untitled
|
|
|
- せせら あんさい
- 4 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Vol. 35 No ISSN Vol.35 No. 3 No Infectious Agents Surveillance Report (IASR) http:// 3, 4, : 5, A ; 6, : 8, 9,, 2, SFTS 3, A(HN)pdm09 4, A(HN)pdm09 : 6, : 7, Agbeni 3 Tel : 8, A 9, HIV AIDS 20,,, 2 :,,, RNA AG, AC, 5 3, 4,,,,,,,,, 45 Lancet Infect Dis 2: 364, 202 :,, 3, kenkou/kekkakukansenshou/0058.html,,, , , go.jp/bunya/kenkou/kekkakukansenshou/ html, *, 2 5 *20422 C A, , jp/byogentai/pdf/dataj.pdf : * 2005/ / / / /0 200/ 20/2 202/3 203/4 G G3 G8 G9 G A G2 G4 C , 60 A, 8 C 2005/ / , 200/, 2 A *98 : 20423, C 63 2
2 264 Vol. 35 No , / / / / /0 200/ 20/2 202/ A A G A G2 A G3 A G C / B A : A, 2 VP7 VP4, G P, GP[8], G2P[4], G3P[8], G4P[8], G9P[8] 5 4,, G, A 3,302, 38, 0 6, 2 6, G, G3, G9 G2, ,, C 27, 5 9 8, 04 5 : , 22, 4 A 4 :,,,, IASR G2 G9 G8 G4 G3 G2 G , * () 3 () 9 (2) ** / 2 2 () () 2 26 () 48 () 3 () 08 (3) * **2 C : 34, 202 & 33: 9798, 202 & 33: 27, 202 & 34: 6970, 203 & 34: , , A 05, C 3 2,, A 202 2, 5 A 4, C, , :, 000 g 0 0 0,, GP[8] 5 G, G2, G3, G4, P[8] 2, 30, 53 9, , , :,, 90,, 203 8,, 2,, 2, 3,,
3 Vol. 35 No VP7,,, 80, 7 8,,, , 2 2, 4,,, HUS DIC,,, Reoviridae,,, 2 RNA 6 VP 6 NSP VP6 AG, VP6 VP4. A C, A, A, VP7 G type VP4 P type, 90 GP[8], G2P[4], G3P[8], G4P[8], G9P[8] 5,,,,,, VP7 VP RCWG, VP7VP4VP6VPVP2VP3NSPNSP2NSP3 NSP4NSP5, GxP[x]IxRx CxMxAxNxTxExHx x,,,, G P I R C M A N T E H
4 466 Vol. 35 No % 202/380% 60% 40% 20% 0% 200/ / / / / /07,, GSK, 20, MSD, ,, G P[8], VP7 G4 VP4 P[8] 5 5 5,,, , VP7 40,, 2, G, G2, G3, G9,, 203 0,,,,,, 202, 2007/ / /0 200/ : A 20/2 G2 G9 G8 G4 G3 G2 G Unknown,, G P[8]I2R2C2M2A2N2T2E2H2,,,,, ELISA, multiplexpcr, VP7, VP4,, 2 RNA A RVA, 2 VP7, VP4 G, P, RTPCR, GG4, G9, P[4], P[6], P[8], 2008, Rotavirus Classif ication Working Group RCWG,
5 Vol. 35 No , VP7, VP4,, VP7VP4VP6VPVP2VP3NSPNSP2NSP3 NSP4NSP5 GPIRCMANT EH,, ORF, NCBI BLAST RNA 2, RotaC ORF , RCWG Wa, DS Wa, DS,, G/3/4P[8]IRCMANT EH, G2P[4]I2R2C2M2A2N2T2E2H2, AU G3P[9]I3R3C3M3A3N3T3 E3H3/6 3, 7,,, 2 G/P, G/P,,,, 5, DC, 24,,, G/P VP7/VP4,,, G/P, 5, 5 GP[8], G2P[4], G3P[8], G4P[8], G9P[8], GP[8] 6 G2 G2P[4], G3P[8], G G9, G8 G5, G6,, G0 G4 7,,, Arch Virol 53: 62629, PLoS Pathog 5 e000634, J Virol 86: , 202 4PLoS ONE, 204 in press 5IASR 32: 6466, 20 6Wkly Epidemiol Rec 88: 27223, 203 7Emerg Infect Dis 9: 32323, A RVA, GxP[x]IxRxCxMx AxNxTxExHx x, RVA VP7 G VP4 P, VP6 I, G P GxP[x],
6 668 Vol. 35 No /2 RVA 5, 7 DS GP[8] GP[8]I2E2H2 5 DS GP[8] VP , VP , VP , NSP4 E , NSP5 H , 203 RVA VP7 VP4, GP[8] ,, I, RVA GPI,,, ELISA, TFB RVA RVA 2009, 200 2, 20 2, 202 9, , 200 2, 3 5 ELISA, RVA VP7, VP4 VP6 RTPCR 2,, RotaC 3 GPI, 5 GP[8]I 5, GP[8]I2 2, G2P[4] I2, G9P[8]I 3, RVA 202, 6 GP[8]I2 GP[8]I2, 99,, BLAST, GP[8]I2 202, VP7 VP4 RVA/Humanwt/USA/ /2007/GP[8], RVA G P, DS GP[8], DS GP[8] G2P[4], DS GP[8], DS GP[8], Matthijnssens J, et al., Arch Virol 56: , 20 2Fujii Y, et al., Microbiol Immunol 56: , 202 3RotaC 2.0 automated genotyping tool for Group A rotaviruses 4Yamamoto SP, et al., Emerg Infect Dis, 204 in press 5Kuzuya M, et al., J Med Virol, 203 Sep 6. doi: 0.002/jmv Epub ahead of print 6,, IASR 34: , 203 VP7, 99.6; VP4, 99.4, GP[8]I2 2 6, GP[8]I2R2C2M2A2N2T2 A 200/202/3 E2H2 4 RVA Wa GP[8]IRCMANTEH DS G2P[4]I2R2C2M2A2N2T2E2H2, GP[8]I2 I2 9 DS GP[8], DS GP[8],, A RVA,, RVA VP7 G
7 Vol. 35 No A, 2, RVA /3 6, / 438, 20/2 : 40, 202/3 : 440, RVA ELISA, Gouvea PCR RTPCR 3 G, RVA 200/ 30., 20/2 8.5, 202/3 2.6, 2 RVA RVA, 3, , 200/ 20/2, 202/3,, 20/2, 202/3, 6, 7 RVA, RVA 262 G 3 G G3 65.7, G 30.5, G9 2.3, G2., G G3, 200/, 20/2 2008/09, 2009/0 G3, 20/2 G, 202/3 6 G, 20/2, RVA 4, VP7 VP4 P G Wa GP[8], VP6, NSP4 NSP5/6 G2 DS, genogroup Wa genogroup DS genogroup RVA. G 200/202/ , G 7.4 4, G P, NSP4 NSP5/6 4, 202/3, GP[8] 49 RT PCR NSP4 NSP5/6,, , genogroup, 2, RVA Rotarix GSK 20, RotaTeq MSD 202 7, 3 RVA,, 2,,,,, 2,,,,, IASR 26: 46, ,, IASR 32: 772, 20 3Gouvea V, et al., J Clin Microbiol 28: , 990 4Kuzuya M, et al., J Med Virol, 203 Sep 6. doi: 0.002/jmv Epub ahead of print
8 870 Vol. 35 No , , A RVA, IASR IASR 32: 7374, RVA G, 2009, 200 G3, 20, 202 G3 RVA 202 G3, G9 G2, 203 G , G G GP[8]I2R2 C2M2A2N2T2E2H2 VP7 GVP4 P[8] DS G2P[4], Kuzuya OH3625/ 202 VP6, VP7, NSP4 VP7 VP GP AG 340 GP GP GP8 O22 GP8 O224 GP8 O242 GP8 G JN RVA/Humanwt/USA/ /2007/GP8 DQ RVA/Humanwt/BEL/B3458/2003/G9P8 I DQ RVA/Humanwt/BGD/Dhaka6/2003/GP8 I AB Human rotavirus KU I K02086 Human Wa rotavirus I AF3724 Porcine rotavirus A3 X69487 Rotavirus YM I5 I O26 GP8 O224 GP8 AB RVA/humanwt/JPN/OH3625/202/GP8 JN RVA/Humanwt/USA/ /2007/GP8 DQ RVA/Humanwt/BGD/Dhaka6/2003/GP8 K02033 Human Wa rotavirus G AB Human rotavirus MKU2G G EF67266 RVA/Humantc/GBR/ST3/975/G4P2A G2P G2P4 KC RVA/Humanwt/USA/VU050666/2005/G2P4 HM ES 2842 G2P4 O28 G2P4 HQ65024 RVA/Humantc/USA/DS/976/G2P4 AY Bovine rotavirus WC3 G6 X00896 UK bovine rotavirus G6 AB07404 Human rotavirus T52 G2 D8627 Human rotavirus AU G3 L35055 Porcine rotavirus A3 G3 K02028 Simian i SA G3 EF RVA/Humanwt/BEL/B3458/2003/G9P8 DQ00520 RVA/Humanwt/COD/DRC86/2003/G8P6 M2394 Porcine rotavirus YM G G2 AB RVA/humanwt/JPN/OH3625/202/GP8 O242 GP8 O26 GP GP GP8 340 GP8 O22 2 GP GP8 HM ES G2P G2P4 O28 G2P4 KC RVA/Humanwt/USA/VU050666/2005/G2P G2P G2P4 DQ0052 RVA/Humanwt/COD/DRC86/2003/G8P6 I2 X53667 Bovine rotavirus UK I2 AF4322 Bovine rotavirus WC3 I2 AY87029 Simian rotavirus A/SA I2 DQ RVA/Humantc/USA/DS/976/G2PB4 I2 DQ RVA/Humantc/JPN/AU/982/G3P39 I3 DQ46702 RVA/Humantc/THA/T52/998/G2P9 VP6 I2 VP7 VP GP[8]G2P[4]VP7VP6
9 Vol. 35 No DS GP[8] 202,, , 2, 203, 7, 20 7, 203, DS GP[8], , , , , 5 8, G2P[4]I2, ,,,,, Kuzuya M, et al., J Med Virol, 203 Sep 6. doi: 0.002/jmv Epub ahead of print,,, 53,, 2007,,,,, 4 5, 24 3, 24, i 3,, ,, ,,,
10 072 Vol. 35 No ,, PCR G P 2 ii 5, 20,,,,,,,,,,,, iii,,, RNA, G, P st PCR, 2nd PCR,, i, / G9P[8] 6% G2P[4] 0%, 55,,,, 5, , 4.9, ii % G3P[8] 85% GP[8] 0% G2P[4] 5% G9P[8] 0% 6% G3P[8] 54% GP[8] 35% G9P[8] 0% G3P[8] 29% 4% GP[8] 67% G2P[4] 0% a 2,549 7, ,775 33,000 b,,000, b 4.4 (95%CI: 3.6, 5.3) 4.7 (95%CI: 3.6, 5.9) (95%CI: 4.0, 5.7) 5.4 (95%CI: 4.3, 6.7) (95%CI: 2.0, 4.0) (95%CI: 2., 4.3) 5 c in 40 in 37 in 6 a 2005 b Fisher s exact test c 2007 (2,434), (,57), (,097)
11 Vol. 35 No , /,000 /, 4 iii PCR,, 2007 G3, G 20 2,, 2.7, 5.2/,000/,,,,,,,,,,, cost effective analysis, : Kamiya H, et al., J Infect Dis 200 Suppl : S4046, Kamiya H, et al., Jpn J Infect Dis 64 6: , 20 Francis Dennis, GSK 5 MSD , 520,946, 5 237,034,,, , ,,,,,,,, 204 6, , ,,,,,
12 274 Vol. 35 No ,, , 0 57, 7,,,,,,, 5,,,,,, 2 3,,,, 5,,, 3.9 /,000 /,.4 /,000 /, 5. /,000 /, 3.7 /,000 /,,, 3,,,,,,, 5,,,,,,,,,, :,, 0,
13 Vol. 35 No , 0,,,,,,,,, 5,,,,, 8, / , 2, , 4.6, , 3.3, EHEC EPEC 3., 0.6, 5 8,,, 4, 7 6 Rotarix 24, Rotateq 32,,,, 8,,,,,,, n=, /00,000, 68.3/ 00,000 35/00,000, 38/00,000, 65/00,000, 66/00,000, 7/00,000, 7800/00,000,,,.84 ; , 4, ,, 0 58 Noguchi A, et al., Jpn J Infect Dis, 202 Jul,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,, SFTS SFTS, 203, 3,,,,,,,,,,, SFTS SFTSV, SFTSV SFTSV SFTSV,, 47 SFTSV,, SFTS, SFTS
14 476 Vol. 35 No , SFTSV SFTSV,,,, : 26,, 8 4,000,,,,,, SFTSV, 5 5, SFTSV,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,, 3,,, SFTSV, SFTSV 2 SFTSV : SFTS, IASR 34: , 203, , 2 SFTSV,, 27, 7,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,, SFTSV, 0,,,,,,,,, ;,,,, 3,, 5, 4,, , SFTS, 9,,,,,,,,,,, 9,,,,,,,,, SFTSV,,,,, SFTSV, SFTSV,, SFTSV, 2 SFTSV, SFTS,,,, SFTSV,,,,, SFTSV,, AHNpdm09 203/4,, AHNpdm09 3,,
15 Vol. 35 No /4 AHNpdm09,, 2 NA H275Y,,,, H275Y 2, 2, NA 203/4 N248D, V24I, N369K N386K, 2, 2 2,, 2, AHNpdm09,, 2, 203/4, 203 2, AHNpdm ,, /4, 204 5, 22 7 AHNpdm09, N44S V24I N369K N200S V06I A/PERTH/265/2009 A/PERTH/26/2009 A/NARITA//2009 A/California/07/2009 A/MIE/27/203 Dec A/SAPPORO/9/203 Dec A/SAPPORO/20/203 Dec A/SAPPORO/07/203 Nov A/YAMAGATA/57/203 Nov A/YAMAGATA/58/203 Nov A/KANAGAWA/46/203 Nov A/SAPPORO/TH/203 Nov A/SAPPORO/6/203 Nov A/SAPPORO/4/203 Nov A/SichuanWuhou/SWL2259/203 Sep A/SichuanQingyang/SWL599/203 Nov A/BeijingXichengNanPian/SWL69/203 Sep A/ChongqingBanan/SWL690/203 Nov N386K A/HubeiWuchang/SWL322/203 Nov A/ShanghaiChangning/SWL62/203 Dec A/SichuanDong/SWL87/203 Oct A/Utah/09/203 Oct A/SichuanQingyang/SWL544/203 Sep A/SichuanYucheng/SWL693/203 Nov A/ChongqingYuzhong/SWL676/203 Nov A/HubeiWujiagang/SWL838/203 Dec A/Louisiana/2/203 Oct A/Louisiana//203 Oct A/Louisiana/23/203 Nov A/Louisiana/20/203 Nov S82P A/Mississippi/29/203 Nov I34V A/Louisiana/08/203 Oct N397K I32V A/Louisiana/0/203 Oct A/Louisiana/07/203 Oct K432E A/Louisiana/3/203 Nov A/Utah/0/203 Oct A/Mississippi/28/203 Dec A/Mississippi//203 Nov A/Mississippi/27/203 Dec A/Mississippi/09/203 Oct A/Utah/3/203 Dec A/OSAKAC/2006/203 Sep A/TOKYO/33409/203 Nov A/TOKYO/3247/203 Nov A/Utah/20/203 Nov A/Mississippi/08/203 Oct A/Louisiana/06/203 Sep A/SHIMANE/23/203 Sep A/SHIMANE/24/203 Sep A/SHIMANE/2/203 Sep A/SHIMANE/22/203 Sep A/SHIMANE/25/203 Sep A38T A/SHIMANE/20/203 Sep A/ShanghaiChangning/SWL568/203 Sep A/MIE/23/203 Sep A/MIE/22/203 Sep A/YAMAGUCHI/42/203 Dec L40I S95N, G20R A/YAMAGUCHI/43/203 Dec A/TOKYO/32432/203 Nov A/WAKAYAMA/53/203 Nov A/MIE/24/203 Sep A/KANAGAWA/49/203 Nov A/YOKOHAMA/56/203 Sep A/WAKAYAMAC/3/203 Sep A/WAKAYAMAC/32/203 Sep A/NEWCASTLE/32/20 A/NEWCASTLE/5/20 A/NEWCASTLE/29/20 A/NEWCASTLE/25/20 A/NEWCASTLE/7/20 A/NEWCASTLE/82/20 A/NEWCASTLE/79/20 A/NEWCASTLE/85/20 A/NEWCASTLE/89/20 A/NEWCASTLE/22/20 A/NEWCASTLE/2/20 A/NEWCASTLE/53/20 V62I A/NEWCASTLE/86/20 V06I A/NEWCASTLE/68/20 N386S A/NEWCASTLE/37/20 A/NEWCASTLE/62/20 A/NEWCASTLE/02/20. NA, AHNpdm09,,,,,, 2, /4,, 203/4 A/California/7/2009,, AHNpdm09,, 4,, 2009 HN
16 678 Vol. 35 No , HA D222G, Q223R 57, /204 8,,,, NA H275Y, 9 0,,, IASR 35: 4243, 204 2Takashita E, et al., Euro Surveill 9: pii: 20666, 204 3IASR 35: 4345, 204 4IASR 35: 442, 204 5Chutinimitkul S, et al., J Virol 84: 80283, 200 6Liu Y, et al., J Virol 84: , 200 7Zhang Y, et al., J Virol 86: , 202 8, 203/204 php?content_id=86 9Saito R, et al., Pediatr Infect Dis J 29: , f ludr/ AHNpdm09 204, 9, 2 AHNpdm09 AHNpdm09, AHNpdm , , A,,,,,,, 3 50, A, A, Glasgow coma scalegcs; EVM4,,,,,, DIC,,,,,, Autopsy imagingai MRI,,,,, Sick contact:, 2 5, 2 A : :,,, : 204 7, RTPCR, AHNpdm09, MDCK AHNpdm09, TaqMan RT
17 PCR NA, H275Y AHNpdm09, AHNpdm09,, 2 AHNpdm09, 2009/0 33, Gu 3 AHNpdm09,,, 4,, DIC, Hemorrhagic shock with encephalopathy syndrome HSE HSE,,, 2, DIC IASR 34: , 203 2IASR 35: 442, 204 3Gu Y, et al., PLoS One 203; 8: e , 20 : 4350, 2008,,, Men who have sex with men: MSM 3, ,, 202 Vol. 35 No , , ,226, , ,, , , , , , I , II , , II, , / , , / 2. 0
18 880 Vol. 35 No / , , 4 88., MSM HIV 5,,, MSM,,,,,,,,, 00 6, 202 Sexually Transmitted Disease Surveillance, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Savage EJ, et al., Euro Surveill. 202; 7 29: pii Bremer V, et al., Euro Surveill. 202; 7 29:pii IASR 29: 23924, IASR 34: 25252, 203 6Kamali A, et al., Lancet 36: , 2003 Agbeni 3, 5 Enteritidis Infantis, 2, tables/525iasrb.html, Agbeni 3, , 2, 4, 4, 3 O3, H g,m, H2, Statens Serum Institute O3 O22, O23, PCR I 2, 3 3 O23, PCR inva, I STM4057, O3, H; g,m, H2; complex H2; e,ncomplex, Agbeni, 3, 23: g, m, [t]:, KirbyBauer, 3,,,,, 6, PFGE
19 Vol. 35 No PCR No. No. PCR O H H2 inva STM4057 O3 H;g, m H2; H2; e, n Sa2675 8/27 O3, 23 g, m Sa2680 9/5 O3, 23 g, m Sa268 9/ O3, 23 g, m (a) (kb) NotI M 2 3 XbaI DNA, NotI, XbaI,,,,,, (b) M M 2 3 M (kb) M: DNA size standard Lambda ladder (BIORAD), : Sa2795, 2: Sa2780, 3: Sa278. PFGEDNA ,,,, PCR, PCR,,,, Lee, et al., Appli Microbio 07: 8058, Franklin, et al., J Clin Microbiol 49: , 20 3 Maurer, et al., J Vis Exp 2: 6, 20 4,, IASR 30: 2223, 2009 A B UVS 4 UVS: Untypable Vi strain group NA NA: CPFX: NA, CPFX NA, CPFX
20 2082 Vol. 35 No HIV AIDS HIV , , 3, , 0 3. AIDS 08 08, 4 0, 7, 02 07, 6, 7 4. HIV AIDS 403. HIV : 205 HIV 69 5 HIV 7 42, 9 2,, AIDS : 59 AIDS AIDS 23 2, 4 3, HIV 34,6 24,533, 26,597, 8,96 7,30, 7, ,077 3,843, 33, , 5,205,89 5,27,03 2. HIV , , HIV, AIDS 2., HIV,, 2, HIV 3.,, HIV HIV, AIDS HIV AIDS,546 2, 20 HIV,,26, AIDS 43,,557. HIV : 760 HIV 7 89 HIV 8 7, 6, AIDS : 268 AIDS 57 0 AIDS 23 7, 4 0, 30, HIV 36, ,56
21 Vol. 35 No , ,09. 25,, HIV AIDS,500, 2. HIV, 20 30, 3. HIV AIDS, 7,, 22,97 4., AIDS AIDS 30 40, 40 63, HIV AIDS AIDS 30
22 2284 Vol. 35 No , 5. 22, HIV,, HIV 6., 0 7., HIV,,
23 Vol. 35 No Verotoxinproducing E.coli ( ) 0 62 ( 2) ( 2) 2 9 ( ) 4 Enterotoxigenic enic E.coli ( 2) 5 3 Enteroinvasive E.coli Enteropathogenic E.coli ( ) Enteroaggregative E.coli ( ) 3 Other diarrheagenic E.coli Salmonella Typhi 3 ( ) 2 ( 2) ( ) 2 ( 2) 2 Salmonella Paratyphi A ( ) 2 ( 2) ( ) 3 ( 2) ( ) ( ) Salmonella O ( ) 8 8 Salmonella O ( ) ( 2) 0 Salmonella O Salmonella O ( 2) 2 Salmonella O3,0 2 3 Salmonella O,3,99 Salmonella O Salmonella O3 Salmonella O8 Salmonella O30 Salmonella O39 Salmonella group unknown 4 2 Vibrio cholerae O:El Tor Ogawa awa,ct+ ( ) Vibrio cholerae nono&o39 Vibrio parahaemolyticus 7 Vibrio furnissii Aeromonas hydrophila Plesiomonas shigelloides Campylobacter jejuni Campylobacter coli Campylobacter jejuni/coli 2 Staphylococcus aureus Clostridium perfringens Bacillus cereus Listeria monocytogenes Yersinia enterocolitica Shigella dysenteriae 4 ( ) Shigella flexneri a Shigella flexneri b ( ) ( ) Shigella flexneri Shigella flexneri 2a 3 Shigella flexneri 2 b ( ) Shigella flexneri 3a Shigella flexneri 4 Shigella flexneri 6 Shigella flexneri other serovars ( ) Shigella flexneri untypable ( ) Shigella boydii 8 Shigella sonnei ( ) 3 ( 8) 2 ( 2) 3 ( 2) 2 ( 2) ( ) 4 ( 2) 2 ( ) ( ) Entamoeba histolytica Streptococcus tococcus group A Streptococcus group B 3 7 Streptococcus group C 2 Streptococcus tococcus group G Streptococcus tococcus other groups 2 S.dysgalactiae subsp.equisimilis Streptococcus pneumoniae Bordetella pertussis Legionella pneumophila Mycobacterium tuberculosis Mycobacterium bovis Mycoplasma pneumoniae Haemophilus influenzae b Haemophilus influenzae nonb Klebsiella pneumoniae 0 Neisseria meningitidis 2 Enterococcus faecalis Enterococcus faecium 20 Enterococcus gallinarum Enterococcus casseliflavus Pseudomonas aeruginosa Leptospira interogans Leptospira sp. 807 ( 2) 622 ( 2) 50 ( 4) 344 ( 4) 339 ( 5) 82 ( 5) 72 ( 6) 206 ( 2) 296 ( 4) 286 ( 3)
24 2486 Vol. 35 No ( 2) ( ) 20 ( ) ( 0) Verotoxinproducing E.coli ( ) 8 ( ) 09 ( 4) Enterotoxigenic enic E.coli Enteroinvasive E.coli ( ) Enteropathogenic E.coli ( ) Enteroaggregative E.coli Other diarrheagenic E.coli 2 ( 2) 4 ( 2) 4 ( ) 2 ( ) 2 ( 2) 25 ( 4) Salmonella Typhi ( ) 2 ( 2) ( ) ( ) 4 ( 3) Salmonella Paratyphi A ( ) ( 4) 24 ( 6) Salmonella O ( 3) Salmonella O ( 2) 5 ( 2) Salmonella O ( 2) 206 ( 4) Salmonella O9 0 Salmonella O3,0 5 Salmonella O,3,99 Salmonella O 2 4 Salmonella O3 Salmonella O8 Salmonella O30 Salmonella O Salmonella group unknown ( ) ( ) 3 ( 3) Vibrio cholerae O:El Tor Ogawa awa,ct+ 2 3 Vibrio cholerae nono&o Vibrio parahaemolyticus Vibrio furnissii 3 Aeromonas hydrophila Plesiomonas shigelloides Campylobacter jejuni Campylobacter coli 3 Campylobacter jejuni/coli Staphylococcus aureus Clostridium perfringens Bacillus cereus 2 Listeria monocytogenes Yersinia enterocolitica ( ) Shigella dysenteriae 4 Shigella flexneri a 2 ( 2) Shigella flexneri b ( ) ( ) Shigella flexneri 4 Shigella flexneri 2a 2 4 ( ) Shigella flexneri 2b ( ) 2 ( ) Shigella flexneri 3a Shigella flexneri 4 ( ) ( ) Shigella flexneri 6 4 ( ) Shigella flexneri other serovars ( ) Shigella flexneri untypable Shigella boydii 8 5 ( 4) 6 ( ) 6 ( 3) 2 ( ) 2 53 ( 29) Shigella sonnei Entamoeba histolytica Streptococcus tococcus group A Streptococcus group B 2 Streptococcus group C Streptococcus tococcus group G 5 Streptococcus tococcus other groups 5 S.dysgalactiae subsp.equisimilis Streptococcus pneumoniae Bordetella pertussis Legionella pneumophila Mycobacterium tuberculosis Mycobacterium bovis Mycoplasma pneumoniae 2 Haemophilus influenzae b Haemophilus influenzae nonb Klebsiella pneumoniae 4 Neisseria meningitidis 4 Enterococcus faecalis 24 Enterococcus faecium Enterococcus gallinarum Enterococcus casseliflavus 0 Pseudomonas aeruginosa 3 Leptospira interogans Leptospira sp. 38 ( 7) 625 ( 3) 64 ( 9) 493 ( 3) 339 ( 5) 249 ( 5) 286 ( ) 5 ( 9) 6857 ( 99)
25 Vol. 35 No Verotoxinproducing E.coli Enteropathogenic E.coli Enteroaggregative E.coli 2 2 Salmonella O4 2 ( 4) 3 ( 4) Salmonella O7 2 2 Salmonella O8 6 ( 2) 7 ( 2) Salmonella O9 4 ( 2) 5 ( 2) Salmonella O3,0 Salmonella O,3,9 Campylobacter jejuni Campylobacter coli 2 4 Staphylococcus aureus Clostridium perfringens 4 4 Yersinia enterocolitica Shigella flexneri ( ) ( ) Streptococcus tococcus group A Streptococcus tococcus group G Streptococcus pneumoniae Bordetella pertussis Legionella pneumophila Mycobacterium tuberculosis 2 2 Mycoplasma pneumoniae 3 3 Haemophilus influenzae nonb ( 9) ( 9) Salmonella O4 Typhimurium 3 ( 2) 3 ( 2) O4 Stanley 4 4 O4 Saintpaul 2 2 O4 Schwarzengrund O4 Coeln O4 Haifa 2 ( 2) 2 ( 2) O7 Thompson O7 Bareilly O8 Litchfield O8 Bovismorbificans ( ) ( ) O8 Manhattan O8 Albany ( ) ( ) O8 Nagoya 2 2 O8 Yovokome O 9 Enteritidis 3 ( ) 4 ( ) O9 Panama ( ) ( ) O3,0 Weltevreden O,3,9 Senftenberg Shigella Shigella flexneri ( ) ( ) T T3 T T TB Untypable
26 2688 Vol. 35 No Verotoxinproducing E.coli 8 8 Enteropathogenic E.coli 2 Enteroaggregative E.coli 2 2 Salmonella O3,0 Staphylococcus aureus Streptococcus pyogenes Mycoplasma pneumoniae 3 4 Moraxella catarrhalis Influenza virus A Hpdm Influenza virus A H3 8 9 Influenza virus B/Victoria 3 Influenza virus B/Yamagat ata 2 Measles virus genotype NT Measles virus genotype B Measles virus genotype D8 2 Measles virus genotype D9 Dengue virus 3 4 Dengue virus 2 Norovirus genogroup II NT Hepatitis A virus NT Hepatitis A virus IA 2 Plasmodium falciparum Dengue virus 4 / NT:
27 Vol. 35 No Picornavirus NT Enterovirus NT Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A4 2 6 Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A2 2 2 Coxsackievirus B Coxsackievirus B Coxsackievirus B Coxsackievirus B Coxsackievirus B Coxsackievirus B6 NT Poliovirus Poliovirus 2 Poliovirus Enterovirus Enterovirus Parechovirus NT Parechovirus Parechovirus Rhinovirus Aichivirus 2 2 Saffold cardiovirus Influenza virus A not subtyped Influenza virus A Hpdm Influenza virus A H Influenza virus B NT Influenza virus B/Victoria Influenza virus B/Yamagata Influenza virus C 2 2 Parainfluenza virus Respiratory syncytial virus Human metapneumovirus Other coronavirus Mumps virus Measles virus genotype NT Measles virus genotype A Measles virus genotype B Measles virus genotype D Measles virus genotype D9 2 9 Measles virus genotype H Rubella virus genotype NT Rubella virus genotype a 3 Rubella virus genotype E Rubella virus genotype 2B Japanese encephalitis virus Dengue virus Chikungunya virus 4 SFTS virus 4 5 Reovirus 2 Rotavirus group unknown 2 Rotavirus group A Rotavirus group C Astrovirus Norovirus genogroup unknown Norovirus genogroup I Norovirus genogroup II Sapovirus genogroup unknown Sapovirus genogroup I Sapovirus genogroup II Sapovirus genogroup III Sapovirus genogroup IV Adenovirus NT Adenovirus Adenovirus Adenovirus Adenovirus Adenovirus Adenovirus Adenovirus 7 Adenovirus Adenovirus 3 Adenovirus 2 Adenovirus 9 3 Adenovirus Adenovirus Adenovirus 40/ Adenovirus Adenovirus 53/ Adenovirus Adenovirus Herpes simplex virus NT Herpes simplex virus Herpes simplex virus Varicellazoster virus Cytomegalovirus Human herpes virus Human herpes virus EpsteinBarr virus Hepatitis A virus NT 2 8 Hepatitis A virus IA Hepatitis A virus IB 2 Hepatitis A virus IIIA 3 4 Hepatitis E virus 2 5 Human papilloma virus B9 virus Human bocavirus Chlamydia trachomatis Chlamydophila pneumoniae Orientia tsutsugamushi Rickettsia japonica NT:
28 Entero N Entero NT Coxsackie A Coxsackie A Coxsackie A Coxsackie A4 Coxsackie A Coxsackie A Coxsackie A Coxsackie A Coxsackie A Coxsackie A8 Coxsackie A Coxsackie A9 2 Coxsackie A Coxsackie A0 2 Coxsackie A Coxsackie A2 2 2 Coxsackie A Coxsackie A Coxsackie B Coxsackie B Coxsackie B Coxsackie B Coxsackie B Coxsackie B Coxsackie B Coxsackie B Coxsackie B Coxsackie B NT cho E cho E cho E 9 cho E cho E 5 8 cho E cho E 3 25 cho E cho E ntero E ntero E Parecho N Parecho NT arecho P 3 arecho P Rhino AFV S Influenza A not subtype Influenza A not subtyped Influenza A Hpdm0 Influenza A Hpdm Influenza A H Influenza A H Influenza B N Influenza B NT Influenza B/Victori Influenza B/Victoria Influenza B/Yamagat Influenza B/Yamagata Parainfluenza Parainfluenza Respiratory syncytial Respiratory syncytial Human metapneum Human metapneumo Other coron Other corona umps M Measles genotype N Measles genotype NT Measles genotype Measles genotype A Measles genotype B Measles genotype B Measles genotype D Measles genotype D Measles genotype D Measles genotype D9 Rubella genotype N Rubella genotype NT Rubella genotype Rubella genotype E Rubella genotype 2 Rubella genotype 2B Japanese encephalitis Japanese encephalitis engue D 2 2 Chikungunya Chikungunya Rota group Rota group A stro A 3 Noro genogroup unknow Noro genogroup unknown Noro genogroup Noro genogroup I 2 Noro genogroup I Noro genogroup II Sapo genogroup unknow Sapo genogroup unknown Sapo genogroup Sapo genogroup I Sapo genogroup I Sapo genogroup II NT deno A deno A deno A Adeno 2 4 deno A deno A deno A 8 deno A 4 2 deno A 3 deno A 37 deno A 3 Adeno 40/4 Adeno 40/ deno A 54 deno A 4 56 deno A 2 Herpes simplex N Herpes simplex NT 8 Herpes simplex Herpes simplex Herpes simplex Herpes simplex 2 4 Varicellazoster Varicellazoster 6 Cytomegal Cytomegalo Human herpes Human herpes Human herpes Human herpes EpsteinBarr EpsteinBarr Hepatitis A N Hepatitis A NT Hepatitis A I Hepatitis A IA 2 Hepatitis A III Hepatitis A IIIA 3 Hepatitis E Hepatitis E Human papilloma Human papilloma B 2 Human boc Human boca Orientia tsutsugamushi Orientia tsutsugamushi 7 Rickettsia japonica Rickettsia japonica NT: Vol. 35 No
29 Entero NT Entero NT Coxsackie A2 Coxsackie A2 5 Coxsackie A4 Coxsackie A Coxsackie A5 Coxsackie A Coxsackie A6 Coxsackie A Coxsackie A8 Coxsackie A Coxsackie A9 Coxsackie A9 5 Coxsackie A0 Coxsackie A0 6 Coxsackie A2 Coxsackie A Coxsackie A6 Coxsackie A Coxsackie B Coxsackie B Coxsackie B2 Coxsackie B Coxsackie B3 Coxsackie B Coxsackie B4 Coxsackie B Coxsackie B5 Coxsackie B5 3 Echo NT Echo NT Echo 6 Echo 6 2 Echo 7 Echo 7 9 Echo 9 Echo Echo Echo Echo 8 Echo Echo 9 Echo Echo 25 Echo Echo 30 Echo Entero 68 Entero Entero 7 Entero Parecho NT Parecho NT Parecho Parecho 2 Parecho 3 Parecho Rhino Rhino SAFV SAFV Influenza A not subtyped Influenza A not subtyped Influenza A Hpdm09 Influenza A Hpdm Influenza A H3 Influenza A H Influenza B NT Influenza B NT Influenza B/Victoria Influenza B/Victoria Influenza B/Yamagata Influenza B/Yamagata Parainfluenza Parainfluenza Respiratory syncytial Respiratory syncytial Human metapneumo Human metapneumo Other corona Other corona Mumps Mumps 3 Measles genotype NT Measles genotype NT 2 Measles genotype A Measles genotype A Measles genotype B3 Measles genotype B3 2 6 Measles genotype D8 Measles genotype D8 3 Measles genotype D9 Measles genotype D Rubella genotype NT Rubella genotype NT Rubella genotype E Rubella genotype E Rubella genotype 2B Rubella genotype 2B Japanese encephalitis Japanese encephalitis Dengue Dengue Chikungunya Chikungunya Rota group A Rota group A Astro Astro Noro genogroup unknown Noro genogroup unknown Noro genogroup I Noro genogroup I Noro genogroup II Noro genogroup II Sapo genogroup unknown Sapo genogroup unknown Sapo genogroup I Sapo genogroup I Sapo genogroup II Sapo genogroup II Adeno NT Adeno NT Adeno Adeno Adeno 2 Adeno Adeno 3 Adeno Adeno 4 Adeno Adeno 5 Adeno Adeno 6 Adeno 6 5 Adeno 8 Adeno 8 Adeno 2 Adeno 2 3 Adeno 3 Adeno 3 5 Adeno 37 Adeno Adeno 40/4 Adeno 40/ Adeno 4 Adeno 4 7 Adeno 54 Adeno 54 5 Adeno 56 Adeno 56 8 Herpes simplex NT Herpes simplex NT Herpes simplex Herpes simplex 6 6 Herpes simplex 2 Herpes simplex Varicellazoster Varicellazoster Cytomegalo Cytomegalo Human herpes 6 Human herpes Human herpes 7 Human herpes EpsteinBarr EpsteinBarr 2 3 Hepatitis A NT Hepatitis A NT Hepatitis A IA Hepatitis A IA 4 Hepatitis A IIIA Hepatitis A IIIA Hepatitis E Hepatitis E 5 5 Human papilloma Human papilloma 8 8 B9 B9 3 3 Human boca Human boca Orientia tsutsugamushi Orientia tsutsugamushi Rickettsia japonica Rickettsia japonica NT: Vol. 35 No
30 Enterovirus NT Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A4 3 5 Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A2 4 6 Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus B Coxsackievirus B Coxsackievirus B Coxsackievirus B Coxsackievirus B NT Enterovirus Enterovirus Parechovirus NT Parechovirus Parechovirus 3 2 Rhinovirus Saffold cardiovirus Influenza virus A not subtyped Influenza virus A Hpdm Influenza virus A H Influenza virus B NT Influenza virus B/Victoria Influenza virus B/Yamagata Parainfluenza virus Respiratory syncytial virus Human metapneumovirus 9 20 Other coronavirus Mumps virus Measles virus genotype NT 2 3 Measles virus genotype A 2 Measles virus genotype B Measles virus genotype D8 6 6 Measles virus genotype D9 2 3 Rubella virus genotype NT Rubella virus genotype E Rubella virus genotype 2B Japanese encephalitis virus Dengue virus Chikungunya virus Rotavirus group A Astrovirus Norovirus genogroup unknown Norovirus genogroup I Norovirus genogroup II Sapovirus genogroup unknown Sapovirus genogroup I Sapovirus genogroup II 8 9 Adenovirus NT Adenovirus Adenovirus Adenovirus Adenovirus Adenovirus Adenovirus Adenovirus Adenovirus 2 Adenovirus Adenovirus Adenovirus 40/4 2 2 Adenovirus Adenovirus Adenovirus Herpes es simplex virus NT 7 8 Herpes es simplex virus Herpes simplex virus Varicellazoster virus Cytomegalovirus Human herpes es virus Human herpes es virus EpsteinBarr virus Hepatitis A virus NT 3 3 Hepatitis A virus IA 9 9 Hepatitis A virus IIIA 4 4 Hepatitis E virus Human papilloma virus B9 virus Human bocavirus Orientia tsutsugamush amushi 3 3 Rickettsia japonica NT: Vol. 35 No
31 Vol. 35 No IASR Vol. 35 No. 3 March 204 Infectious Agents Surveillance Report Overview of rotavirus Genotyping of human rotavirus using genomewide nucleotide sequencingglobal trends Rotavirus infection outbreaks and characteristics of the causative strains, Osaka City Detection of group A rotavirus, 200/202/3 seasonsokayama Prefecture Detection of rotavirus from Niigata Prefecture s infectious disease surveillance system, Rotavirus gastroenteritis surveillance in Mie Prefecture, evidencebased policy and assessment for vaccine introduction... 7 Introduction of rotavirus vaccine and its evaluation Incidence of intussusception in Japan prior to rotavirus vaccination implementation, ISSN National Institute of Infectious Diseases and Tuberculosis and Infectious Diseases Control Division, Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare Geographical distribution of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS) virus in Japan (2 nd report) Antiviral drugresistant A(HN)pdm09 detected in Yamagata Prefecture, 203/4 influenza season Fatal case of acute encephalopathy attributed to influenza A(HN)pdm09 infection in a previously healthy child, 203 Nagano Prefecture Increase in the number of syphilis cases reported to the National Epidemiological Surveillance of Infectious Diseases (NESID) system in Japan, Identification of a rare serovar Agbeni from three patients infected with Salmonella, 203Akita Prefecture HIV/AIDS in Japan, OctoberDecember <THE TOPIC OF THIS MONTH> Rotavirus, , Japan Rotavirus belongs to the family Reoviridae, whose genome consists of segments of doublestranded RNA. Rotavirus is classified into groups AG according to the inner core protein s antigenicity, among which groups AC are detected from humans. Group A rotavirus is often referred to simply as rotavirus since this group makes up most of the circulating rotavirus in the world. Rotavirus is a major cause of acute viral gastroenteritis among infants, and majority of the people are believed to have experienced infection at least once by 5 years of age (see p. 65 of this issue). The virus is transmitted by the fecaloral route, and after an incubation of 4 days, clinical manifestations consisting of diarrhea, vomiting and fever appear. Treatment is oral or intravenous rehydration, as no specific treatment is available. While patients usually recover within a week, dehydration is often more severe compared with other viral gastroenteritis. Complications include seizures, which, if sustained, are associated with poor prognosis and increased risk of sequelae. Less frequent complications include renal or hepatic failures and encephalitis/encephalopathy. Although rare in developed countries, much of pediatric diarrheal deaths in developing countries is attributed to rotavirus infection (estimated 450,000 deaths/year) (Lancet Infect Dis 2: 364, 202). Infectious gastroenteritis under the National Epidemiological Surveillance of Infectious Diseases (NESID) system: Under the Infectious Diseases Control Law, rotavirus infection is included under infectious gastroenteritis (notification criteria in a Category V infectious disease to be reported from approximately 3,000 nationwide pediatric sentinel clinics. An amendment on 4 October 203 introduced an additional reporting system; approximately Figure. Weekly number of infectious gastroenteritis cases reported from sentinel clinics and monthly number of rotavirus detections from clinical specimens, September 2004 December 203 Number of rotavirus detections Rotavirus Group C Group A Infectious gastroenteritis (cases/week) (National Epidemiological Surveillance of Infectious Diseases: as of February 2, 204) Month Year (Infectious Agents Surveillance Report: as of February 3, 204) Table. Detection of rotaviruses during 2005/06203/4 seasons Group/genotype Detections from specimens collected during September through August in the following year* 2005/ / / / /0 200/ 20/2 202/3 203/4 Group unknown Group A Not typed G G G G4 2 G8 G G2 Group C Total *Data based on reports received from local public health institutes. (Infectious Agents Surveillance Report: as of February 3, 204) Cases/sentinel clinic 500 select key medical institutions (sentinel hospitals) in Japan are requested to notify patients of gastroenteritis specifically caused by rotavirus infection (notification criteria in go.jp/niid/images/iasr/35/409/de4092.pdf). If a pediatric sentinel clinic is selected as a key medical institution, the clinic is requested to notify a rotavirus gastroenteritis patient as infectious gastroenteritis and also as infectious gastroenteritis specifically caused by rotavirus infection. With these measures, it is believed that epidemiologic features of rotavirus infection (particularly those of severe cases) will become clearer. Every year, infectious gastroenteritis increases sharply during November/December with a wide peak in February/March to May followed by a decline (Fig. ). The FebruaryMay peak of infectious gastroenteritis overlaps with the rotavirus detection peak and the November/December peak overlaps with the norovirus detection peak ( mhlw.go.jp/byogentai/pdf/datae.pdf). Reports of rotavirus detection from public health institutes: Prefectural and municipal public health institutes (PHIs) conduct laboratory diagnosis of infectious gastroenteritis cases based on fecal specimens sent from approximately 0% of the pediatric sentinel clinics and also from specimens collected from out 63 Continued on page 64
32 Figure 2. Genotyping of group A rotaviruses 2005/06202/3 seasons No. cases 64, Vol. 35 No THE TOPIC OF THIS MONTHContinued / / / / /0 200/ 20/2 202/3 Sampled seasons (Infectious Agents Surveillance Report: as of February 3, 204) Genotyping Untyped breaks. During the past 4 years from 200 to 203, 60 PHIs reported group A and 8 PHIs reported group C rotavirus detections. During 2005/062009/0 seasons, rotavirus detections/year were reported, but increased during 200/ (Table, Fig 2). Group A rotavirus has been the majority with few group C detections (0. 2.2% since 200/ season). Group B rotavirus has not been reported in Japan. Genotyping of group A rotavirus: Group A rotavirus is classified according to combination of serotyperelated G and P genotypes, which are respectively determined by the genetic sequences of the outerlayer capsid proteins VP7 and VP4 (neutralizing antibody epitopes). Most human isolates are currently GP[8], G2 G9 G8 G4 G3 G2 G Figure 3. Age distribution of patients from whom rotavirus was detected, M 5 Y 02 M 68 M 9 M *M refers to months and Y refers to years 04 Y No. cases Rotavirus group A Y 2 Y 3 Y 4 Y 59 Y 3,302 Group A genotype G Group A genotype G2 Group A genotype G3 Group A genotype G9 IASR Vol. 35 No. 3 Mar % 2 Y 3 Y 5 Y No. cases Rotavirus group C 59 Y 04 Y % (Infectious Agents Surveillance Report: as of February 3, 204) Table 2. Number of rotavirus infection outbreaks, * Suspected place of Year of onset infection Total Nursery Primary school 6 9 () 3 () 9 (2) Welfare facility 4 5 Kindergarten 4 5 Nursing home 4 Restaurant 2** 2 Junior high school 2 2 High school Dormitory Other/Unknown 2 2 () () Total 2 26 () 48 () 3 () 08 (3) *Data based on reports received fromlocal public health institutes. **2 foodborne outbreaks Numbers in parentheses refer to number of rotavirus group C outbreaks. (Infectious Agents Surveillance Report: as of February 3, 204) G2P[4], G3P[8], G4P[8], and G9P[8] (see p. 66 of this issue). Currently, some PHIs are conducting G genotyping (see pp. 677 of this issue). Among 3,302 patients from whom group A rotavirus were detected during , 38% were year of age, 6% < year of age, and 6% 2 years of age; children under 2 years of age comprised 70% of the patients whose age was known (Fig. 3). Among those < year, those aged 6 months or older composed the majority. The same age distribution was observed across genotypes G, G3 and G9. Genotype G2 had a slightly different age distribution; following those aged year (28%), those aged 5 years were frequent (2%). Of the 27 group C rotavirusdetected cases, 8 were children aged 59 years and 5 were children aged 04 years. Complications: During , rotavirus was detected in 22 cases of encephalitis/encephalopathy and 4 cases of meningitis had rotavirus detection. Additionally, group A rotavirus was detected from 4 cases of intussusception. Outbreak incidents: Rotavirus outbreaks occur frequently in nurseries and in kindergartens, but also occasionally in primary schools, junior high schools, nursing homes for the elderly, and welfare facilities (IASR 33: 34, 202; ibid. 33: 9798, 202; ibid. 33: 27, 202; ibid. 34: 6979, 203; ibid. 34: , 203) (Table 2). Among rotavirus gastroenteritis outbreaks in , 05 were group A and 3 group C (Table 2). Majority of these incidents were attributable to persontoperson transmission except for two food poisoning outbreaks caused by group A rotavirus. Five outbreaks involved more than 50 patients (4 outbreaks due to group A and outbreak due to group C); two were in AprilMay 20 and three MarchApril 202. Prevention: Rotavirus s infectivity is very high and 000 virions are sufficient in establishing infection. An infected patient s stool contains as many as virions per gram, making rotavirus prevention difficult even in developed countries where sanitation and hygiene are well developed. Currently two oral attenuated live vaccines, GP[8] monovalent vaccine and a pentavalent vaccine containing GG4 and P[8] antigens, have been approved and used in more than 30 countries for preventing severe outcomes and introduced as a routine immunization in 53 countries (see p. 7 of this issue). The vaccines are available on a voluntary basis since November 20 and July 202, respectively, in Japan. The estimated vaccine coverage among the target age population was 35% in July 202, and 45% in April 203 (see p. 73 of this issue). Challenges: Japan is currently evaluating incorporation of rotavirus vaccine as a routine immunization. Studies from abroad have indicated that rotavirus vaccine can prevent an estimated 90% of severe outcomes due to rotavirus infection in developed countries (The Immunization and Vaccine Committee of the Health Science Council, Basic Direction of Immunization Policy Subcommittee, Rotavirus Vaccine Task Force Interim Report, 8 November 203). If rotavirus vaccination is to be introduced in Japan, its effectiveness and safety must be evaluated by: ) monitoring trends in rotavirus cases, particularly of severe ones; 2) with regards to safety, given the slight increase in the incidence of intussusception reported from countries that have implemented rotavirus immunization, there is a need for careful monitoring of the occurrence of intussusception (see p.74 of this issue); and 3) to monitor the virus populations in circulation, considering vaccination s potential selection pressure on circulating rotaviruses. Rotavirus surveillance should thus be further strengthened and coordinated between the National Institute of Infectious Diseases and partners such as PHIs and universities. The statistics in this report are based on ) the data concerning patients and laboratory findings obtained by the National Epidemiological Surveillance of Infectious Diseases undertaken in compliance with the Law Concerning the Prevention of Infectious Diseases and Medical Care for Patients of Infections, and 2) other data covering various aspects of infectious diseases. The prefectural and municipal health centers and public health institutes (PHIs), the Department of Food Safety, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, and quarantine stations, have provided the above data. Infectious Disease Surveillance Center, National Institute of Infectious Diseases Toyama 23, Shinjukuku, Tokyo , JAPAN Tel (+83)
untitled
 Infectious Agents Surveillance Report (IASR) http://www.nih.go.jp/niid/ja/iasr.html EHEC 202 3, EHEC O57 : 4 O57 ISprinting system 5, 6, O57 : 20 7, O57 : 8, O26 : 9, O26 : 0, O26 : 2, O03 O : 3, O45 :
Infectious Agents Surveillance Report (IASR) http://www.nih.go.jp/niid/ja/iasr.html EHEC 202 3, EHEC O57 : 4 O57 ISprinting system 5, 6, O57 : 20 7, O57 : 8, O26 : 9, O26 : 0, O26 : 2, O03 O : 3, O45 :
untitled
 Infectious Agents Surveillance Report (IASR) http://www.nih.go.jp/niid/ja/iasr.html : 3, : 5, NESID 6, : 7, : 9, L. pneumophila SG3 ST93 : 0,, ATP 3, 4, 5, Human coronavirus : 6, AH7N9 : 8, A H7N9 : 9,
Infectious Agents Surveillance Report (IASR) http://www.nih.go.jp/niid/ja/iasr.html : 3, : 5, NESID 6, : 7, : 9, L. pneumophila SG3 ST93 : 0,, ATP 3, 4, 5, Human coronavirus : 6, AH7N9 : 8, A H7N9 : 9,
untitled
 Infectious Agents Surveillance Report (IASR) http://www.nih.go.jp/niid/ja/iasr.html SFTS 3, SFTS 4, SFTSV 5, SFTSV : 7, 03 SFTS 40 8, SFTS 9, SFTS 0, AHpdm09, 03/4 AHpdm09, 3, Zika fever 5, 6, CA 8, 03
Infectious Agents Surveillance Report (IASR) http://www.nih.go.jp/niid/ja/iasr.html SFTS 3, SFTS 4, SFTSV 5, SFTSV : 7, 03 SFTS 40 8, SFTS 9, SFTS 0, AHpdm09, 03/4 AHpdm09, 3, Zika fever 5, 6, CA 8, 03
Fig. 1 Trends of TB incidence rates for all forms and smear-positive pulmonary TB in Kawasaki City and Japan. Incidence=newly notified cases of all fo
 Kekkaku Vol. 79, No. 1: 17-24, 2004 17 (Received 21 Aug. 2003/Accepted 18 Nov. 2003) Fig. 1 Trends of TB incidence rates for all forms and smear-positive pulmonary TB in Kawasaki City and Japan. Incidence=newly
Kekkaku Vol. 79, No. 1: 17-24, 2004 17 (Received 21 Aug. 2003/Accepted 18 Nov. 2003) Fig. 1 Trends of TB incidence rates for all forms and smear-positive pulmonary TB in Kawasaki City and Japan. Incidence=newly
SARS HIV/AIDS n = 672; % 5% 2% 8% 16% 43% 20%
 SARS HIV/AIDS n = 672; 20074 20108 6% 5% 2% 8% 16% 43% 20% 1999 2008 HIV/AIDS B A 0% 50% 100% 1049 552 17 186 867 431 739 3847 332 7556 102 2420 3648 449 802 2709 31774 1286 13651 1611 207 95 8 162 667
SARS HIV/AIDS n = 672; 20074 20108 6% 5% 2% 8% 16% 43% 20% 1999 2008 HIV/AIDS B A 0% 50% 100% 1049 552 17 186 867 431 739 3847 332 7556 102 2420 3648 449 802 2709 31774 1286 13651 1611 207 95 8 162 667
CHEMOTHERAPY aureus 0.10, Enterococcus faecalis 3.13, Escherichia coli 0.20, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter spp., Serratia marcescens 0.78, Prote
 aureus 0.10, Enterococcus faecalis 3.13, Escherichia coli 0.20, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter spp., Serratia marcescens 0.78, Proteus mirabilis 3.13, Proteus vulgaris 1.56, Citrobacter freundii 0.39,
aureus 0.10, Enterococcus faecalis 3.13, Escherichia coli 0.20, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter spp., Serratia marcescens 0.78, Proteus mirabilis 3.13, Proteus vulgaris 1.56, Citrobacter freundii 0.39,
Table 1. Antibacterial activitiy of grepafloxacin and other antibiotics against clinical isolates
 Table 1. Antibacterial activitiy of grepafloxacin and other antibiotics against clinical isolates Table 2-1. Summary of patients treated with grepafloxacin for respiratory infection 1) Out: outpatient,
Table 1. Antibacterial activitiy of grepafloxacin and other antibiotics against clinical isolates Table 2-1. Summary of patients treated with grepafloxacin for respiratory infection 1) Out: outpatient,
Key words: bacterial meningitis, Haemophilus influenzae type b, Streptococcus pneumoniae, rapid diagnosis, childhood
 Key words: bacterial meningitis, Haemophilus influenzae type b, Streptococcus pneumoniae, rapid diagnosis, childhood Fig.1 Distribution of the cases with bacterial meningitis by age and pathogens Chiba
Key words: bacterial meningitis, Haemophilus influenzae type b, Streptococcus pneumoniae, rapid diagnosis, childhood Fig.1 Distribution of the cases with bacterial meningitis by age and pathogens Chiba
CHEMOTHERAPY
 CHEMOTHERAPY VOL.41 S-2 Laboratory and clinical evaluation of teicoplanin CHEMOTHERAPY AUG. 1993 VOL.41 S-2 Laboratory and clinical evaluation of teicoplanin Table 1. Comparative in vitro activity of teicoplanin
CHEMOTHERAPY VOL.41 S-2 Laboratory and clinical evaluation of teicoplanin CHEMOTHERAPY AUG. 1993 VOL.41 S-2 Laboratory and clinical evaluation of teicoplanin Table 1. Comparative in vitro activity of teicoplanin
 2) Goetz, A., Tsuneishi, N.: Application of molecular filter membranes to the bacteriological analysis of water, J. Am. Water Works Assn., 43 (12): 943-969,1951. 3) Clark, H.F. et al.: The membrane filter
2) Goetz, A., Tsuneishi, N.: Application of molecular filter membranes to the bacteriological analysis of water, J. Am. Water Works Assn., 43 (12): 943-969,1951. 3) Clark, H.F. et al.: The membrane filter
untitled
 Seminal paper Anhalt JP Pioneering paper Claydon MA Kishnamurthy T Enterobacter B. cereus Routine identification paper Eigner U Seng P Cherkaoui A Saureus S. Saureus* S. Vagococcus Haemophilus Mycobacterium
Seminal paper Anhalt JP Pioneering paper Claydon MA Kishnamurthy T Enterobacter B. cereus Routine identification paper Eigner U Seng P Cherkaoui A Saureus S. Saureus* S. Vagococcus Haemophilus Mycobacterium
CHEMOTHERAPY JUNE 1993 Table 1. Background of patients in pharmacokinetic study
 CHEMOTHERAPY JUNE 1993 Table 1. Background of patients in pharmacokinetic study VOL. 41 S 1 Table 2. Levels (Đg/ml or Đg/g) of S-1006 in serum, bile, and tissue (gallbladder) after oral administration
CHEMOTHERAPY JUNE 1993 Table 1. Background of patients in pharmacokinetic study VOL. 41 S 1 Table 2. Levels (Đg/ml or Đg/g) of S-1006 in serum, bile, and tissue (gallbladder) after oral administration
CHEMOTHERAPY FEB Table 1. Activity of cefpirome and others against clinical isolates
 VOL.39 S-1 CHEMOTHERAPY FEB. 1981 Table 1. Activity of cefpirome and others against clinical isolates VOL.39 S-1 CHEMOTHERAPY FEB. 1991 72 M, 55.5 kg 66 F, 53 kg Chronic bronchitis Bronchopneumonia Peak
VOL.39 S-1 CHEMOTHERAPY FEB. 1981 Table 1. Activity of cefpirome and others against clinical isolates VOL.39 S-1 CHEMOTHERAPY FEB. 1991 72 M, 55.5 kg 66 F, 53 kg Chronic bronchitis Bronchopneumonia Peak
小児感染免疫第30巻第1号
 26 2018 314 1 2 2 2 polymerase chain reaction PCR reverse transcription RT -PCR enzyme immunoassay EIA2009 2015 6 315 144 144 6.1 1 28.9% 1 2 1,2 3 4 1999 22 23 1 2 5 2008 2009 1 2015 12 31 6 315 polymerase
26 2018 314 1 2 2 2 polymerase chain reaction PCR reverse transcription RT -PCR enzyme immunoassay EIA2009 2015 6 315 144 144 6.1 1 28.9% 1 2 1,2 3 4 1999 22 23 1 2 5 2008 2009 1 2015 12 31 6 315 polymerase
 1) i) Barber, M. et al.: Brit. Med J, 2, 565, 19'49. ii) Barber, M.F.G. J. Hayhoe and J. E. M. Whithead: Lancet, 1120 `1125, 1949.-2) Bergey: Bergey's Manual of Determinative Bacteriology 7 th Ed: (1958).-3)
1) i) Barber, M. et al.: Brit. Med J, 2, 565, 19'49. ii) Barber, M.F.G. J. Hayhoe and J. E. M. Whithead: Lancet, 1120 `1125, 1949.-2) Bergey: Bergey's Manual of Determinative Bacteriology 7 th Ed: (1958).-3)
Key words: Antibodies to Leptospira, Tokyo, Uveitis
 Key words: Antibodies to Leptospira, Tokyo, Uveitis Fig. 1 Distribution of Antibody Titers in Age Decade Fig. 3 Distribution of Antibody Titers in each Strain Fig. 2 Correlation between Antibody Titers
Key words: Antibodies to Leptospira, Tokyo, Uveitis Fig. 1 Distribution of Antibody Titers in Age Decade Fig. 3 Distribution of Antibody Titers in each Strain Fig. 2 Correlation between Antibody Titers
_念3)医療2009_夏.indd
 Evaluation of the Social Benefits of the Regional Medical System Based on Land Price Information -A Hedonic Valuation of the Sense of Relief Provided by Health Care Facilities- Takuma Sugahara Ph.D. Abstract
Evaluation of the Social Benefits of the Regional Medical System Based on Land Price Information -A Hedonic Valuation of the Sense of Relief Provided by Health Care Facilities- Takuma Sugahara Ph.D. Abstract
Fig. 1 Chemical structure of DL-8280
 Fig. 1 Chemical structure of DL-8280 Fig. 2 Susceptibility of cl in ical isolates to DL4280 Fig. 5 Susceptibility of clinical isolates to DL-8280 Fig. 3 Susceptibility of clinical isolates to DL-8280 Fig.
Fig. 1 Chemical structure of DL-8280 Fig. 2 Susceptibility of cl in ical isolates to DL4280 Fig. 5 Susceptibility of clinical isolates to DL-8280 Fig. 3 Susceptibility of clinical isolates to DL-8280 Fig.
2 The Bulletin of Meiji University of Integrative Medicine 3, Yamashita 10 11
 1-122013 1 2 1 2 20 2,000 2009 12 1 2 1,362 68.1 2009 1 1 9.5 1 2.2 3.6 0.82.9 1.0 0.2 2 4 3 1 2 4 3 Key words acupuncture and moxibustion Treatment with acupuncture, moxibustion and Anma-Massage-Shiatsu
1-122013 1 2 1 2 20 2,000 2009 12 1 2 1,362 68.1 2009 1 1 9.5 1 2.2 3.6 0.82.9 1.0 0.2 2 4 3 1 2 4 3 Key words acupuncture and moxibustion Treatment with acupuncture, moxibustion and Anma-Massage-Shiatsu
400 46 THE JAPANESE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS 65 6 Dec. 2012 LVFX 100 mg 3 / 7 150 mg 2 / 7 2 2006 2008 9 LVFX PK PD 2009 7 100 mg 1 3 500 mg 1 1 AUC/MIC
 Dec. 2012 THE JAPANESE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS 65 6 399 45 2012 11 5 LVFX 500 mg 1 1 20 Chlamydia trachomatis C. trachomatismycoplasma genitalium M. genitalium LVFX 1 500 mg 1 1 7 22 22 C. trachomatis 17
Dec. 2012 THE JAPANESE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS 65 6 399 45 2012 11 5 LVFX 500 mg 1 1 20 Chlamydia trachomatis C. trachomatismycoplasma genitalium M. genitalium LVFX 1 500 mg 1 1 7 22 22 C. trachomatis 17
Fig. 1 Chemical structure of TE-031 Code number: TE-031 Chemical name: (-) (3R, 4S, 5S, 6R, 7R, 9R, 11R, 12R, 13S, 14R)-4-[(2, 6-dideoxy-3-C-methyl-3-
 Fig. 1 Chemical structure of TE-031 Code number: TE-031 Chemical name: (-) (3R, 4S, 5S, 6R, 7R, 9R, 11R, 12R, 13S, 14R)-4-[(2, 6-dideoxy-3-C-methyl-3-O-methyl-a-L-ribo-hexopyranosyl) oxy]-14-ethyl-12,
Fig. 1 Chemical structure of TE-031 Code number: TE-031 Chemical name: (-) (3R, 4S, 5S, 6R, 7R, 9R, 11R, 12R, 13S, 14R)-4-[(2, 6-dideoxy-3-C-methyl-3-O-methyl-a-L-ribo-hexopyranosyl) oxy]-14-ethyl-12,
Core Ethics Vol. -
 Core Ethics Vol. - Core Ethics Vol. - Core Ethics Vol. % NICU - Core Ethics Vol. - - - - Core Ethics Vol. - NICU NICU NICU NICU http://www.arsvi.com/d/i.htm -. http://www.normanet.ne.jp/~ww/,,.,,, -.
Core Ethics Vol. - Core Ethics Vol. - Core Ethics Vol. % NICU - Core Ethics Vol. - - - - Core Ethics Vol. - NICU NICU NICU NICU http://www.arsvi.com/d/i.htm -. http://www.normanet.ne.jp/~ww/,,.,,, -.
coccus aureus Corynebacterium sp, Haemophilus parainfluenzae Klebsiella pneumoniae Pseudornonas aeruginosa Pseudomonas sp., Xanthomonas maltophilia, F
 VOL.43 S-1 coccus aureus Corynebacterium sp, Haemophilus parainfluenzae Klebsiella pneumoniae Pseudornonas aeruginosa Pseudomonas sp., Xanthomonas maltophilia, Flavobacter- Table 1. Concentration of grepafloxacin
VOL.43 S-1 coccus aureus Corynebacterium sp, Haemophilus parainfluenzae Klebsiella pneumoniae Pseudornonas aeruginosa Pseudomonas sp., Xanthomonas maltophilia, Flavobacter- Table 1. Concentration of grepafloxacin
semen quality or those without WBC in semen. In the patients with azoospermia and normal FSH levels (normogonadotropic azzospermia), the antibody (IgG
 CLINICAL STUDIES OF UROGENITAL INFECTIONS WITH CHLAMYDIA TRACHOMA TIS Report 2. The Epidemiology of Chlamydial Infections in Okayama District in Japan and Detection of Antibodies to Chlamydiae in the Sera
CLINICAL STUDIES OF UROGENITAL INFECTIONS WITH CHLAMYDIA TRACHOMA TIS Report 2. The Epidemiology of Chlamydial Infections in Okayama District in Japan and Detection of Antibodies to Chlamydiae in the Sera
The Journal of the Japan Academy of Nursing Administration and Policies Vol 7, No 2, pp 19 _ 30, 2004 Survey on Counseling Services Performed by Nursi
 The Journal of the Japan Academy of Nursing Administration and Policies Vol 7, No 2, pp 19 _ 30, 2004 Survey on Counseling Services Performed by Nursing Professionals for Diabetic Outpatients Not Using
The Journal of the Japan Academy of Nursing Administration and Policies Vol 7, No 2, pp 19 _ 30, 2004 Survey on Counseling Services Performed by Nursing Professionals for Diabetic Outpatients Not Using
366 12 THE JAPANESE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS 65 6 Dec. 2012 1 8 DNA 2,3 16 12 20 171 2008 12 2010 11 2 3,558 4.44% 1.65% 1.17% 90% 9 Escherichia coli -
 Dec. 2012 THE JAPANESE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS 65 6 365 11 sita oxacin 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 3 3 1 1 1 2 3 2012 9 14 sita oxacin STFX 50 mg 10% 2008 1 2008 12 2010 11 2 STFX 1,452 91.4% 1,235/1,351 95.9% 466/486
Dec. 2012 THE JAPANESE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS 65 6 365 11 sita oxacin 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 3 3 1 1 1 2 3 2012 9 14 sita oxacin STFX 50 mg 10% 2008 1 2008 12 2010 11 2 STFX 1,452 91.4% 1,235/1,351 95.9% 466/486
 1) Garner J. S.: The Hospital Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee, CDC, Guidelines for Isolation Precautions in Hospitals, 1996. http://wonder.cdc.gov/wonder/prevguid/ p0000419/p0000419.asp.
1) Garner J. S.: The Hospital Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee, CDC, Guidelines for Isolation Precautions in Hospitals, 1996. http://wonder.cdc.gov/wonder/prevguid/ p0000419/p0000419.asp.
220 28;29) 30 35) 26;27) % 8.0% 9 36) 8) 14) 37) O O 13 2 E S % % 2 6 1fl 2fl 3fl 3 4
 Vol. 12 No. 2 2002 219 239 Λ1 Λ1 729 1 2 29 4 3 4 5 1) 2) 3) 4 6) 7 27) Λ1 701-0193 288 219 220 28;29) 30 35) 26;27) 0 6 7 12 13 18 59.9% 8.0% 9 36) 8) 14) 37) 1 1 1 13 6 7 O O 13 2 E S 1 1 17 0 6 1 585
Vol. 12 No. 2 2002 219 239 Λ1 Λ1 729 1 2 29 4 3 4 5 1) 2) 3) 4 6) 7 27) Λ1 701-0193 288 219 220 28;29) 30 35) 26;27) 0 6 7 12 13 18 59.9% 8.0% 9 36) 8) 14) 37) 1 1 1 13 6 7 O O 13 2 E S 1 1 17 0 6 1 585
 Key words : R-plasmid, Urinary tract infection, E. coli Fig. 1. MIC distribution against E. coli isolated from urinary tract (366 strains) and isolation - frequencies of drug-resistant strains Table 1.
Key words : R-plasmid, Urinary tract infection, E. coli Fig. 1. MIC distribution against E. coli isolated from urinary tract (366 strains) and isolation - frequencies of drug-resistant strains Table 1.
udc-2.dvi
 13 0.5 2 0.5 2 1 15 2001 16 2009 12 18 14 No.39, 2010 8 2009b 2009a Web Web Q&A 2006 2007a20082009 2007b200720082009 20072008 2009 2009 15 1 2 2 2.1 18 21 1 4 2 3 1(a) 1(b) 1(c) 1(d) 1) 18 16 17 21 10
13 0.5 2 0.5 2 1 15 2001 16 2009 12 18 14 No.39, 2010 8 2009b 2009a Web Web Q&A 2006 2007a20082009 2007b200720082009 20072008 2009 2009 15 1 2 2 2.1 18 21 1 4 2 3 1(a) 1(b) 1(c) 1(d) 1) 18 16 17 21 10
Studies of Foot Form for Footwear Design (Part 9) : Characteristics of the Foot Form of Young and Elder Women Based on their Sizes of Ball Joint Girth
 Studies of Foot Form for Footwear Design (Part 9) : Characteristics of the Foot Form of Young and Elder Women Based on their Sizes of Ball Joint Girth and Foot Breadth Akiko Yamamoto Fukuoka Women's University,
Studies of Foot Form for Footwear Design (Part 9) : Characteristics of the Foot Form of Young and Elder Women Based on their Sizes of Ball Joint Girth and Foot Breadth Akiko Yamamoto Fukuoka Women's University,
日本化学療法学会雑誌第59巻第5号
 Streptococcus pneumoniae Haemophilus influenzae Moraxella catarrhalis S. pneumoniae H. influenzae M. catarrhalis S. pneumoniae H. influenzae M. catarrhalis S. pneumoniae H. influenzae M. catarrhalis S.
Streptococcus pneumoniae Haemophilus influenzae Moraxella catarrhalis S. pneumoniae H. influenzae M. catarrhalis S. pneumoniae H. influenzae M. catarrhalis S. pneumoniae H. influenzae M. catarrhalis S.
 A comparison of abdominal versus vaginal hysterectomy for leiomyoma and adenomyosis Kenji ARAHORI, Hisasi KATAYAMA, Suminori NIOKA Department of Obstetrics and Gnecology, National Maizuru Hospital,Kyoto,
A comparison of abdominal versus vaginal hysterectomy for leiomyoma and adenomyosis Kenji ARAHORI, Hisasi KATAYAMA, Suminori NIOKA Department of Obstetrics and Gnecology, National Maizuru Hospital,Kyoto,
Yamagata Journal of Health Sciences, Vol. 16, 2013 Tamio KEITOKU 1 2 Katsuko TANNO 3 Kiyoko ARIMA 4 Noboru CHIBA 1 Abstract The present study aimed to
 Yamagata Journal of Health Sciences, Vol. 16, 2013 Tamio KEITOKU 12Katsuko TANNO 3Kiyoko ARIMA 4Noboru CHIBA 1 Abstract The present study aimed to clarify differences in awareness regarding future residence
Yamagata Journal of Health Sciences, Vol. 16, 2013 Tamio KEITOKU 12Katsuko TANNO 3Kiyoko ARIMA 4Noboru CHIBA 1 Abstract The present study aimed to clarify differences in awareness regarding future residence
<30372D985F95B62D8E52967B8C4F8E7190E690B62E706466>
 312013 95 Changes and Restructuring of Social Issues of the Urban Underclass Area with Increasing Welfare Needs in Kotobuki, Yokohama Kahoruko YAMAMOTO This paper explains social changes and restructuring
312013 95 Changes and Restructuring of Social Issues of the Urban Underclass Area with Increasing Welfare Needs in Kotobuki, Yokohama Kahoruko YAMAMOTO This paper explains social changes and restructuring
indd
 24 61 1 2011 調査 研究 1 2 1 1 2 4 1 3 4 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 2 1 1 2 3 4 2010 11 11 2011 1 7 Infection Control in an Endoscopy Room Multi - society Guideline and Current Status at Fukushima Medical University
24 61 1 2011 調査 研究 1 2 1 1 2 4 1 3 4 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 2 1 1 2 3 4 2010 11 11 2011 1 7 Infection Control in an Endoscopy Room Multi - society Guideline and Current Status at Fukushima Medical University
<95DB8C9288E397C389C88A E696E6462>
 2011 Vol.60 No.2 p.138 147 Performance of the Japanese long-term care benefit: An International comparison based on OECD health data Mie MORIKAWA[1] Takako TSUTSUI[2] [1]National Institute of Public Health,
2011 Vol.60 No.2 p.138 147 Performance of the Japanese long-term care benefit: An International comparison based on OECD health data Mie MORIKAWA[1] Takako TSUTSUI[2] [1]National Institute of Public Health,
 1) Kojima H: Culture of ejaculate for Neisseria gonorrhoeae, 1st Serually Transmitted Diseases World Congress, San Juan, 11. 19, 1981. 9) Kojima H, Mori C: Clinical studies on Conococcal and Chlamydial
1) Kojima H: Culture of ejaculate for Neisseria gonorrhoeae, 1st Serually Transmitted Diseases World Congress, San Juan, 11. 19, 1981. 9) Kojima H, Mori C: Clinical studies on Conococcal and Chlamydial
CHEMOTHERAPY Table 1 Clinical effect of Sultamicillin
 CHEMOTHERAPY CHEMOTHERAPY Table 1 Clinical effect of Sultamicillin CHEMOTHERAPY Fig. 1 MICs of sultamicillin against respiratory pathogenic Branhamella catarrhalis 62 strains, inoculum size 106CFU/m1 Fig.
CHEMOTHERAPY CHEMOTHERAPY Table 1 Clinical effect of Sultamicillin CHEMOTHERAPY Fig. 1 MICs of sultamicillin against respiratory pathogenic Branhamella catarrhalis 62 strains, inoculum size 106CFU/m1 Fig.
VOL. 23 NO. 3 CHEMOTHERAPY 1067 Table 2 Sensitivity of gram positive cocci isolated from various diagnostic materials Table 3 Sensitivity of gram nega
 1066 CHEMOTHERAPY MAR. 1975 Table 1 Sensitivity of standard strains VOL. 23 NO. 3 CHEMOTHERAPY 1067 Table 2 Sensitivity of gram positive cocci isolated from various diagnostic materials Table 3 Sensitivity
1066 CHEMOTHERAPY MAR. 1975 Table 1 Sensitivity of standard strains VOL. 23 NO. 3 CHEMOTHERAPY 1067 Table 2 Sensitivity of gram positive cocci isolated from various diagnostic materials Table 3 Sensitivity
A Nutritional Study of Anemia in Pregnancy Hematologic Characteristics in Pregnancy (Part 1) Keizo Shiraki, Fumiko Hisaoka Department of Nutrition, Sc
 A Nutritional Study of Anemia in Pregnancy Hematologic Characteristics in Pregnancy (Part 1) Keizo Shiraki, Fumiko Hisaoka Department of Nutrition, School of Medicine, Tokushima University, Tokushima Fetal
A Nutritional Study of Anemia in Pregnancy Hematologic Characteristics in Pregnancy (Part 1) Keizo Shiraki, Fumiko Hisaoka Department of Nutrition, School of Medicine, Tokushima University, Tokushima Fetal
1272 CHEMOTHERAPY MAR. 1975
 1272 CHEMOTHERAPY MAR. 1975 VOL. 23 NO. 3 CHEMOTHERAPY 1273 Fig. 2 Minimal inhibitory concentration of aminoglycosides against 50 strains of Klebsiella Fig. 1 Minimal inhibitory concentration of aminoglycosides
1272 CHEMOTHERAPY MAR. 1975 VOL. 23 NO. 3 CHEMOTHERAPY 1273 Fig. 2 Minimal inhibitory concentration of aminoglycosides against 50 strains of Klebsiella Fig. 1 Minimal inhibitory concentration of aminoglycosides
Key words : 7432-S, Oral cephem, Urinary tract infection Fig. 1. Chemical structure of 7432-S.
 Key words : 7432-S, Oral cephem, Urinary tract infection Fig. 1. Chemical structure of 7432-S. Table 1. Clinical summary of acute uncomplicated cystitis patients treated with 7432-S UTI : Criteria by the
Key words : 7432-S, Oral cephem, Urinary tract infection Fig. 1. Chemical structure of 7432-S. Table 1. Clinical summary of acute uncomplicated cystitis patients treated with 7432-S UTI : Criteria by the
 ON A FEW INFLUENCES OF THE DENTAL CARIES IN THE ELEMENTARY SCHOOL PUPIL BY Teruko KASAKURA, Naonobu IWAI, Sachio TAKADA Department of Hygiene, Nippon Dental College (Director: Prof. T. Niwa) The relationship
ON A FEW INFLUENCES OF THE DENTAL CARIES IN THE ELEMENTARY SCHOOL PUPIL BY Teruko KASAKURA, Naonobu IWAI, Sachio TAKADA Department of Hygiene, Nippon Dental College (Director: Prof. T. Niwa) The relationship
 2014Vol.63No.4p.383393 Thermal environment for health and safety Hirohumi HAYAMA Masaya SAITO Haruka MIKAMI Faculty of Engineering, Hokkaido University School of Design, Sapporo City University Graduate
2014Vol.63No.4p.383393 Thermal environment for health and safety Hirohumi HAYAMA Masaya SAITO Haruka MIKAMI Faculty of Engineering, Hokkaido University School of Design, Sapporo City University Graduate
/fiÁ1-1/‹Éfi¡ıæ„[’æ’¶
 59 1 pp.53-58 2009 1. H5N1 3 H5N1 2007 1 2 2008 4 5 2003 H5N1 2005 50 1 429 262 2009 5 22 2 680-8553 4 101 TEL/FAX : 0857-31-5437 E-mail: toshiito@muses.tottori-u.ac.jp 3 H5N1 1 A A A 54 59 1 4 A A 5 1997
59 1 pp.53-58 2009 1. H5N1 3 H5N1 2007 1 2 2008 4 5 2003 H5N1 2005 50 1 429 262 2009 5 22 2 680-8553 4 101 TEL/FAX : 0857-31-5437 E-mail: toshiito@muses.tottori-u.ac.jp 3 H5N1 1 A A A 54 59 1 4 A A 5 1997
 1) University Group Diabetes Program: A study of hypoglycemic agents on vascular complica- in patients with adult-onset tions diabetes. I. Design, methods and baseline results. Diabetes 19 (suppl. 2):
1) University Group Diabetes Program: A study of hypoglycemic agents on vascular complica- in patients with adult-onset tions diabetes. I. Design, methods and baseline results. Diabetes 19 (suppl. 2):
11_渡辺_紀要_2007
 56 1 19 Bull. Nara Univ. Educ., Vol. 56, No.1 (Cult. & Soc.), 2007 115 19 Why is Kidney Dysfunction Caused by Cadmium (Cadmium Nephropathy) not Officially Recognized as a Pollution-related Disease by the
56 1 19 Bull. Nara Univ. Educ., Vol. 56, No.1 (Cult. & Soc.), 2007 115 19 Why is Kidney Dysfunction Caused by Cadmium (Cadmium Nephropathy) not Officially Recognized as a Pollution-related Disease by the
 Table 1.Distribution and number of cases with acute upper respiratory tract infections classified according to antimicrobial agents administered Table 2. Distribution of cases which were enrolled to set
Table 1.Distribution and number of cases with acute upper respiratory tract infections classified according to antimicrobial agents administered Table 2. Distribution of cases which were enrolled to set
HPV HPV HPV HPV 7 HPV 8 9 HPV 3 HPV HPV HPV , Becker Ajzen H
 3 26 3 Journal of Junshin Gakuen University, HPV Faculty of Health Sciences Vol.3, March 2014 99 HPV Knowledge of and attitudes towards human papillomavirus vaccinations among mothers who have daughters
3 26 3 Journal of Junshin Gakuen University, HPV Faculty of Health Sciences Vol.3, March 2014 99 HPV Knowledge of and attitudes towards human papillomavirus vaccinations among mothers who have daughters
<8ED089EF8B D312D30914F95742E696E6464>
 * 1 The problem of privacy in the news of newspapers and weekly magazines The analysis of the articles on the child serial killing incidents in Kobe Akihiko SHIMAZAKI Kenzo SHIDA Toshihiko KATANO *2 1
* 1 The problem of privacy in the news of newspapers and weekly magazines The analysis of the articles on the child serial killing incidents in Kobe Akihiko SHIMAZAKI Kenzo SHIDA Toshihiko KATANO *2 1
Oda
 No.53 pp.2334, 2017 Komazawa Journal of Geography Distribution of Christianity and the Division of the Region in Prewar Japan ODA Masayasu Oda1999 1. 18991939 1 2. 18991939 1918 3. 190019391939 4. 5. 6.
No.53 pp.2334, 2017 Komazawa Journal of Geography Distribution of Christianity and the Division of the Region in Prewar Japan ODA Masayasu Oda1999 1. 18991939 1 2. 18991939 1918 3. 190019391939 4. 5. 6.
Key words : influenza, nested-pcr, serotype
 Key words : influenza, nested-pcr, serotype Table 1 Sequence of PCR primers used to detect HA gene of influenza virus 524 清水 Fig. 1 Detection of PCR product 英明 他 (lstpcr) Table 2 Results method Fig. 2
Key words : influenza, nested-pcr, serotype Table 1 Sequence of PCR primers used to detect HA gene of influenza virus 524 清水 Fig. 1 Detection of PCR product 英明 他 (lstpcr) Table 2 Results method Fig. 2
ñ{ï 01-65
 191252005.2 19 *1 *2 *3 19562000 45 10 10 Abstract A review of annual change in leading rice varieties for the 45 years between 1956 and 2000 in Japan yielded 10 leading varieties of non-glutinous lowland
191252005.2 19 *1 *2 *3 19562000 45 10 10 Abstract A review of annual change in leading rice varieties for the 45 years between 1956 and 2000 in Japan yielded 10 leading varieties of non-glutinous lowland
/‚“1/ŒxŒ{‚×›î’æ’¶
 60 1 pp.3-8 2010 1. H1N1 1) 2) 3) 4) ERATO 2009 H1N1 21 H1N1 HA PB2 2009 3 Pandemic H1N1 2009 WHO 6 11 21 2009 11 2010 4 21 H1N1 H1N1 2009 4 15 CDC 108-8639 4-6-1 TEL: 03-5449-5281 FAX: 03-5449-5408 E-mail:
60 1 pp.3-8 2010 1. H1N1 1) 2) 3) 4) ERATO 2009 H1N1 21 H1N1 HA PB2 2009 3 Pandemic H1N1 2009 WHO 6 11 21 2009 11 2010 4 21 H1N1 H1N1 2009 4 15 CDC 108-8639 4-6-1 TEL: 03-5449-5281 FAX: 03-5449-5408 E-mail:
Abstract Objectives: This article presents a review of cancer control measures implemented in Phase One of the National Cancer Control Plan (
 2012Vol.61No.6p.524542 The Japanese National Cancer Control Plan: A Review of Phase One and lessons learned for Phase Two Ken-ichi HANIOKA Cancer Policy Information Center, Health and Global Policy Institute
2012Vol.61No.6p.524542 The Japanese National Cancer Control Plan: A Review of Phase One and lessons learned for Phase Two Ken-ichi HANIOKA Cancer Policy Information Center, Health and Global Policy Institute
 Table 1 Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates 1. Escherichia coli Inoculum size: 106cells/ml 2. Klebsiella pneumoniae 3. Enterobacter cloacae 4. Serratia marcescens Inoculum size: 106cells/nil
Table 1 Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates 1. Escherichia coli Inoculum size: 106cells/ml 2. Klebsiella pneumoniae 3. Enterobacter cloacae 4. Serratia marcescens Inoculum size: 106cells/nil
 29 33 58 2005 1970 1997 2002, pp.3-8 2001 2002 2005b 2000 pp.137-146 2005c 7 34 Ma and Cartier eds. 2003 1970 1980 1979 2002 2000 1) 1980 1990 1991 1993 1995 1998 1994 1993 20031972 2003 2005 1997 2005a
29 33 58 2005 1970 1997 2002, pp.3-8 2001 2002 2005b 2000 pp.137-146 2005c 7 34 Ma and Cartier eds. 2003 1970 1980 1979 2002 2000 1) 1980 1990 1991 1993 1995 1998 1994 1993 20031972 2003 2005 1997 2005a
16_.....E...._.I.v2006
 55 1 18 Bull. Nara Univ. Educ., Vol. 55, No.1 (Cult. & Soc.), 2006 165 2002 * 18 Collaboration Between a School Athletic Club and a Community Sports Club A Case Study of SOLESTRELLA NARA 2002 Rie TAKAMURA
55 1 18 Bull. Nara Univ. Educ., Vol. 55, No.1 (Cult. & Soc.), 2006 165 2002 * 18 Collaboration Between a School Athletic Club and a Community Sports Club A Case Study of SOLESTRELLA NARA 2002 Rie TAKAMURA
日本化学療法学会雑誌第65巻第4号
 Mycoplasma pneumoniae M. pneumoniae M. pneumoniae M. pneumoniae M. pneumoniae M. pneumoniae Key words Mycoplasma pneumoniae Mycoplasma pneumoniae M. pneumoniae I M. pneumoniae M. pneumoniae M. pneumoniae
Mycoplasma pneumoniae M. pneumoniae M. pneumoniae M. pneumoniae M. pneumoniae M. pneumoniae Key words Mycoplasma pneumoniae Mycoplasma pneumoniae M. pneumoniae I M. pneumoniae M. pneumoniae M. pneumoniae
 Influences of mortality from main causes of death on life expectancy. \ An observation for the past 25 years, 1950-1975, in Japan \ Takao SHIGEMATSU* and Zenji NANJO** With the Keyfitz-Nanjo method an
Influences of mortality from main causes of death on life expectancy. \ An observation for the past 25 years, 1950-1975, in Japan \ Takao SHIGEMATSU* and Zenji NANJO** With the Keyfitz-Nanjo method an
Key words: E. coli O 157: H7, fosfomycin, verotoxin, mouse infection
 Key words: E. coli O 157: H7, fosfomycin, verotoxin, mouse infection Table 1. Bacterial cell counts in feces of mice infected with Esclwrichia coli O 157: H7 NK2 before and during oral dosing with fosfomycin
Key words: E. coli O 157: H7, fosfomycin, verotoxin, mouse infection Table 1. Bacterial cell counts in feces of mice infected with Esclwrichia coli O 157: H7 NK2 before and during oral dosing with fosfomycin
52-2.indb
 Jpn. J. Health Phys., 52 (2) 55 60 (2017) DOI: 10.5453/jhps.52.55 * 1 * 2 * 2 * 3 * 3 2016 10 28 2017 3 8 Enhancement of Knowledge on Radiation Risk Yukihiko KASAI,* 1 Hiromi KUDO,* 2 Masahiro HOSODA,*
Jpn. J. Health Phys., 52 (2) 55 60 (2017) DOI: 10.5453/jhps.52.55 * 1 * 2 * 2 * 3 * 3 2016 10 28 2017 3 8 Enhancement of Knowledge on Radiation Risk Yukihiko KASAI,* 1 Hiromi KUDO,* 2 Masahiro HOSODA,*
 6 1Bulletin of Tokyo University and Graduate School of Social Welfarepp73-86 2015, 10 372-0831 2020-1 2015 5 29 2015 7 9 : : : 1 A B C D E 4 A B A B A B A ] AB C D E 4 8 73 17 2 22 750 1 2 26 2 16 17 32
6 1Bulletin of Tokyo University and Graduate School of Social Welfarepp73-86 2015, 10 372-0831 2020-1 2015 5 29 2015 7 9 : : : 1 A B C D E 4 A B A B A B A ] AB C D E 4 8 73 17 2 22 750 1 2 26 2 16 17 32
Fig. 1 Clinical findings and extent of inflammation area in female urethrocystitis Fig. 2 Classification and distribution of female patients with blad
 Key words: Female with bladder irritability, Subjective symptoms, Pyuria, Bacteriuria Fig. 1 Clinical findings and extent of inflammation area in female urethrocystitis Fig. 2 Classification and distribution
Key words: Female with bladder irritability, Subjective symptoms, Pyuria, Bacteriuria Fig. 1 Clinical findings and extent of inflammation area in female urethrocystitis Fig. 2 Classification and distribution
Table 1 Profiles of 28 patients with Legionella pneumonia in Japan, 1980-1990 a) Y Taguchi, personal communication b) M. Hayase, personal communicatio
 Key words: Legionella pneumonia, culture-positive, Japanese patients Legionella (L. pneumophila (L. micdadei, L. bozemanii, Table 1 Profiles of 28 patients with Legionella pneumonia in Japan, 1980-1990
Key words: Legionella pneumonia, culture-positive, Japanese patients Legionella (L. pneumophila (L. micdadei, L. bozemanii, Table 1 Profiles of 28 patients with Legionella pneumonia in Japan, 1980-1990
untitled
 Quantitative Risk Assessment on the Public Health Impact of Pathogenic Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Raw Oyster 1 15 5 23 48 2 21 1 16 1 16 1 11 3 1 3 4 23 1 2 16 12 16 5 6 Hazard IdentificationExposure
Quantitative Risk Assessment on the Public Health Impact of Pathogenic Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Raw Oyster 1 15 5 23 48 2 21 1 16 1 16 1 11 3 1 3 4 23 1 2 16 12 16 5 6 Hazard IdentificationExposure
Feb THE JAPANESE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS Tebipenem pivoxil 1 1, Meiji Seika 2 Meiji Seika G 3 Meiji Seika Tebipen
 Feb. 2016 THE JAPANESE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS 69 1 53 53 Tebipenem pivoxil 1 1, 3 2 2 1 1 Meiji Seika 2 Meiji Seika G 3 Meiji Seika 2015 12 15 Tebipenem pivoxil 10% 2010 4 2013 3 3,547 3,540 3,540 3,331
Feb. 2016 THE JAPANESE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS 69 1 53 53 Tebipenem pivoxil 1 1, 3 2 2 1 1 Meiji Seika 2 Meiji Seika G 3 Meiji Seika 2015 12 15 Tebipenem pivoxil 10% 2010 4 2013 3 3,547 3,540 3,540 3,331
_??_ Fig. 1. Annual number of subjects who were bitten by possibly rabid animals in the rabies endemic regions and thereafter visited our vaccine clin
 _??_ Fig. 1. Annual number of subjects who were bitten by possibly rabid animals in the rabies endemic regions and thereafter visited our vaccine clinic to receive the rabies post-exposure prophylaxis.
_??_ Fig. 1. Annual number of subjects who were bitten by possibly rabid animals in the rabies endemic regions and thereafter visited our vaccine clinic to receive the rabies post-exposure prophylaxis.
Highlights Employment increased in Ontario, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba. There was little change in the other provinces. More people were employed in c
 商工会事務局より (From Shokokai) カナダ統計局より 6 月雇用統計発表 : 失業率 6.0%(+0.2) Labour Force Survey: June Unemployment 6.0%(+0.2) 会員各位 7 月 6 日 カナダ統計局 (Statistics Canada) より 2018 年 6 月の雇用統計が発表になりました 下記概要ポイント仮訳は あくまで商工会事務局で訳したものであり英語の微妙な表現を保証したものではありません
商工会事務局より (From Shokokai) カナダ統計局より 6 月雇用統計発表 : 失業率 6.0%(+0.2) Labour Force Survey: June Unemployment 6.0%(+0.2) 会員各位 7 月 6 日 カナダ統計局 (Statistics Canada) より 2018 年 6 月の雇用統計が発表になりました 下記概要ポイント仮訳は あくまで商工会事務局で訳したものであり英語の微妙な表現を保証したものではありません
在日外国人高齢者福祉給付金制度の創設とその課題
 Establishment and Challenges of the Welfare Benefits System for Elderly Foreign Residents In the Case of Higashihiroshima City Naoe KAWAMOTO Graduate School of Integrated Arts and Sciences, Hiroshima University
Establishment and Challenges of the Welfare Benefits System for Elderly Foreign Residents In the Case of Higashihiroshima City Naoe KAWAMOTO Graduate School of Integrated Arts and Sciences, Hiroshima University
Table 1. Antibacterial spectrum SBT ABPC ABPC CPZ : sulbactamiampicillin : ampicillin : cefoperazone
 Table 1. Antibacterial spectrum SBT ABPC ABPC CPZ : sulbactamiampicillin : ampicillin : cefoperazone (inoculum size= 106 CFU/ml) (Ĉ-lactamase producer : 2 strains) Fig. 1. Sensitivity distribution of
Table 1. Antibacterial spectrum SBT ABPC ABPC CPZ : sulbactamiampicillin : ampicillin : cefoperazone (inoculum size= 106 CFU/ml) (Ĉ-lactamase producer : 2 strains) Fig. 1. Sensitivity distribution of
 Title 社 会 化 教 育 における 公 民 的 資 質 : 法 教 育 における 憲 法 的 価 値 原 理 ( fulltext ) Author(s) 中 平, 一 義 Citation 学 校 教 育 学 研 究 論 集 (21): 113-126 Issue Date 2010-03 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2309/107543 Publisher 東 京
Title 社 会 化 教 育 における 公 民 的 資 質 : 法 教 育 における 憲 法 的 価 値 原 理 ( fulltext ) Author(s) 中 平, 一 義 Citation 学 校 教 育 学 研 究 論 集 (21): 113-126 Issue Date 2010-03 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2309/107543 Publisher 東 京
 840 Geographical Review of Japan 73A-12 835-854 2000 The Mechanism of Household Reproduction in the Fishing Community on Oro Island Masakazu YAMAUCHI (Graduate Student, Tokyo University) This
840 Geographical Review of Japan 73A-12 835-854 2000 The Mechanism of Household Reproduction in the Fishing Community on Oro Island Masakazu YAMAUCHI (Graduate Student, Tokyo University) This
10-渡部芳栄.indd
 COE GCOE GP ) b a b ) () ) () () ) ) .. () ) ) ) ) () ........... / / /.... 交付税額 / 経常費 : 右軸交付税額 /( 経常費 授業料 ): 右軸 . ) ()... /.. 自治体負担額 / 交付税額 : 右軸 ()......... / 自治体負担額 / 経常費 : 右軸 - No. - Vol. No. - IDE
COE GCOE GP ) b a b ) () ) () () ) ) .. () ) ) ) ) () ........... / / /.... 交付税額 / 経常費 : 右軸交付税額 /( 経常費 授業料 ): 右軸 . ) ()... /.. 自治体負担額 / 交付税額 : 右軸 ()......... / 自治体負担額 / 経常費 : 右軸 - No. - Vol. No. - IDE
VOL.35 S-2 CHEMOTHERAPY Table 1 Sex and age distribution Table 2 Applications of treatment with carumonam Table 3 Concentration of carumonam in human
 CHEMOTHERAPY Fig. 1 Chemical structure of carumonam Disodium(+)-(Z)-CCE1-(2-amino-4-thiazoly1)-2-[[(2S, -(carbamoyloxymethyl)-4-oxo-1-sulfonato-3-azetidinyll -2-oxoethylidene] amino] oxy] acetate 3S)-2
CHEMOTHERAPY Fig. 1 Chemical structure of carumonam Disodium(+)-(Z)-CCE1-(2-amino-4-thiazoly1)-2-[[(2S, -(carbamoyloxymethyl)-4-oxo-1-sulfonato-3-azetidinyll -2-oxoethylidene] amino] oxy] acetate 3S)-2
I 1) 2) 51 (1976) 6.9 ha 9 (1934) 2km 15, (1955) 6 (1620)
 I 1) 2) 51 (1976) 6.9 ha 9 (1934) 2km 15,000 30 (1955) 6 (1620) 3 1 1 45 16 2003 50 (1975) 2 150 49 (1974) II (1) 3) 1 49 50 51 53 54 56 57 59 61 63 3 8 9 10 11 12 NHK 46 2 44 (1969) 2 40 50 240 60 (1985)
I 1) 2) 51 (1976) 6.9 ha 9 (1934) 2km 15,000 30 (1955) 6 (1620) 3 1 1 45 16 2003 50 (1975) 2 150 49 (1974) II (1) 3) 1 49 50 51 53 54 56 57 59 61 63 3 8 9 10 11 12 NHK 46 2 44 (1969) 2 40 50 240 60 (1985)
 Title < 論文 > 公立学校における在日韓国 朝鮮人教育の位置に関する社会学的考察 : 大阪と京都における 民族学級 の事例から Author(s) 金, 兌恩 Citation 京都社会学年報 : KJS = Kyoto journal of so 14: 21-41 Issue Date 2006-12-25 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/192679 Right
Title < 論文 > 公立学校における在日韓国 朝鮮人教育の位置に関する社会学的考察 : 大阪と京都における 民族学級 の事例から Author(s) 金, 兌恩 Citation 京都社会学年報 : KJS = Kyoto journal of so 14: 21-41 Issue Date 2006-12-25 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/192679 Right
Core Ethics Vol. : - NICU : : - A B C D
 Core Ethics Vol.,NMR...... Core Ethics Vol. : - NICU : : - A B C D b: Duff and Campbell A B C: D : a B C b Core Ethics Vol. : -, : C D :.. D.. bd D CD AB CD : Duff C b C B : Core Ethics Vol. C D B A D
Core Ethics Vol.,NMR...... Core Ethics Vol. : - NICU : : - A B C D b: Duff and Campbell A B C: D : a B C b Core Ethics Vol. : -, : C D :.. D.. bd D CD AB CD : Duff C b C B : Core Ethics Vol. C D B A D
 b) Gram-negative bacteria Fig. 2 Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates : E. coli Fig. 3 Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates : Pseudomonas Fig. 1 Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates
b) Gram-negative bacteria Fig. 2 Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates : E. coli Fig. 3 Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates : Pseudomonas Fig. 1 Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates
lagged behind social progress. During the wartime Chonaikai did cooperate with military activities. But it was not Chonaikai alone that cooperated. Al
 The Development of Chonaikai in Tokyo before The Last War Hachiro Nakamura The urban neighborhood association in Japan called Chonaikai has been more often than not criticized by many social scientists.
The Development of Chonaikai in Tokyo before The Last War Hachiro Nakamura The urban neighborhood association in Japan called Chonaikai has been more often than not criticized by many social scientists.
 Title 生活年令による学級の等質化に関する研究 (1) - 生活年令と学業成績について - Author(s) 与那嶺, 松助 ; 東江, 康治 Citation 研究集録 (5): 33-47 Issue Date 1961-12 URL http://hdl.handle.net/20.500.12000/ Rights 46 STUDIES ON HOMOGENEOUS
Title 生活年令による学級の等質化に関する研究 (1) - 生活年令と学業成績について - Author(s) 与那嶺, 松助 ; 東江, 康治 Citation 研究集録 (5): 33-47 Issue Date 1961-12 URL http://hdl.handle.net/20.500.12000/ Rights 46 STUDIES ON HOMOGENEOUS
7 2000b 2000b 2000b A Vol 8, No 2,
 The Journal of the Japan Academy of Nursing Administration and Policies Vol 8, No 2, pp 37 _ 47, 2005 The Real and the Factors of Hiyari-hatto Experiences of Nursing Students during Clinical Training Analyzed
The Journal of the Japan Academy of Nursing Administration and Policies Vol 8, No 2, pp 37 _ 47, 2005 The Real and the Factors of Hiyari-hatto Experiences of Nursing Students during Clinical Training Analyzed
Table 1 Distribution,by type and classroom,of group B hemolytic streptococcal strains isolated from throat of pupils in A elementary school in Nishime
 Key words: Group B hemolytic streptococci, Types, Elementary & Junior high school pupils, 7 prefectures Table 1 Distribution,by type and classroom,of group B hemolytic streptococcal strains isolated from
Key words: Group B hemolytic streptococci, Types, Elementary & Junior high school pupils, 7 prefectures Table 1 Distribution,by type and classroom,of group B hemolytic streptococcal strains isolated from
988 CHEMOTHERAPY NOV. 1971
 988 CHEMOTHERAPY NOV. 1971 VOL. 19 NO. 8 CHEMOTHERAPY 989 Effect of medium-ph and inoculum size on activity of SB-PC heart infusion agar, mcg/ml Sensitivity distribution of Staphylococci to SB-PC in surgical
988 CHEMOTHERAPY NOV. 1971 VOL. 19 NO. 8 CHEMOTHERAPY 989 Effect of medium-ph and inoculum size on activity of SB-PC heart infusion agar, mcg/ml Sensitivity distribution of Staphylococci to SB-PC in surgical
Validation of a Food Frequency Questionnaire Based on Food Groups for Estimating Individual Nutrient Intake Keiko Takahashi *', Yukio Yoshimura *', Ta
 Validation of a Food Frequency Questionnaire Based on Food Groups for Estimating Individual Nutrient Intake Keiko Takahashi *', Yukio Yoshimura *', Tae Kaimoto *', Daisuke Kunii *', Tatsushi Komatsu *2
Validation of a Food Frequency Questionnaire Based on Food Groups for Estimating Individual Nutrient Intake Keiko Takahashi *', Yukio Yoshimura *', Tae Kaimoto *', Daisuke Kunii *', Tatsushi Komatsu *2
 Fig. 1 The district names and their locations A dotted line is the boundary of school-districts. The district in which 10 respondents and over live is indicated in italics. Fig. 2 A distribution of rank
Fig. 1 The district names and their locations A dotted line is the boundary of school-districts. The district in which 10 respondents and over live is indicated in italics. Fig. 2 A distribution of rank
NIES ASEAN4.. NIES.....EU.. ASEAN4 NIES
 NIES ASEAN4.. NIES.....EU.. ASEAN4 NIES NIES ASEAN4 EU NIES ASEAN4 EU On-line UN Comtrade Database NIES NIES.AEAN4..EU.NIESASEAN4 NIES NIES ASEAN4. EU NIES ASEAN4. TPS: Toyota Production System.... Dunning
NIES ASEAN4.. NIES.....EU.. ASEAN4 NIES NIES ASEAN4 EU NIES ASEAN4 EU On-line UN Comtrade Database NIES NIES.AEAN4..EU.NIESASEAN4 NIES NIES ASEAN4. EU NIES ASEAN4. TPS: Toyota Production System.... Dunning
 CHEMOTHERAPY APRIL 1992 Table 2. Concentration of meropenem in human prostatic fluid Table 1. Background of 21 chronic complicated UTI cases * NB + BPH, NB + Kidney tumor, NB + Kidney tuberculosis Table
CHEMOTHERAPY APRIL 1992 Table 2. Concentration of meropenem in human prostatic fluid Table 1. Background of 21 chronic complicated UTI cases * NB + BPH, NB + Kidney tumor, NB + Kidney tuberculosis Table
過去26年間のスギ花粉飛散パターンのクラスター分析
 117 681 : 2A 2B 2C 2A 2B 2C 2A 2A 2B 2C 2A 2B 2C 2A : DNA Phöbus Blackly 1cm 117 682 2014 1 SYSTAT χ Complete linkage method χ 2A 2B 2C /cm /cm /cm 2A 2B 2C 2A 2B 2C 2A 2B 2C 2 A /cm 2A 2C 117 683 2 2A
117 681 : 2A 2B 2C 2A 2B 2C 2A 2A 2B 2C 2A 2B 2C 2A : DNA Phöbus Blackly 1cm 117 682 2014 1 SYSTAT χ Complete linkage method χ 2A 2B 2C /cm /cm /cm 2A 2B 2C 2A 2B 2C 2A 2B 2C 2 A /cm 2A 2C 117 683 2 2A
00.\...ec5
 Yamagata Journal of Health Science, Vol. 6, 23 Kyoko SUGAWARA, Junko GOTO, Mutuko WATARAI Asako HIRATUKA, Reiko ICHIKAWA Recently in Japan, there has been a gradual decrease in the practice of community
Yamagata Journal of Health Science, Vol. 6, 23 Kyoko SUGAWARA, Junko GOTO, Mutuko WATARAI Asako HIRATUKA, Reiko ICHIKAWA Recently in Japan, there has been a gradual decrease in the practice of community
Table 1 Hospitalized patients with M. pneumoniae infection during November 1975-October 1978
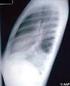 Key words: Mycoplasmal pneumonia, Eruption, Pleurisy, Thrombocytopenia, Stevens-Johnson' s syndrome Table 1 Hospitalized patients with M. pneumoniae infection during November 1975-October 1978 Table 2
Key words: Mycoplasmal pneumonia, Eruption, Pleurisy, Thrombocytopenia, Stevens-Johnson' s syndrome Table 1 Hospitalized patients with M. pneumoniae infection during November 1975-October 1978 Table 2
Fig.1 Chemical structure of BAY o 9867
 Fig.1 Chemical structure of BAY o 9867 CHEMOTHERAPY 43 Table 3 Antibacterial spectrum of gram negative bacteria Medium:Heart infusion agar (Nissui) Method:Agar dilution (Streak) CHEMOTHERAPY DEC 1985
Fig.1 Chemical structure of BAY o 9867 CHEMOTHERAPY 43 Table 3 Antibacterial spectrum of gram negative bacteria Medium:Heart infusion agar (Nissui) Method:Agar dilution (Streak) CHEMOTHERAPY DEC 1985
_原著03_濱田_責.indd
 The Journal of the Japan Academy of Nursing Administration and Policies Vol 9, No 2, pp 3140, 2006 原著 看護師の内服与薬業務における 確認エラー に関する検討 Study of Confirmation Errors for Internal Use by Nurses 濱田康代 1) 田口大介 2)
The Journal of the Japan Academy of Nursing Administration and Policies Vol 9, No 2, pp 3140, 2006 原著 看護師の内服与薬業務における 確認エラー に関する検討 Study of Confirmation Errors for Internal Use by Nurses 濱田康代 1) 田口大介 2)
Table 1 Characteristics of the study participants in Imari municipal hospital
 Key words: tuberculosis, booster phenomenon, two-step tuberculin test Table 1 Characteristics of the study participants in Imari municipal hospital Fig. 1 Frequency distributions of size of the first tuberculin
Key words: tuberculosis, booster phenomenon, two-step tuberculin test Table 1 Characteristics of the study participants in Imari municipal hospital Fig. 1 Frequency distributions of size of the first tuberculin
日本化学療法学会雑誌第59巻第6号
 P P Streptococcus pneumoniae S. pneumoniae Key words Streptococcus pneumoniae Fig. 1. Capsular swelling reaction of S. pneumoniae type 6B. Cells are stained dark blue using a methylene blue. Capsule is
P P Streptococcus pneumoniae S. pneumoniae Key words Streptococcus pneumoniae Fig. 1. Capsular swelling reaction of S. pneumoniae type 6B. Cells are stained dark blue using a methylene blue. Capsule is
CHEMOTHERAPY Fig. 1 Chemical structure of CXM-AX
 Fig. 1 Chemical structure of CXM-AX NOV. 1986 Fig. 2 Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates organisms (106 cells/ml) a Smurcus 27 strains d) P.m irabilis 15 strains b Ecol i 27 strains 111.morganii
Fig. 1 Chemical structure of CXM-AX NOV. 1986 Fig. 2 Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates organisms (106 cells/ml) a Smurcus 27 strains d) P.m irabilis 15 strains b Ecol i 27 strains 111.morganii
 ABSTRACT The Social Function of Boys' Secondary Schools in Modern Japan: From the Perspectives of Repeating and Withdrawal TERASAKI, Satomi (Graduate School, Ochanomizu University) 1-4-29-13-212, Miyamaedaira,
ABSTRACT The Social Function of Boys' Secondary Schools in Modern Japan: From the Perspectives of Repeating and Withdrawal TERASAKI, Satomi (Graduate School, Ochanomizu University) 1-4-29-13-212, Miyamaedaira,
Juntendo Medical Journal
 * Department of Health Science Health Sociology Section, Juntendo University School of Health and Sports Science, Chiba, Japan (WHO: Ottawa Charter for Health promotion, 1986.) (WHO: Bangkok Charter
* Department of Health Science Health Sociology Section, Juntendo University School of Health and Sports Science, Chiba, Japan (WHO: Ottawa Charter for Health promotion, 1986.) (WHO: Bangkok Charter
E. coli E. coli é H. influenzae Helicobacter pylori
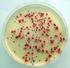 é C.pneumoniae C.trachomatis C.trachomatis 1 é Chlamydia pneumoniae Chlamydia psittaci Chlamydia trachomatis 3 E. coli E. coli é H. influenzae Helicobacter pylori K. pneumoniae L. monocytogenes ü l Staphylococcus
é C.pneumoniae C.trachomatis C.trachomatis 1 é Chlamydia pneumoniae Chlamydia psittaci Chlamydia trachomatis 3 E. coli E. coli é H. influenzae Helicobacter pylori K. pneumoniae L. monocytogenes ü l Staphylococcus
