方法である 例えば は指数表現で 3 書く
 変数 入出力 演算子ここまでに C 言語プログラミングの様子を知ってもらうため printf 文 変数 scanf 文 if 文を使った簡単なプログラムを紹介した 今回は変数の詳細について習い それに併せて使い方が増える入出力処理の方法を習う また 演算子についての復習と供に新しい演算子を紹介する 変数の宣言プログラムでデータを取り扱う場合には対象となるデータを保存する必要がでてくる このデータを保存する場所のことを
変数 入出力 演算子ここまでに C 言語プログラミングの様子を知ってもらうため printf 文 変数 scanf 文 if 文を使った簡単なプログラムを紹介した 今回は変数の詳細について習い それに併せて使い方が増える入出力処理の方法を習う また 演算子についての復習と供に新しい演算子を紹介する 変数の宣言プログラムでデータを取り扱う場合には対象となるデータを保存する必要がでてくる このデータを保存する場所のことを
double 2 std::cin, std::cout 1.2 C fopen() fclose() C++ std::fstream 1-3 #include <fstream> std::fstream fout; int a = 123; fout.open( "data.t
 C++ 1 C C++ C++ C C C++ 1.1 C printf() scanf() C++ C 1-1 #include int a; scanf( "%d", &a ); printf( "a = %d\n", a ); C++ 1-2 int a; std::cin >> a; std::cout
C++ 1 C C++ C++ C C C++ 1.1 C printf() scanf() C++ C 1-1 #include int a; scanf( "%d", &a ); printf( "a = %d\n", a ); C++ 1-2 int a; std::cin >> a; std::cout
PowerPoint プレゼンテーション
 プログラミング初級 第 7 回 2017 年 5 月 29 日 配列 ( 復習 )~ 文字列 1 配列とは 2 配列 : 複数の変数をグループとしてまとめて扱うもの 配列 変数 int data[10]; 整数型の配列 同種のデータ型を連続して確保したものを配列とよぶ = 整数がそれぞれにひとつずつ入る箱を 10 個用意したようなもの int data; 整数型の変数 = 整数がひとつ入る dataという名前の箱を用意したようなもの
プログラミング初級 第 7 回 2017 年 5 月 29 日 配列 ( 復習 )~ 文字列 1 配列とは 2 配列 : 複数の変数をグループとしてまとめて扱うもの 配列 変数 int data[10]; 整数型の配列 同種のデータ型を連続して確保したものを配列とよぶ = 整数がそれぞれにひとつずつ入る箱を 10 個用意したようなもの int data; 整数型の変数 = 整数がひとつ入る dataという名前の箱を用意したようなもの
2 P.S.P.T. P.S.P.T. wiki 26
 P.S.P.T. C 2011 4 10 2 P.S.P.T. P.S.P.T. wiki p.s.p.t.since1982@gmail.com http://www23.atwiki.jp/pspt 26 3 2 1 C 8 1.1 C................................................ 8 1.1.1...........................................
P.S.P.T. C 2011 4 10 2 P.S.P.T. P.S.P.T. wiki p.s.p.t.since1982@gmail.com http://www23.atwiki.jp/pspt 26 3 2 1 C 8 1.1 C................................................ 8 1.1.1...........................................
tuat2.dvi
 ( 2 ) http://ist.ksc.kwansei.ac.jp/ tutimura/ 2012 7 7 ( 2 ) 1 / 54 (1) (2) (?) (1) (2) 2 ( 2 ) 2 / 54 1. 30 2. 2012 6 30 25 OS ( 2 ) 3 / 54 10 20 1993 1996 2000 2003 = 30 ( 2 ) 4 / 54 1 2 2 ( 2 ) 5 /
( 2 ) http://ist.ksc.kwansei.ac.jp/ tutimura/ 2012 7 7 ( 2 ) 1 / 54 (1) (2) (?) (1) (2) 2 ( 2 ) 2 / 54 1. 30 2. 2012 6 30 25 OS ( 2 ) 3 / 54 10 20 1993 1996 2000 2003 = 30 ( 2 ) 4 / 54 1 2 2 ( 2 ) 5 /
1-4 int a; std::cin >> a; std::cout << "a = " << a << std::endl; C++( 1-4 ) stdio.h iostream iostream.h C++ include.h 1-4 scanf() std::cin >>
 1 C++ 1.1 C C++ C++ C C C++ 1.1.1 C printf() scanf() C++ C hello world printf() 1-1 #include printf( "hello world\n" ); C++ 1-2 std::cout
1 C++ 1.1 C C++ C++ C C C++ 1.1.1 C printf() scanf() C++ C hello world printf() 1-1 #include printf( "hello world\n" ); C++ 1-2 std::cout
プログラミング基礎
 C プログラミング Ⅱ 演習 2-1(a) BMI による判定 文字列, 身長 height(double 型 ), 体重 weight (double 型 ) をメンバとする構造体 Data を定義し, それぞれのメンバの値をキーボードから入力した後, BMI を計算するプログラムを作成しなさい BMI の計算は関数化すること ( ) [ ] [ ] [ ] BMI = 体重 kg 身長 m 身長
C プログラミング Ⅱ 演習 2-1(a) BMI による判定 文字列, 身長 height(double 型 ), 体重 weight (double 型 ) をメンバとする構造体 Data を定義し, それぞれのメンバの値をキーボードから入力した後, BMI を計算するプログラムを作成しなさい BMI の計算は関数化すること ( ) [ ] [ ] [ ] BMI = 体重 kg 身長 m 身長
超初心者用
 3 1999 10 13 1. 2. hello.c printf( Hello, world! n ); cc hello.c a.out./a.out Hello, world printf( Hello, world! n ); 2 Hello, world printf n printf 3. ( ) int num; num = 100; num 100 100 num int num num
3 1999 10 13 1. 2. hello.c printf( Hello, world! n ); cc hello.c a.out./a.out Hello, world printf( Hello, world! n ); 2 Hello, world printf n printf 3. ( ) int num; num = 100; num 100 100 num int num num
2004
 2008 3 20 400 1 1,222 7 1 2 3 55.8 54.8 3 35.8 6 64.0 50.5 93.5 1 1,222 1 1,428 1 1,077 6 64.0 52.5 80.5 56.6 81.5 30.2 1 2 3 7 70.5 1 65.6 2 61.3 3 51.1 1 54.0 2 49.8 3 32.0 68.8 37.0 34.3 2008 3 2 93.5
2008 3 20 400 1 1,222 7 1 2 3 55.8 54.8 3 35.8 6 64.0 50.5 93.5 1 1,222 1 1,428 1 1,077 6 64.0 52.5 80.5 56.6 81.5 30.2 1 2 3 7 70.5 1 65.6 2 61.3 3 51.1 1 54.0 2 49.8 3 32.0 68.8 37.0 34.3 2008 3 2 93.5
joho07-1.ppt
 0xbffffc5c 0xbffffc60 xxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx 00001010 00000000 00000000 00000000 01100011 00000000 00000000 00000000 xxxxxxxx x y 2 func1 func2 double func1(double y) { y = y + 5.0; return y; } double func2(double*
0xbffffc5c 0xbffffc60 xxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx 00001010 00000000 00000000 00000000 01100011 00000000 00000000 00000000 xxxxxxxx x y 2 func1 func2 double func1(double y) { y = y + 5.0; return y; } double func2(double*
C B
 C 095707B 2010 6 8 1 LEVE1 2 1.1 LEVEL 1.1................................................ 2 1.1.1 1................................................ 2 1.1.2 1.2..............................................
C 095707B 2010 6 8 1 LEVE1 2 1.1 LEVEL 1.1................................................ 2 1.1.1 1................................................ 2 1.1.2 1.2..............................................
スライド 1
 プログラミング 第 3 週 静岡大学工学部機械工学科知能 材料コースロボット 計測情報分野臼杵深光電 精密コース光ナノバイオ分野居波渉 講義の前に 講義資料や演習課題 LiveCampusよりダウンロード可能 成績評価期末試験および課題により行う. 評価の配分は, おおむね試験 90%, 課題 10% である. 再試験期末試験で40 点以上 60 点未満の場合, 再試験となる. 2 月 26 日 (
プログラミング 第 3 週 静岡大学工学部機械工学科知能 材料コースロボット 計測情報分野臼杵深光電 精密コース光ナノバイオ分野居波渉 講義の前に 講義資料や演習課題 LiveCampusよりダウンロード可能 成績評価期末試験および課題により行う. 評価の配分は, おおむね試験 90%, 課題 10% である. 再試験期末試験で40 点以上 60 点未満の場合, 再試験となる. 2 月 26 日 (
#define N1 N+1 double x[n1] =.5, 1., 2.; double hokan[n1] = 1.65, 2.72, 7.39 ; double xx[]=.2,.4,.6,.8,1.2,1.4,1.6,1.8; double lagrng(double xx); main
![#define N1 N+1 double x[n1] =.5, 1., 2.; double hokan[n1] = 1.65, 2.72, 7.39 ; double xx[]=.2,.4,.6,.8,1.2,1.4,1.6,1.8; double lagrng(double xx); main #define N1 N+1 double x[n1] =.5, 1., 2.; double hokan[n1] = 1.65, 2.72, 7.39 ; double xx[]=.2,.4,.6,.8,1.2,1.4,1.6,1.8; double lagrng(double xx); main](/thumbs/88/114913669.jpg) =1= (.5, 1.65), (1., 2.72), (2., 7.39).2,.4,.6,.8, 1., 1.2, 1.4, 1.6 1 1: x.2 1.4128.4 1.5372.6 1.796533.8 2.198 1.2 3.384133 1.4 4.1832 1.6 5.1172 8 7 6 5 y 4 3 2 1.5 1 1.5 2 x 1: /* */ #include
=1= (.5, 1.65), (1., 2.72), (2., 7.39).2,.4,.6,.8, 1., 1.2, 1.4, 1.6 1 1: x.2 1.4128.4 1.5372.6 1.796533.8 2.198 1.2 3.384133 1.4 4.1832 1.6 5.1172 8 7 6 5 y 4 3 2 1.5 1 1.5 2 x 1: /* */ #include
Microsoft PowerPoint - program.ppt [互換モード]
![Microsoft PowerPoint - program.ppt [互換モード] Microsoft PowerPoint - program.ppt [互換モード]](/thumbs/86/93202628.jpg) プログラミング演習 バージョン 1 担当教員 : 綴木馴 プログラムの決まりについて学ぶ おすすめする参考書 ザ C 戸川隼人サイエンス社 本日の予定 1. 授業の説明. 2. コンパイラーのインストール. プログラムの決まりについて学ぶ,P31 /* The most in C */ /* hello.c */ printf("hello,world n"); プログラムの決まり ( コメント )
プログラミング演習 バージョン 1 担当教員 : 綴木馴 プログラムの決まりについて学ぶ おすすめする参考書 ザ C 戸川隼人サイエンス社 本日の予定 1. 授業の説明. 2. コンパイラーのインストール. プログラムの決まりについて学ぶ,P31 /* The most in C */ /* hello.c */ printf("hello,world n"); プログラムの決まり ( コメント )
Microsoft Word - C.....u.K...doc
 C uwêííôöðöõ Ð C ÔÖÐÖÕ ÐÊÉÌÊ C ÔÖÐÖÕÊ C ÔÖÐÖÕÊ Ç Ê Æ ~ if eíè ~ for ÒÑÒ ÌÆÊÉÉÊ ~ switch ÉeÍÈ ~ while ÒÑÒ ÊÍÍÔÖÐÖÕÊ ~ 1 C ÔÖÐÖÕ ÐÊÉÌÊ uê~ ÏÒÏÑ Ð ÓÏÖ CUI Ô ÑÊ ÏÒÏÑ ÔÖÐÖÕÎ d ÈÍÉÇÊ ÆÒ Ö ÒÐÑÒ ÊÔÎÏÖÎ d ÉÇÍÊ
C uwêííôöðöõ Ð C ÔÖÐÖÕ ÐÊÉÌÊ C ÔÖÐÖÕÊ C ÔÖÐÖÕÊ Ç Ê Æ ~ if eíè ~ for ÒÑÒ ÌÆÊÉÉÊ ~ switch ÉeÍÈ ~ while ÒÑÒ ÊÍÍÔÖÐÖÕÊ ~ 1 C ÔÖÐÖÕ ÐÊÉÌÊ uê~ ÏÒÏÑ Ð ÓÏÖ CUI Ô ÑÊ ÏÒÏÑ ÔÖÐÖÕÎ d ÈÍÉÇÊ ÆÒ Ö ÒÐÑÒ ÊÔÎÏÖÎ d ÉÇÍÊ
C による数値計算法入門 ( 第 2 版 ) 新装版 サンプルページ この本の定価 判型などは, 以下の URL からご覧いただけます. このサンプルページの内容は, 新装版 1 刷発行時のものです.
 C による数値計算法入門 ( 第 2 版 ) 新装版 サンプルページ この本の定価 判型などは, 以下の URL からご覧いただけます. http://www.morikita.co.jp/books/mid/009383 このサンプルページの内容は, 新装版 1 刷発行時のものです. i 2 22 2 13 ( ) 2 (1) ANSI (2) 2 (3) Web http://www.morikita.co.jp/books/mid/009383
C による数値計算法入門 ( 第 2 版 ) 新装版 サンプルページ この本の定価 判型などは, 以下の URL からご覧いただけます. http://www.morikita.co.jp/books/mid/009383 このサンプルページの内容は, 新装版 1 刷発行時のものです. i 2 22 2 13 ( ) 2 (1) ANSI (2) 2 (3) Web http://www.morikita.co.jp/books/mid/009383
プログラミング基礎
 C プログラミング Ⅰ 条件分岐 if~else if~else 文,switch 文 条件分岐 if~else if~else 文 if~else if~else 文 複数の条件で処理を分ける if~else if~else 文の書式 if( 条件式 1){ 文 1-1; 文 1-2; else if( 条件式 2){ 文 2-1; 文 2-2; else { 文 3-1; 文 3-2; 真条件式
C プログラミング Ⅰ 条件分岐 if~else if~else 文,switch 文 条件分岐 if~else if~else 文 if~else if~else 文 複数の条件で処理を分ける if~else if~else 文の書式 if( 条件式 1){ 文 1-1; 文 1-2; else if( 条件式 2){ 文 2-1; 文 2-2; else { 文 3-1; 文 3-2; 真条件式
Microsoft Word - Cプログラミング演習(7)
 第 7 回 (6/4) 2. 構造体 構造体とは, 同じ型に限定されない複数の関連するデータメンバの集合である 構造体の宣言構造体指定子 struct を用いて struct 構造体タグ名 { メンバ 1 の宣言 ; メンバ 2 の宣言 ; メンバ n の宣言 ; }; 注 ) 構造体タグ名は構造体の型名で, 内容を定義するものでオブジェクトではなく, 論理的なテンプレートである 構造体の変数の宣言実際の記憶領域を占める物理的実体を確保する
第 7 回 (6/4) 2. 構造体 構造体とは, 同じ型に限定されない複数の関連するデータメンバの集合である 構造体の宣言構造体指定子 struct を用いて struct 構造体タグ名 { メンバ 1 の宣言 ; メンバ 2 の宣言 ; メンバ n の宣言 ; }; 注 ) 構造体タグ名は構造体の型名で, 内容を定義するものでオブジェクトではなく, 論理的なテンプレートである 構造体の変数の宣言実際の記憶領域を占める物理的実体を確保する
プログラミング基礎
 C プログラミング 演習 プログラミング基礎 II 演習 II 2012 年 12 月 10 日 第 11 回 今後の予定 2012/12/10 C プログラミング及びプログラミング演習 II 2 2012/12/17 期末試験 (60 分間 ) 場所 :A0542 時間 :4 時限 (15:00~16:00) 2012/12/16 課題の最終提出締切 課題の提出方法 電子メールで提出 提出先 (
C プログラミング 演習 プログラミング基礎 II 演習 II 2012 年 12 月 10 日 第 11 回 今後の予定 2012/12/10 C プログラミング及びプログラミング演習 II 2 2012/12/17 期末試験 (60 分間 ) 場所 :A0542 時間 :4 時限 (15:00~16:00) 2012/12/16 課題の最終提出締切 課題の提出方法 電子メールで提出 提出先 (
II ( ) prog8-1.c s1542h017%./prog8-1 1 => 35 Hiroshi 2 => 23 Koji 3 => 67 Satoshi 4 => 87 Junko 5 => 64 Ichiro 6 => 89 Mari 7 => 73 D
 II 8 2003 11 12 1 6 ( ) prog8-1.c s1542h017%./prog8-1 1 => 35 Hiroshi 2 => 23 Koji 3 => 67 Satoshi 4 => 87 Junko 5 => 64 Ichiro 6 => 89 Mari 7 => 73 Daisuke 8 =>. 73 Daisuke 35 Hiroshi 64 Ichiro 87 Junko
II 8 2003 11 12 1 6 ( ) prog8-1.c s1542h017%./prog8-1 1 => 35 Hiroshi 2 => 23 Koji 3 => 67 Satoshi 4 => 87 Junko 5 => 64 Ichiro 6 => 89 Mari 7 => 73 Daisuke 8 =>. 73 Daisuke 35 Hiroshi 64 Ichiro 87 Junko
/* sansu1.c */ #include <stdio.h> main() { int a, b, c; /* a, b, c */ a = 200; b = 1300; /* a 200 */ /* b 200 */ c = a + b; /* a b c */ }
 C 2: A Pedestrian Approach to the C Programming Language 2 2-1 2.1........................... 2-1 2.1.1.............................. 2-1 2.1.2......... 2-4 2.1.3..................................... 2-6
C 2: A Pedestrian Approach to the C Programming Language 2 2-1 2.1........................... 2-1 2.1.1.............................. 2-1 2.1.2......... 2-4 2.1.3..................................... 2-6
Microsoft PowerPoint - 説明2_演算と型(C_guide2)【2015新教材対応確認済み】.pptx
 情報ネットワーク導入ユニット Ⅰ C 言語 演算と型 演算 代入 演算と型 +,-,*,/,% = C 言語では 代入 の意味 vx = a + b; //a+b の結果を vx に代入 型 : int 型 ( 整数 ) double 型 ( 実数 ) 演算での型変換 ( 整数, 実数の混在 ) キャスト演算子 型を一時的に変更 書式指定 :printf("%6d n", a); 加減, 剰余演算
情報ネットワーク導入ユニット Ⅰ C 言語 演算と型 演算 代入 演算と型 +,-,*,/,% = C 言語では 代入 の意味 vx = a + b; //a+b の結果を vx に代入 型 : int 型 ( 整数 ) double 型 ( 実数 ) 演算での型変換 ( 整数, 実数の混在 ) キャスト演算子 型を一時的に変更 書式指定 :printf("%6d n", a); 加減, 剰余演算
x h = (b a)/n [x i, x i+1 ] = [a+i h, a+ (i + 1) h] A(x i ) A(x i ) = h 2 {f(x i) + f(x i+1 ) = h {f(a + i h) + f(a + (i + 1) h), (2) 2 a b n A(x i )
![x h = (b a)/n [x i, x i+1 ] = [a+i h, a+ (i + 1) h] A(x i ) A(x i ) = h 2 {f(x i) + f(x i+1 ) = h {f(a + i h) + f(a + (i + 1) h), (2) 2 a b n A(x i ) x h = (b a)/n [x i, x i+1 ] = [a+i h, a+ (i + 1) h] A(x i ) A(x i ) = h 2 {f(x i) + f(x i+1 ) = h {f(a + i h) + f(a + (i + 1) h), (2) 2 a b n A(x i )](/thumbs/92/107866678.jpg) 1 f(x) a b f(x)dx = n A(x i ) (1) ix [a, b] n i A(x i ) x i 1 f(x) [a, b] n h = (b a)/n y h = (b-a)/n y = f (x) h h a a+h a+2h a+(n-1)h b x 1: 1 x h = (b a)/n [x i, x i+1 ] = [a+i h, a+ (i + 1) h] A(x
1 f(x) a b f(x)dx = n A(x i ) (1) ix [a, b] n i A(x i ) x i 1 f(x) [a, b] n h = (b a)/n y h = (b-a)/n y = f (x) h h a a+h a+2h a+(n-1)h b x 1: 1 x h = (b a)/n [x i, x i+1 ] = [a+i h, a+ (i + 1) h] A(x
gengo1-10
 関数 C 言語では 関数を組み合わせてプログラムを構成する pritnf(), scanf() などは 処理系があらかじめ備えている標準ライブラリ関数 math.h で定義されている算術関数も標準ライブラリ関数の 1 つ データを与えて それに基づき何か動作をおこなうものが関数 数学の関数 y = f(x) のイメージ f(x) x を与える f(x) を計算して返す f(x) はある意味ブラックボックス
関数 C 言語では 関数を組み合わせてプログラムを構成する pritnf(), scanf() などは 処理系があらかじめ備えている標準ライブラリ関数 math.h で定義されている算術関数も標準ライブラリ関数の 1 つ データを与えて それに基づき何か動作をおこなうものが関数 数学の関数 y = f(x) のイメージ f(x) x を与える f(x) を計算して返す f(x) はある意味ブラックボックス
新版明解C言語 実践編
 2 List - "max.h" a, b max List - max "max.h" #define max(a, b) ((a) > (b)? (a) : (b)) max List -2 List -2 max #include "max.h" int x, y; printf("x"); printf("y"); scanf("%d", &x); scanf("%d", &y); printf("max(x,
2 List - "max.h" a, b max List - max "max.h" #define max(a, b) ((a) > (b)? (a) : (b)) max List -2 List -2 max #include "max.h" int x, y; printf("x"); printf("y"); scanf("%d", &x); scanf("%d", &y); printf("max(x,
£Ã¥×¥í¥°¥é¥ß¥ó¥°ÆþÌç (2018) - Â裵²ó ¨¡ À©¸æ¹½Â¤¡§¾ò·ïʬ´ô ¨¡
 (2018) 2018 5 17 0 0 if switch if if ( ) if ( 0) if ( ) if ( 0) if ( ) (0) if ( 0) if ( ) (0) ( ) ; if else if ( ) 1 else 2 if else ( 0) 1 if ( ) 1 else 2 if else ( 0) 1 if ( ) 1 else 2 (0) 2 if else
(2018) 2018 5 17 0 0 if switch if if ( ) if ( 0) if ( ) if ( 0) if ( ) (0) if ( 0) if ( ) (0) ( ) ; if else if ( ) 1 else 2 if else ( 0) 1 if ( ) 1 else 2 if else ( 0) 1 if ( ) 1 else 2 (0) 2 if else
Microsoft PowerPoint - 説明3_if文switch文(C_guide3)【2015新教材対応確認済み】.pptx
 情報ネットワーク導入ユニット Ⅰ C 言語 if 文 switch 文 3 章 : プログラムの流れの分岐 if 文 if( 条件 ) 条件が成立すれば実行 if( 条件 ) ~ else 場合分け ( 成立, 不成立 ) if( 条件 A) ~ else if( 条件 B) ~ else if( 条件 C) ~ else 場合分け ( 複数の条件での場合分け ) 等価演算子 : == ( 等しい
情報ネットワーク導入ユニット Ⅰ C 言語 if 文 switch 文 3 章 : プログラムの流れの分岐 if 文 if( 条件 ) 条件が成立すれば実行 if( 条件 ) ~ else 場合分け ( 成立, 不成立 ) if( 条件 A) ~ else if( 条件 B) ~ else if( 条件 C) ~ else 場合分け ( 複数の条件での場合分け ) 等価演算子 : == ( 等しい
Informatics 2015
 C 計算機の歴史 新旧のソロバン バベッジの階差機関 19C前半 手回し計算機 19C後半 20C後半 スパコン 1960年代 ENIAC (1946) 大型汎用計算機 1950年代 1980年代 電卓 1964 パソコン 1970年代 現在のコンピュータ Input Output Device Central Processing Unit I/O CPU Memory OS (Operating
C 計算機の歴史 新旧のソロバン バベッジの階差機関 19C前半 手回し計算機 19C後半 20C後半 スパコン 1960年代 ENIAC (1946) 大型汎用計算機 1950年代 1980年代 電卓 1964 パソコン 1970年代 現在のコンピュータ Input Output Device Central Processing Unit I/O CPU Memory OS (Operating
スライド 1
 数値解析 2019 年度前期第 13 週 [7 月 11 日 ] 静岡大学創造科学技術大学院情報科学専攻工学部機械工学科計測情報講座 三浦憲二郎 講義アウトライン [7 月 11 日 ] 関数近似と補間 最小 2 乗近似による関数近似 ラグランジュ補間 T.Kanai, U.Tokyo 関数近似 p.116 複雑な関数を簡単な関数で近似する 関数近似 閉区間 [a,b] で定義された関数 f(x)
数値解析 2019 年度前期第 13 週 [7 月 11 日 ] 静岡大学創造科学技術大学院情報科学専攻工学部機械工学科計測情報講座 三浦憲二郎 講義アウトライン [7 月 11 日 ] 関数近似と補間 最小 2 乗近似による関数近似 ラグランジュ補間 T.Kanai, U.Tokyo 関数近似 p.116 複雑な関数を簡単な関数で近似する 関数近似 閉区間 [a,b] で定義された関数 f(x)
プログラミング基礎
 C プログラミング 演習 アルゴリズム基礎論 演習 第 10 回 今後の予定 12/22( 月 ) 期末試験 (60 分間 ) 場所 :A1611 時間 :16:20~17:20 課題の最終提出締切 :12/19( 金 ) これ以降の新規提出は評価されない 12/22までに最終状況を提示するので, 提出したのに や になってる人は自分の提出内容や提出先を再確認した上で12/26までに問い合わせること
C プログラミング 演習 アルゴリズム基礎論 演習 第 10 回 今後の予定 12/22( 月 ) 期末試験 (60 分間 ) 場所 :A1611 時間 :16:20~17:20 課題の最終提出締切 :12/19( 金 ) これ以降の新規提出は評価されない 12/22までに最終状況を提示するので, 提出したのに や になってる人は自分の提出内容や提出先を再確認した上で12/26までに問い合わせること
Informatics 2014
 C 計算機の歴史 手回し計算機 新旧のソロバン バベッジの階差機関 スパコン ENIAC (1946) パソコン 大型汎用計算機 電卓 現在のコンピュータ Input Output Device Central Processing Unit I/O CPU Memory OS (Operating System) OS Windows 78, Vista, XP Windows Mac OS X
C 計算機の歴史 手回し計算機 新旧のソロバン バベッジの階差機関 スパコン ENIAC (1946) パソコン 大型汎用計算機 電卓 現在のコンピュータ Input Output Device Central Processing Unit I/O CPU Memory OS (Operating System) OS Windows 78, Vista, XP Windows Mac OS X
untitled
 II yacc 005 : 1, 1 1 1 %{ int lineno=0; 3 int wordno=0; 4 int charno=0; 5 6 %} 7 8 %% 9 [ \t]+ { charno+=strlen(yytext); } 10 "\n" { lineno++; charno++; } 11 [^ \t\n]+ { wordno++; charno+=strlen(yytext);}
II yacc 005 : 1, 1 1 1 %{ int lineno=0; 3 int wordno=0; 4 int charno=0; 5 6 %} 7 8 %% 9 [ \t]+ { charno+=strlen(yytext); } 10 "\n" { lineno++; charno++; } 11 [^ \t\n]+ { wordno++; charno+=strlen(yytext);}
II 3 yacc (2) 2005 : Yacc 0 ~nakai/ipp2 1 C main main 1 NULL NULL for 2 (a) Yacc 2 (b) 2 3 y
 II 3 yacc (2) 2005 : Yacc 0 ~nakai/ipp2 1 C 1 6 9 1 main main 1 NULL NULL 1 15 23 25 48 26 30 32 36 38 43 45 47 50 52 for 2 (a) 2 2 1 Yacc 2 (b) 2 3 yytext tmp2 ("") tmp2->next->word tmp2 yytext tmp2->next->word
II 3 yacc (2) 2005 : Yacc 0 ~nakai/ipp2 1 C 1 6 9 1 main main 1 NULL NULL 1 15 23 25 48 26 30 32 36 38 43 45 47 50 52 for 2 (a) 2 2 1 Yacc 2 (b) 2 3 yytext tmp2 ("") tmp2->next->word tmp2 yytext tmp2->next->word
gengo1-2
 変数 プログラム中で 値を格納するには変数 variable を用いる変数は 格納する値の型によって 整数型 文字型 などの型 type をもつ変数を使うには 利用に先立って変数の宣言 declaration をしなければならない 値 変数の値はコンピュータのメモリ上に格納される 具体的にメモリのどの場所に格納されるかは言語処理系が自動的に扱うので プログラマ ( 特に初級者 ) が意識する必要はない
変数 プログラム中で 値を格納するには変数 variable を用いる変数は 格納する値の型によって 整数型 文字型 などの型 type をもつ変数を使うには 利用に先立って変数の宣言 declaration をしなければならない 値 変数の値はコンピュータのメモリ上に格納される 具体的にメモリのどの場所に格納されるかは言語処理系が自動的に扱うので プログラマ ( 特に初級者 ) が意識する必要はない
printf("5つの整数を入力して下さい \n"); /* データ入力 */ for( /*** 02 ***/ ){ printf("%dつ目の入力 :",i+1); scanf("%d", /*** 03 ***/ ); sum=dat[0]; /* 合計値の初期設定 */ n_max= 0
![printf(5つの整数を入力して下さい \n); /* データ入力 */ for( /*** 02 ***/ ){ printf(%dつ目の入力 :,i+1); scanf(%d, /*** 03 ***/ ); sum=dat[0]; /* 合計値の初期設定 */ n_max= 0 printf(5つの整数を入力して下さい \n); /* データ入力 */ for( /*** 02 ***/ ){ printf(%dつ目の入力 :,i+1); scanf(%d, /*** 03 ***/ ); sum=dat[0]; /* 合計値の初期設定 */ n_max= 0](/thumbs/89/98884504.jpg) 電子情報競技会ソフトウェア課題 1 Question_1 プロジェクト内のソースプログラムの /*** XX ***/ に適当な語句 式等を入れ プログラムを完成させなさい ここで 同じ番号の /*** XX ***/ には同じ語句 式等が入る /*** XX ***/ の部分以外は書き換えてはならないが 別のソースファイルにてテストしてもかまわない [ プログラムの説明 ] 1. 処理内容 2 桁の整数データ
電子情報競技会ソフトウェア課題 1 Question_1 プロジェクト内のソースプログラムの /*** XX ***/ に適当な語句 式等を入れ プログラムを完成させなさい ここで 同じ番号の /*** XX ***/ には同じ語句 式等が入る /*** XX ***/ の部分以外は書き換えてはならないが 別のソースファイルにてテストしてもかまわない [ プログラムの説明 ] 1. 処理内容 2 桁の整数データ
Prog1_6th
 2012 年 5 月 24 日 ( 木 ) 実施 多分岐のプログラム 前回は多段階の 2 分岐を組み合わせて 3 種類以上の場合分けを実現したが, 式の値の評価によって, 一度に多種類の場合分けを行う多分岐の利用によって見通しのよいプログラムを作成できる場合がある ( 流れ図は右図 ) 式の評価 : 値 1 : 値 2 : 値 n : 該当値無し 処理 1 処理 2 処理 n 既定の処理 switch
2012 年 5 月 24 日 ( 木 ) 実施 多分岐のプログラム 前回は多段階の 2 分岐を組み合わせて 3 種類以上の場合分けを実現したが, 式の値の評価によって, 一度に多種類の場合分けを行う多分岐の利用によって見通しのよいプログラムを作成できる場合がある ( 流れ図は右図 ) 式の評価 : 値 1 : 値 2 : 値 n : 該当値無し 処理 1 処理 2 処理 n 既定の処理 switch
新・明解C言語 実践編
 第 1 章 見 21 1-1 見えないエラー 見 List 1-1 "max2x1.h" a, b max2 List 1-1 chap01/max2x1.h max2 "max2x1.h" #define max2(a, b) ((a) > (b)? (a) : (b)) max2 List 1-2 List 1-2 chap01/max2x1test.c max2 #include
第 1 章 見 21 1-1 見えないエラー 見 List 1-1 "max2x1.h" a, b max2 List 1-1 chap01/max2x1.h max2 "max2x1.h" #define max2(a, b) ((a) > (b)? (a) : (b)) max2 List 1-2 List 1-2 chap01/max2x1test.c max2 #include
ex01.dvi
 ,. 0. 0.0. C () /******************************* * $Id: ex_0_0.c,v.2 2006-04-0 3:37:00+09 naito Exp $ * * 0. 0.0 *******************************/ #include int main(int argc, char **argv) double
,. 0. 0.0. C () /******************************* * $Id: ex_0_0.c,v.2 2006-04-0 3:37:00+09 naito Exp $ * * 0. 0.0 *******************************/ #include int main(int argc, char **argv) double
I. Backus-Naur BNF : N N 0 N N N N N N 0, 1 BNF N N 0 11 (parse tree) 11 (1) (2) (3) (4) II. 0(0 101)* (
 2016 2016 07 28 10:30 12:00 I. I VI II. III. IV. a d V. VI. 80 100 60 1 I. Backus-Naur BNF : 11011 N N 0 N N 11 1001 N N N N 0, 1 BNF N N 0 11 (parse tree) 11 (1) 1100100 (2) 1111011 (3) 1110010 (4) 1001011
2016 2016 07 28 10:30 12:00 I. I VI II. III. IV. a d V. VI. 80 100 60 1 I. Backus-Naur BNF : 11011 N N 0 N N 11 1001 N N N N 0, 1 BNF N N 0 11 (parse tree) 11 (1) 1100100 (2) 1111011 (3) 1110010 (4) 1001011
配列, 関数, 構造体
 配列, 関数, 構造体 配列とは 今まではintやcharという宣言の単体であっちこっちからメモリを確保していました それを同一の型のデータをメモリ上に列にして連続で並べたものを配列といいます 配列の使い方 簡単にいうと配列を使えば int 型なら int 型の変数を同時にいくつも作ることが出来ちゃいます 例 : int array[15]; array[0] から array[14] まで,15
配列, 関数, 構造体 配列とは 今まではintやcharという宣言の単体であっちこっちからメモリを確保していました それを同一の型のデータをメモリ上に列にして連続で並べたものを配列といいます 配列の使い方 簡単にいうと配列を使えば int 型なら int 型の変数を同時にいくつも作ることが出来ちゃいます 例 : int array[15]; array[0] から array[14] まで,15
Microsoft PowerPoint - C言語の復習(配布用).ppt [互換モード]
![Microsoft PowerPoint - C言語の復習(配布用).ppt [互換モード] Microsoft PowerPoint - C言語の復習(配布用).ppt [互換モード]](/thumbs/96/127138597.jpg) if 文 (a と b の大きい方を表示 ) C 言語 Ⅰ の復習 条件判定 (if, 条件式 ) ループ (for[ 二重まで ], while, do) 配列 ( 次元 次元 ) トレース int a, b; printf( 整数 a: ); scanf( %d, &a); printf( 整数 b: ); scanf( %d, &b); //つのif 文で表現する場合間違えやすい どっちに =
if 文 (a と b の大きい方を表示 ) C 言語 Ⅰ の復習 条件判定 (if, 条件式 ) ループ (for[ 二重まで ], while, do) 配列 ( 次元 次元 ) トレース int a, b; printf( 整数 a: ); scanf( %d, &a); printf( 整数 b: ); scanf( %d, &b); //つのif 文で表現する場合間違えやすい どっちに =
 1 5 13 4 1 41 1 411 1 412 2 413 3 414 3 415 4 42 6 43 LU 7 431 LU 10 432 11 433 LU 11 44 12 441 13 442 13 443 SOR ( ) 14 444 14 445 15 446 16 447 SOR 16 448 16 45 17 4 41 n x 1,, x n a 11 x 1 + a 1n x
1 5 13 4 1 41 1 411 1 412 2 413 3 414 3 415 4 42 6 43 LU 7 431 LU 10 432 11 433 LU 11 44 12 441 13 442 13 443 SOR ( ) 14 444 14 445 15 446 16 447 SOR 16 448 16 45 17 4 41 n x 1,, x n a 11 x 1 + a 1n x
C言語10
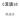 C 言語 10 構造体 構造体の記述 例 typedef struct Soseki{ char title[30]; int year; Soseki; 実行結果 題名 : 吾輩は猫である発行年 :1911 Soseki soseki1 = {" 吾輩は猫である ", 1911; printf(" 題名 :%s n", soseki1.title); printf(" 発行年 :%d n", soseki1.year);
C 言語 10 構造体 構造体の記述 例 typedef struct Soseki{ char title[30]; int year; Soseki; 実行結果 題名 : 吾輩は猫である発行年 :1911 Soseki soseki1 = {" 吾輩は猫である ", 1911; printf(" 題名 :%s n", soseki1.title); printf(" 発行年 :%d n", soseki1.year);
ex01.dvi
 ,. 0. 0.0. C () /******************************* * $Id: ex_0_0.c,v.2 2006-04-0 3:37:00+09 naito Exp $ * * 0. 0.0 *******************************/ #include int main(int argc, char **argv) { double
,. 0. 0.0. C () /******************************* * $Id: ex_0_0.c,v.2 2006-04-0 3:37:00+09 naito Exp $ * * 0. 0.0 *******************************/ #include int main(int argc, char **argv) { double
関数の動作 / printhw(); 7 printf(" n"); printhw(); printf("############ n"); 4 printhw(); 5 関数の作り方 ( 関数名 ) 戻り値 ( 後述 ) void である. 関数名 (
 概要 プログラミング 関数 http://www.ns.kogakuin.ac.jp/~ct40/progc/ A- 関数の作り方を学ぶ 関数名, 引数, 戻り値 プログラミング で最も重要な事項 関数 プログラミング で最も重要な事項 制御 (for, if) プログラミング で最も重要な事項 ポインタ A- 関数名 引数 戻り値 E- E-4 関数の概要 0/ 関数とは, 複数の処理をひとまとめにしたもの.
概要 プログラミング 関数 http://www.ns.kogakuin.ac.jp/~ct40/progc/ A- 関数の作り方を学ぶ 関数名, 引数, 戻り値 プログラミング で最も重要な事項 関数 プログラミング で最も重要な事項 制御 (for, if) プログラミング で最も重要な事項 ポインタ A- 関数名 引数 戻り値 E- E-4 関数の概要 0/ 関数とは, 複数の処理をひとまとめにしたもの.
C プログラミング演習 1( 再 ) 2 講義では C プログラミングの基本を学び 演習では やや実践的なプログラミングを通して学ぶ
 C プログラミング演習 1( 再 ) 2 講義では C プログラミングの基本を学び 演習では やや実践的なプログラミングを通して学ぶ 今回のプログラミングの課題 次のステップによって 徐々に難易度の高いプログラムを作成する ( 参照用の番号は よくわかる C 言語 のページ番号 ) 1. キーボード入力された整数 10 個の中から最大のものを答える 2. 整数を要素とする配列 (p.57-59) に初期値を与えておき
C プログラミング演習 1( 再 ) 2 講義では C プログラミングの基本を学び 演習では やや実践的なプログラミングを通して学ぶ 今回のプログラミングの課題 次のステップによって 徐々に難易度の高いプログラムを作成する ( 参照用の番号は よくわかる C 言語 のページ番号 ) 1. キーボード入力された整数 10 個の中から最大のものを答える 2. 整数を要素とする配列 (p.57-59) に初期値を与えておき
r08.dvi
 19 8 ( ) 019.4.0 1 1.1 (linked list) ( ) next ( 1) (head) (tail) ( ) top head tail head data next 1: NULL nil ( ) NULL ( NULL ) ( 1 ) (double linked list ) ( ) 1 next 1 prev 1 head cur tail head cur prev
19 8 ( ) 019.4.0 1 1.1 (linked list) ( ) next ( 1) (head) (tail) ( ) top head tail head data next 1: NULL nil ( ) NULL ( NULL ) ( 1 ) (double linked list ) ( ) 1 next 1 prev 1 head cur tail head cur prev
6 6.1 sound_wav_files flu00.wav.wav 44.1 khz 1/44100 spwave Text with Time spwave t T = N t N 44.1 khz t = 1 sec j t f j {f 0, f 1, f 2,, f N 1
 6 6.1 sound_wav_files flu00.wav.wav 44.1 khz 1/44100 spwave Text with Time spwave t T = t 44.1 khz t = 1 sec 44100 j t f j {f 0, f 1, f 2,, f 1 6.2 T {f 0, f 1, f 2,, f 1 T ft) f j = fj t) j = 0, 1, 2,,
6 6.1 sound_wav_files flu00.wav.wav 44.1 khz 1/44100 spwave Text with Time spwave t T = t 44.1 khz t = 1 sec 44100 j t f j {f 0, f 1, f 2,, f 1 6.2 T {f 0, f 1, f 2,, f 1 T ft) f j = fj t) j = 0, 1, 2,,

 2 1 list0415.c forfor #include int i, j; for (i = 1; i
2 1 list0415.c forfor #include int i, j; for (i = 1; i 