untitled
|
|
|
- としみ よせ
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Infectious Agents Surveillance Report (IASR) SFTS 3, SFTS 4, SFTSV 5, SFTSV : 7, 03 SFTS 40 8, SFTS 9, SFTS 0, AHpdm09, 03/4 AHpdm09, 3, Zika fever 5, 6, CA 8, 03 CA6 9, HHV6 0, CRS, Vol. 35 No Vol.35 No. No.408 ISSN Tel ,,, :,,, severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome: SFTS, SFTS virus SFTSV, ,,,,,,,,, AST, ALT, LDH,, SFTS 0, 03 SFTSV : SFTSV, SFTSV, SFTSV, Haemaphysalis longicornis Rhipicephalus microplus SFTSV, SFTSV, SFTS Amblyomma testudinarium SFTSV SFTSV,,, SFTS : 0,,,, SFTSV,, SFTSV, SFTS IASR 34: 404, 03, SFTS rapid/graph/pt398.gif , SFTS SFTS 8 SFTS IASR 34: 0809 & 0, 03, 0 3 SFTS SFTS, 4, 6 3
2 , 5,, 8 SFTSV,,,,, 5 03 SFTS : SFTS 4 : kekkakukansenshou/00443.html, SFTSV IASR 34: 0, 03, 4 7 SFTS 4, 03 48,, , , 00, 0 5 : IASR 34: 0, ,,, 3 4, 6, 4895, SFTS, SFTS, SFTS 9, IASR 34: 0708, 03, SFTSV, Vol. 35 No , SFTS, SFTS 8 :, SFTSV, RTPCR SFTSV, SFTSV IgG,,, RTPCR SFTSV, SFTSV SFTSV IgGELISA 0, SFTSV SFTSV IASR 34: , 03 : 03 SFTS,, SFTS, SFTS 5 3, SFTS SFTS, SFTS, SFTS,, SFTS, 3, 4SFTSV, 5 SFTSV SFTSV,
3 病原微生物検出情報 Vol. 35 No 表. SFTS患者の症状 特集関連情報 参考文献 6) 臨床症状 中国での重症熱性血小板減少症候群の発生状況 参考文献 7) 97% 00% 㣗ḧ 75% ປ 65% 94% fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome: SFTS の 䛝Ẽ 69% 76% 発生は 006 年秋の安 省の事例 患者数 4 名 が最も ③ 49% 56% 早いものと考えられる この事例はヒト顆粒球性アナ 47% 64% ᛰឤ 46% 8% ⑩ に類似していたことから, 当初同感染症との診断がな 4% 66% 䝸䞁䝟 33% されていたが, SFTS が新興感染症として認識され ③ 7% 中国における重症熱性血小板減少症候群 severe プラズマ症の症状 発熱, 白血球減少, 血小板減少等 9% 54% 69% た後に再調査の結果, SFTS であると明らかになった ものである イルスは咽頭スワブ 尿 便からも検出されるが, こ これまで中部を中心とする 省 安 省, 湖北省, れは出血した血液由来のウイルス量を反映したものと 河南省, 山東省, 遼寧省, 陝西省, 四川省, 雲南省, 広 考えられる9 回復者は抗体陽性となり, 長期にわた 西省, 江西省, 浙江省, 江蘇省 で SFTS の発生が報 り持続する6 告されている 図 Dingらの 0 0 年の 年 SFTS の原因ウイルス SFTSV の伝播経路のひと 間のまとめの報告によると, 患者数は計,047 名 男性 つは SFTSV 保有マダニの刺伵である Haemaphysalis 955 名, 女 性,09 名, 年 齢 は 90 歳 中 央 値 は 58 longicornis フ タ ト ゲ チ マ ダ ニ や Rhipicephalus 歳, 死亡は9名 男性 7名, 女性58名, 致死率 6.3, microplus オウシマダニ から SFTSV 遺伝子が検出 死亡患者の年齢中央値は 64 歳で回復者と比べ優位に もしくは SFTSV が分離されている6, 7 血液や気道分 高い, 患者の 80 以上が山岳地帯の農業もしくは林業 泌物を介したヒトからヒトへの感染例も複数報告され 従事者, 発生時期は 3 月で 5 8 月の発生が 75 ている, 03 しかしマダニの刺伵, ヒトヒト感染の 以上を占める, 非農業従事者の致死率 0. は農業 いずれも確認されない事例もある 従事者のそれ 5.8 より高い, 移入者の致死率.0 SFTS 患者が発生した地域における家畜の抗体保有 は地元民のそれ 6.3 より高い, 患者数の多い 率は高く, 特にヤギやヒツジでは が抗体陽性 省は河南省 48, 湖北省, 山東省 6 の順 である5, 46 ウシ 34 6 やニワトリ 47 にお である3 Liuらによる患者年齢の分布を図 に示す4 ける抗体陽性率も比較的高い5, 6 これらの家畜やイ 潜伏期は 6 3 日で, 発熱 血小板減少 白血球減 ヌ げっ歯類から SFTSV が分離あるいは遺伝子が検 少 血中肝酵素上昇等は 7 日間程度みられ, 血中 出されるが, 症状を示す動物は今のところ知られてい ウイルス量は copies/ml に達する5 SFTS 患 ない5, 7, 8 家畜に刺伵するマダニから SFTSV が検 回復者で 出されており6, 9, これらの動物への SFTSV の伝播 はこれらの数値は改善し, 発症後 週間程度で正常値 経路もマダニの刺伵であると考えられる 発生地域の 者に多く認められる症状を表 に示す 6, 7 に戻るが, 死亡例では経過中数値は悪化を続け, 発症 後 9 日 中央値 で多臓器不全や播種性血管内凝固症 候群により死亡する5 血中ウイルス量 肝酵素値 サイトカイン量 IL6, IL0, IFNγ ケモカイン量 IL8, MCP, MIPβ は重篤度と相関する8, 9 ウ 健常人でもわずかながら抗体陽性者が認められている 参考文献 Zhang, et al., JAMA : 6370, 008 Liu, et al., Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis : 㻝㻞㻡 㻝㻜㻜 患者数 遼寧省 㻣㻡 㻡㻜 山東省 雲南省 広西省 㻤㻡 㸺 㻤㻜 㹼 㻣㻡 㹼 㻣㻜 㹼 㻢㻡 㹼 㻢㻜 㹼 㻡㻡 㹼 㻡㻜 㹼 㻠㻡 㹼 㻠㻜 㹼 㻟㻡 㹼 㻟㻜 㹼 㻞㻡 㹼 㻞㻜 㹼 㻝㻡 㹼 㻜 㻡㹼 浙江省 江西省 㻞㻡 㻝㻜 㹼 江蘇省 省 㻜㹼 陝西省 河南省 安 湖北省 四川省 年齢 図. 0年の中国におけるSFTS患者649名の年齢分布 図. 0年の中国におけるSFTS患者の分布 Liu, et al., Rev Med Virol, 03 Dec 6. doi: 0.00/rmv.776. [Epub ahead of print]䜘䜚ᨵኚ
4 434 Vol. 35 No , 0 3Ding, et al., Clin Infect Dis 56 : 68683, 03 4Liu, et al., Rev Med Virol, 03 Dec 6, doi: 0. 00/rmv.776 [Epub ahead of print] 5Dexin, Emerg Microbes Infect : e, 03 6Yu, et al., N Engl J Med 364 6: 5353, 0 7Xu, et al., PLoS Pathogens, 7 : e00369, 0 8Zhang, et al., Clin Infect Dis 54 4: 57533, 0 9Sun, et al., J Infect Dis 06 7: , 0 0Gai, et al., Clin Infect Dis 54 : 495, 0 Bao, et al., Clin Infect Dis 53 : 084, 0 Chen, et al., Int J Infect Dis 7 3: e06e08, 03 3Tang, et al., J Infect Dis 07 5: , 03 4Zhao, et al., Emerg Infect Dis 8 6:963965, 0 5Cui, et al., Am J Trop Med Hyg 88 3: 50 5, 03 6Jiao, et al., J Clin Microbiol 50 : 37377, 0 7Bao, et al., N Engl J Med 365 9: 86865, 0 8Niu, et al., Emerg Infect Dis 9 5: , 03 9Zhang, et al., J Virol 86 5: , 0 :, severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome: SFTS, ,, SFTS 0 3,,,,,,,,,,, SFTS SFTSV,,,,. SFTS,,,,, SFTS,,,,, SFTS, ,, SFTS ,,, nih.go.jp/niid/images/iasr/rapid/graph/pt398. gif,,,, 0 4 SFTS 0, SFTS,,,,,, Q & A,,,,,,. SFTS, 3,, SFTS,
5 Vol. 35 No SFTSV, SFTS, SFTS,,,,,,, SFTSV,, 3 4 SFTS, SFTSV,,, SFTS,, SFTS, 3. SFTS SFTS,, SFTS, SFTS, CDC SFTSV, SFTS,, PCR, 3 SFTS, SFTS,,, SFTSV,,,, 5,, SFTS,,,,, SFTSV,,,,,,,,, SFTSV,,,,, SFTS, SFTS,, SFTS,,,,,,,,,,, SFTS SFTS severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome: SFTS 0 8, SFTS SFTSVSFTSV S, M, L RTPCR, SFTSV 4, 8 SFTSV, S, M, L, SFTSV, 8 SFTSV,, 3 6, SPL004A 7,
6 636 Vol. 35 No. 04. (A) Segment S A (B) Segment M A (C) Segment L A B B B Japan Japan Japan. SFTSV. SFTSV Chinese Lineage S Japanese Lineage A B 3 N NS JS4 HN6 HB9 JS3 YG 003A 004A 005A 00A 030A 03A 035A JS HN HB JS YG SPL003A SPL004A SPL005A SPL00A SPL030A SPL03A SPL035A M Chinese Lineage A B 3 Japanese Lineage GPC JS4 HN6 HB9 JS3 YG 003A 004A 005A 00A 030A 03A 035A JS HN HB JS YG SPL003A SPL004A SPL005A SPL00A SPL030A SPL03A SPL035A L Chinese Lineage Japanese Lineage A B 3 RdRp JS4 HN6 HB9 JS3 YG 003A 004A 005A 00A 030A 03A 035A JS HN HB JS YG SPL003A SPL004A SPL005A SPL00A SPL030A SPL03A SPL035A
7 Vol. 35 No SFTSV S, M, L, L RNA RNA RdRp, M GPC, S N, NS, S, M, L, SPL004A 98, M 94 7, 99, 97 SFTSV, SFTS,, :. severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus: SFTSV,,, CFR the Code of Federal Regulations:, SFTSV,,,, BSL3 SFTS,,, BSL3, SFTSV, 03 3, SFTSV 7 SFTSV 56 6, SFTSV,,,,,, SFTSV SFTS,, SFTSV BSL,, SFTS 4, SFTS,,., SFTSV, 6,, 5, 9070,,,, SFTSV 6, SFTSV, SFTSV SFTSV,,,, SFTSV,, SFTS,,,,,,, SFTSV, 7,, 0 9 /ml
8 838 Vol. 35 No. 04.,, SFTS, SFTSV,,, 8 SFTS,, Bao CJ, et al., Clin Infect Dis 53: 084, 0 Liu Y, et al., Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis : 56 60, 0 3Gai Z, et al., Clin Infect Dis 54: 495, 0 4Tang X, et al., J Infect Dis 07: , 03 5Chen H, et al., Int J Infect Dis 7: e06e08, 03 6,, IASR 34: 333, 03 7Zhang YZ, et al., Clin Infect Dis 54: 57533, 0 8,, IASR 34: 6970, severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome: SFTS 03, 3 4 8, 4 48, , 5, SFTSn=40 03SFTSn= , 73, , , 83, p0.0, Wilcoxon rank sam test , n=8, 8 5,,, , 3 53, 53, 7 8 SFTS,,, SFTS, SFTS SFTS, ,,,, , 5,,, SFTS 30,,,,
9 Vol. 35 No Takahashi T, et al., J Infect Dis, 03 Dec, doi: 0.093/infdis/jit603 [Epub ahead of print] Zhang YZ, et al., Clin Infect Dis 54 4: 57533, 0 3 SFTS 030, Yu XJ, et al., New Engl J Med 364 6: 53 53, 0 5Ding F, et al., Clin Infect Dis 56 : 68683, 03 severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome: SFTS, 0 SFTS SFTSV 03, 005 SFTS, 3.5,,, : 60 :, : : 990 :, 03, 3 :,, : , 4 39,, cefepime 3 4 6, WBC,000/l, Plt 5./l, AST 607 IU/l, ALT 09 IU/l,,,,, : 65cm, 63kg,, 0/70mmHg, 76/min, 39., SpO 94, :, :,,, :, :, :, : WBC,700/l, Plt 4.4/l, AST 64 IU/l, ALT IU/l,GTP 5 IU/l, LDH 77 IU/ l, CK 530 IU/l, BUN mg/dl, Cr 0.97 mg/dl, CRP 0. mg/dl, BUN 6.6 mg/dl, 0.9 ng/ml,,90 ng/ml, silr,8 U/ml, PT INR.07, APTT 40. sec, FDP.9g/ml, Ddimer 6.3g/ml, 4, 3, : slight hypocellular bone marrow,, X, CT, CT : : SFTSV RTPCR :, IgG, IgM : 4/6 5/5 Orientia tsutsugamushi, Rickettsia japonica IgG, IgM : 4/6, 5/5 : 5,,,, SFTSV,, minocycline, ciprof loxacin,, DIC,,,, minocycline ciprof loxacin,, DAY DAY7 DAY4 MINO 00mg/ CPFX 600mg/ WB (μl),700 3,500 3,900 3,800 4,900 Platelet (/μl) AST (IU/l) LDH (IU/l) CK (IU/l) CRP (mg/dl)
10 040 Vol. 35 No. 04.,, SFTSV SFTS 3,, SFTS,,, Yu XJ, et al., N Engl J Med 364 6: 53 53, 0 Takahashi T, et al., J Infect Dis, 03 Dec, doi: 0.093/infdis/jit603 [Epub ahead of print] 3Gai ZT, et al., J Infect Dis 06 7: 0950, 0,,, SFTSV SFTSV PCR,,, SFTS SFTSV RTPCR,, SFTSV, RTPCR,,,,,,,, SFTSV PCR PCR, 0 severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome: SFTS, SFTS SFTSV SFTSV SFTS 03 SFTS,,, SFTS SFTS EcoRI, EcoRI 03 3, SFTSV SFTSV,,, SFTSV primer set primer set primer set primer set NTC P.C NTC P.C Uncut Cut Uncut Cut PCR
11 Vol. 35 No IgGIgM, IgG IgM SFTSV : 3,, SFTSV IgG IgM, SFTS, SFTSV IgG ELISA Vero,, SFTSV SFTSV SFTSV, BSL3,, SFTSV, SFTSV, PCR,, SFTSV ELISA SFTS, Yu XJ, et al., N Engl J Med 364: 5353, 0 AHpdm09, 03, AHpdm09 : 39, HIV, 0, 03 37, 6, 38.0 A, 9 CT, A ARDS, ICU MRSA,, 3, : 9 Lamp, Lamp AHpdm09, 0 HI, A/California/07/ 009HNpdm09 HI : 0, : 30, A/Texas/50/0H3N, B/ Massachusetts//0, B/Brisbane/60/ 008Victoria : 0, AHpdm09,, 9 3, 300mg/, 50mg/ 8, 30, : 03 4 AH3, 5AHpdm09,, AHpdm09, 00900
12 4 Vol. 35 No. 04., 3, 4, 5,,,, A,,,,,,,, 48 sapporo.jp/eiken/infect/trend/graph/l50.html Chowell G, et al., N Eng J Med 36: , 009 3CDC, MMWR 58: 07074, 009 4IASR 33: 8594, 0 5Inf luenza update, WHO, luenza/surveillance_ monitoring/updates/03 09_surveillance_ update_00.pdf 03/4 AHNpdm09 03/4, AH3N, AHNpdm09, B 7 AH3N 3, AHNpdm09 5, B AHNpdm09, AHNpdm09 NA H75Y,, 03/4 AHNpdm09 5,, 5 H75Y,,,, H75Y 5,,,, AHNpdm09, RNA,, 5 H75Y 03/4 6, 4 0,,, 6 HA NA, 6,, 3,, 9 AH3N, AHNpdm09, 03/ AHNpdm09, 0.3% 4,, AHNpdm09 57,
13 Vol. 35 No , 4, 007/08 AHN, 008/09, 00, H75Y,,, AHN NA, H75Y, RQV34M, HA T8K, K4E R89K 3,, 5, 6, AHNpdm09, NA V4I, N369K N386S 3 H75Y 7, 3 V4I N369K, 6, V4I N369K, N386K 386 K S H75Y, NA H75Y,, 80,,,, AHNpdm09, 4,, 500,,,,, Takashita E, et al., Euro Surveill 9: pii: 0666, 04,, IASR 35: 44, 04 lum/f luiasrs/ 46pr4073.html 3Takashita E, et al., Inf luenza Other Respir Viruses 7: , 03 4US CDC, FluView 0304 Inf luenza Season Week 5 ending December, 03 5Bloom JD, et al., Science 38: 775, 00 6Ginting TE, et al., J Virol 86: 7, 0 7Hurt AC, et al., J Infect Dis 06: 4857, 0 8Kawai N, et al., J Infect 59: 07, 009 9Kawai N, et al., Clin Infect Dis 49: 88835, 009 0Saito R, et al., Pediatr Infect Dis J 9: , 00 Baum EZ, et al., Antiviral Res 59: 3, 003 Baz M, et al., Antiviral Res 74: 596, 007 AHNpdm09 03/4, AHNpdm09, AHNpdm09 5, 03, 03, AHNpdm09, ,, AHNpdm NA TaqMan RTPCR
14 444 Vol. 35 No AHNpdm0903/4 75 H Y H75Y H75Y : H75Y S43G MDCK A97T AHNpdm09 RNA NA 7 S85T A/Mie/7/03, MDCK H75Y A/Mie/7/03 TaqMan RT D97N PCR, A/Mie/7/03 NA, V4I, N369K, N386K NA : A/Mie/7/03NA S03T,,,, P83S I3V IC nM, 6.5nM, 0.8nM, 0.93nM,, HA : 7 6 AHNpdm09 HA, HA D97N, S85T 6 A/Mie/7/03, 03/ A/Mie//03, A/Mie/3/03 4 HA, 3 : 5, 69, 83 H75Y :,, 03 0 H75Y /9/4 03/9/ A/Mie// /9/4 03/9/ A/Mie/3/ /9/5 03/9/ A/Mie/4/ //5 03// H75Y A/Mie/7/ //3 04// A/Mie// //5 04//6 40 A/Mie// //9 04// A/Mie/3/04 03/4 0/3 S84G H38Q A/Turkey/605/03 JAN A/Saipan/697/03 FEB A/MIE//03 JAN A/New Mexico/07/03 MAR A/Slovenia/505/03 FEB A/FUKUOKAC/8/03 MAY K63I A/YOKOHAMA//03 JAN A/MIE//03 JAN A/NAGANOC/3/03 JAN A/SAPPORO/63/0 MAR A/Hong Kong/0/03 JAN A/NAGANO/3/03 MAY A86T A/Bangladesh/0/0 JUL A/Cambodia/3/03 JAN A/OSAKA/34/03 APR A/Wisconsin//03 JUN A/Florida/0/03 JUL A/MIE//03 MAY K83E A/KANAGAWA/4/03 MAY A/Haiti/030/03 JUN A/MIE//04 JAN A/MIE/4/03SEP T5S E83D A/SAPPORO/07/03 NOV A/MIE/7/03 DEC 4,, 5,,,,, A AHNpdm09, 7 H75Y A/Stockholm/3/0 OCT A/Florida/9/03 JUL A/England/358/03 FEB A/Hawaii/0/03 MAY A/MIE//04 JAN K63Q V34I A/MIE//03 SEP 039 A56T D69E A/MIE/3/03 SEP A/Delaware/03/0 /03/0 FEB 5 A/Georgia/07/0 MAR A/Christchurch/6/00 JUL A/Brisbane/0/00 APR 4 A/NARA/59/0 MAR A/Kenya/04/03 FEB A/SAITAMA/88/0 NOV 8 A/Cameroon/LEID/07//870/0 JUL A/Nigeria/538/0 AUG A/Mexico/08/0 MAR A/FUKUI/67/0 MAR A/GuangdongXiangzhou/63/0 JUL A/New Mexico/07/0 MER A/ISHIKAWA/70/0 MAR A/Pakistan/680/0 JUL A/Narita/0/009 MAY A/Mexico/InDRE4487/009 APR A/California/07/009 APR 3. AHNpdm09HA 6
15 Vol. 35 No ,,, 03, AHNpdm09 5, 009,, 6,,,,, AHNpdm09, :, NA,,,, lum/068f lu/ f ludr/,, IASR 35: 443, 04 lum/f luiasrs/ 43pr408.html 3, 03/4 lu/ bunri/bunrihyou34.htm 4,, IASR 34: ,, IASR 35: 44, 04 lum/f luiasrs/ 46pr4073.html 6, 38 : 060, 00 Zika fever, Zika Zika fever Zika fever : , 38 0, 3, 37.,,, 3,30/l, 4.9/l NS, IgM IgG 3 realtime RTPCR Zika virus ZIKVRNA,, : , 337, 9, 3,,,, ,,,,, 3,470/ l, 4.7/l NS, IgM IgG 3, realtime RTPCR ZIKV RNA, Zika fever ZIKV, Aedes africanus, Ae. apicoargenteus, Ae. luteocephalus, Ae. aegypti, Ae. vittatus, Ae. furcifer, Ae. hensilii ZIKV,,, ZIKV 007, Centers for Disease Control and
16 646 Vol. 35 No. 04. Prevention CDC 03 ZIKV, Zika fever,,,,,, 4 7 PCR ZIKV RNA, IgM,,,,,,,,,,, Zika fever Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Zika Fever in French Polynesia Tahiti Hayes EB, Emerg Infect Dis 5 9: , ,, 999 4, PCV , 00 5 PCV7 007, 0 0, 7, 5, 008 Haemophilus inf luenzae b Hib, 00 5 Hib, 03 4 Hib, 0 0, 9, PCV7 Hib A, invasive pneumococcal disease: IPD invasive Haemophilus inf luenzae disease : IHD 5,, 03 : NESID ,,,,,,. : PCR,. :, PCR,, 3. :,.,,., 3., 3 : IPD 67, IHD 89 IHD IPD 3.3 IPD, IHD IPD IHD, IPD, IHD 5 60,, IHD, IPD, IHD 6 IPD, IHD 5.8, 8.0, IPD, 64,,, IPD,, 4,
17 Vol. 35 No IHD, 64, IHD, 60, 6 : IPD IHD IPD 6, 64,,, PCV7, 70, 50, IPD, PCV7 NSW IPD 3 IPD 4, NSW IPD 7 8, IPD, PCV7 6B, 4, 3F, 9F, PCV7, 9A, 6B, 4, 3F, PCV7 9A, 5A, 5B, 5C, F, 6C, PCV7 IPD 77., 44.4, PCV7 PCV7 IPD, 03 5 PCV7 3, 9A IPD Hib, IHD 9, 8, IHD, 5, IHD, IHD,, 4 IHD, Hib 97, nontypable H. inf luenzae; NTHi 3, Hib 83, NTHi 7 NTHi Hib NTHi IHD 5, 6, a Hia IHD 7 PCV Hib IPD IHD,,,,, 5, 0 IPD IHD 8,
18 848 Vol. 35 No. 04. :,, IASR 34: 5556, 03 IASR 34: 8586, 03 3McIntyre P, et al., NSW Public Health Bulletin 4: 8589, 003 4Livorsi DJ, et al., J Infect 65: , 0 5Dworkin MS, et al., Clin Infect Dis 44: 8086, 007 6Kastrin T, et al., Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 9: 66668, 00 7Ulanova M, Tsang RSW, Lancet Infect Dis 4: 708, A,, , A CA, , 7, 38.3, 39,,,,,,,, PCR, NCBI Blast, CA VP CODEHOP PCR VP, 35bp, CA JN , C VP, CA, A549, CPE, C, CA 0, CA CA4 0 4 CA, CA CA, CA, 3, 00, 85 AB863033/F360P/Tokyo/03 * AB863034/F37P/Tokyo/03 * JN69053./Humancoxsackievirus A GQ3976./Human coxsackievirus A4 AY9958./Human coxsackievirus A JX53567./Human coxsackievirus A3 AY994./Human coxsackievirus A AF08307./Human coxsackievirus A8 AY99568./Human coxsackievirus A7 KC76377./Human enterovirus A7 FJ5595./Human coxsackievirus A6 *
19 Vol. 35 No ,,,, CA,,, J Clin Microbiol 44: , 006 Emerg Infect Dis 8: 884, 0 3Virus Genes 45: 077, 0 03 A6 03, 5, , 0 6., RDA 37 3 CPE,,, VP VP4, RNA, CODEHOP PCR VP,,, , CPE, A6CVA6, 6, 0 6 CPE, 4 CVA6 7 CVA6 6, CVA, 6 CODEHOP PCR,, CVA6 4, 3, CVA CVA6 CODEHOP PCR 376bp, 330bp,, CVA6 VP, 0JapanB 4, 0 CVA6, 3 03Kumamoto, CVA6 0 CVA6, CVA6,, 5 0JapanA CVA6, 0 8, 0 03, 3 03Kumamoto, CVA6, 03 7 RDA CPE,, 0 CVA6,,
20 050 Vol. 35 No CVA6VP85bp Allan W, et al., J Clin Microbiol 44: , 006 IASR 33: 606, 0 3IASR 34: 33, 03 HHV ,, , 3 : 63, 6 HHV6: 68, : 40, RS RSV: 7, : 7, HPeV: HHV6/RSV / 5, 4, HHV6, 68 EV68, HPeV A6 CA6, ,,,, 39.3,, RSV, HHV6,, EV,, 3 0 /l HHV6, RSV,, EV, EV68, RDA, Vero E6, FL, LLCMK, Caco HEp, RDA CPE, EV, EV CPE HPeV 3, HPeV realtime RTPCR 4, HPeV 03, EV7 CA6 CA6,, CA6 HHV6, HHV7 5 HPeV,,
21 Vol. 35 No Day Day , EV HPeV 03 9, 4, 3 4,, EV68, HPeV, 8 Echo8 HPeV,, HHV6, HHV6 DNA,, EV68, HPeV CA6 NESID HHV6,,,,, HHV6,,,,,,, Saito Y, et al., Brain & Development 34: , 0,, 7: 8393, 999 3Pham NTK, et al., J Clin Microbiol 48: 59, 00 4Nix WA, et al., J Clin Microbiol 46: 5954, 008 5
22 5 Vol. 35 No. 04., , WHO RCV RCV, , RCV, RCV 3, 4 94 RCV, 8 6 RCV, 89 0, EUR30,536 WPR44,75 9,9,000,,,, RCV AMR, 009 CRS, CRS EUR, 0 30,536, 000 6,039 95, 0 EURWPR,,,,, 0 RCV 83 vs 43,, CRS CDC, MMWR 6 48: , 03, , WPV, 0 98, 0 58, , 0 WPV 0, 9 84 FATA KP, WPV , 45 4 OPV, 6 5 3, WPV 5, cvdpv, OPV VDPV 0 5 cvdpv cvdpv 0 4,, 03 FATA 30, cvdpv 5, , 6 50 OPV, 4 OPV 7 33 WPV 3, 0, 0 FATA 3, 0 4 AFP 89, FATA 73, KP 85, 5 0 AFP NPAFP 6.3, FATA 7.9, KP 9. AFP, 80, NPAFP OPV3 89, 0 NPAFP, 6 3 NPAFP 65, 8, FATA 38, KP , 5, SIAs 7, SIAs 9, 0 7, 5 7 FATA SIAs SIAs , FATA, KP, 0,,,,, WHO, WER, 88 47: 50508, 03 :,,
23 Vol. 35 No Verotoxinproducing E.coli ( ) 0 6 ( ) ( ) 9 ( ) Enterotoxigenic enic E.coli ( ) 5 Enteroinvasive E.coli Enteropathogenic E.coli ( ) Enteroaggregative E.coli ( ) Other diarrheagenic E.coli Salmonella Typhi 3 ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) Salmonella Paratyphi A ( ) ( ) ( ) 3 ( ) ( ) Salmonella O ( ) 8 Salmonella O ( ) ( ) Salmonella O Salmonella O ( ) Salmonella O3,0 3 Salmonella O,3,99 Salmonella O Salmonella O3 Salmonella O8 Salmonella O30 Salmonella O35 Salmonella O39 Salmonella group unknown 4 Vibrio cholerae O:El Tor Ogawa,CT+ ( ) Vibrio cholerae nono&o39 Vibrio parahaemolyticus 7 Vibrio furnissii Aeromonas hydrophila Plesiomonas shigelloides Campylobacter jejuni Campylobacter coli 7 5 Campylobacter jejuni/coli Staphylococcus aureus Clostridium perfringens Bacillus cereus 7 Listeria monocytogenes Yersinia enterocolitica 4 Shigella dysenteriae 4 ( ) Shigella flexneri a Shigella flexneri b ( ) ( ) Shigella flexneri a 3 Shigella flexneri b ( ) Shigella flexneri 3a Shigella flexneri 4 Shigella flexneri 6 Shigella flexneri other serovars ( ) Shigella flexneri untypable ( ) Shigella boydii 4 Shigella boydii 8 Shigella sonnei ( ) 3 ( 8) ( ) 3 ( ) ( ) ( ) 4 ( ) ( ) Entamoeba histolytica Streptococcus tococcus group A Streptococcus group B Streptococcus group C Streptococcus tococcus group G 3 Streptococcus tococcus other groups S.dysgalactiae subsp.equisimilis Streptococcus pneumoniae Bordetella pertussis Legionella pneumophila Mycobacterium tuberculosis Mycobacterium bovis Mycoplasma pneumoniae Haemophilus influenzae b Haemophilus influenzae nonb Klebsiella pneumoniae 0 Neisseria meningitidis Enterococcus faecalis Enterococcus faecium Enterococcus gallinarum Enterococcus casseliflavus Pseudomonas aeruginosa Leptospira interogans Leptospira sp. Cryptococcus neoformans 595 ( ) 807 ( ) 6 ( ) 50 ( 4) 344 ( 4) 339 ( 5) 8 ( 5) 7 ( 6) 06 ( ) 96 ( 4)
24 454 Vol. 35 No ( ) ( ) 09 ( ) ( 0) Verotoxinproducing E.coli ( ) 8 ( ) ( 4) Enterotoxigenic enic E.coli Enteroinvasive E.coli ( ) Enteropathogenic E.coli ( ) Enteroaggregative E.coli 4 98 Other diarrheagenic E.coli ( ) 4 ( ) 4 ( ) ( ) ( ) 5 ( 4) Salmonella Typhi ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) 4 ( 3) Salmonella Paratyphi A ( ) 5 5 ( ) Salmonella O ( 3) Salmonella O Salmonella O ( ) Salmonella O9 9 Salmonella O3,0 4 Salmonella O,3,99 Salmonella O 5 Salmonella O3 Salmonella O8 Salmonella O30 Salmonella O35 Salmonella O39 Salmonella group unknown ( ) ( ) ( ) 4 ( 4) Vibrio cholerae O:El Tor Ogawa awa,ct+ 4 Vibrio cholerae nono&o Vibrio parahaemolyticus Vibrio furnissii 3 Aeromonas hydrophila Plesiomonas shigelloides Campylobacter jejuni Campylobacter coli 3 Campylobacter jejuni/coli Staphylococcus aureus Clostridium perfringens 3 Bacillus cereus Listeria monocytogenes Yersinia enterocolitica ( ) Shigella dysenteriae 4 Shigella flexneri a ( ) Shigella flexneri b 4 Shigella flexneri a 4 ( ) Shigella flexneri b ( ) ( ) Shigella flexneri 3a Shigella flexneri 4 ( ) ( ) Shigella flexneri 6 4 ( ) Shigella flexneri other serovars ( ) Shigella flexneri untypable Shigella boydii 4 Shigella boydii 8 ( ) 5 ( 4) 6 ( ) 6 ( 3) ( ) 54 ( 9) Shigella sonnei Entamoeba histolytica Streptococcus tococcus group A 4 Streptococcus group B Streptococcus group C 3 Streptococcus tococcus group G 5 Streptococcus tococcus other groups 6 S.dysgalactiae subsp.equisimilis Streptococcus pneumoniae Bordetella pertussis Legionella pneumophila Mycobacterium tuberculosis Mycobacterium bovis Mycoplasma pneumoniae Haemophilus influenzae b Haemophilus influenzae nonb Klebsiella pneumoniae 5 Neisseria meningitidis 5 Enterococcus faecalis 0 5 Enterococcus faecium Enterococcus gallinarum Enterococcus casseliflavus 0 Pseudomonas aeruginosa 3 Leptospira interogans Leptospira sp. Cryptococcus neoformans 86 ( 3) 38 ( 7) 65 ( 3) 64 ( 9) 49 ( 3) 335 ( 5) 43 ( 5) 83 ( ) 787 ( 9)
25 Vol. 35 No Verotoxinproducing E.coli 7 47 Enteropathogenic E.coli Enteroaggregative E.coli Other diarrheagenic E.coli Salmonella Paratyphi A Salmonella O4 Salmonella O7 9 Salmonella O8 Salmonella O9 Salmonella O3,0 Campylobacter jejuni Campylobacter coli Campylobacter jejuni/coli Staphylococcus aureus 3 Clostridium perfringens Shigella sonnei Streptococcus tococcus group A Streptococcus tococcus group B Streptococcus tococcus group G Streptococcus pneumoniae 7 Legionella pneumophila Mycobacterium tuberculosis Mycoplasma pneumoniae 7 Enterococcus faecium Salmonella O4 Saintpaul O4 Schwarzengrund O4 Brandenburg O4 I 4:i: O7 Infantis 3 O7 Thompson O7 Oranienburg O7 Braenderup 5 O7 Rissen O7 Not typed O8 Corvallis O8 Not typed O9 Enteritidis O9 Not typed O3,0 Weltevreden T T4 T6 T 3 T5 T8 TB364 Untypable
26 656 Vol. 35 No Verotoxinproducing E.coli 3 Enteropathogenic E.coli 4 Enteroaggregative E.coli Other diarrheagenic E.coli ( ) ( ) Salmonella Paratyphi A 5 Salmonella O4 3 Salmonella O7 3 Salmonella O8 Salmonella O9 Salmonella O3,0 64 Campylobacter jejuni Campylobacter coli Campylobacter jejuni/coli 3 Staphylococcus aureus 43 Clostridium perfringens Shigella sonnei Streptococcus tococcus group A Streptococcus tococcus group B Streptococcus tococcus group G 0 Streptococcus pneumoniae Legionella pneumophila Mycobacterium tuberculosis 8 Mycoplasma pneumoniae Enterococcus faecium 3 ( ) 4 83 ( ) Salmonella O4 Saintpaul O4 Schwarzengrund O4 Brandenburg O4 I 4:i: 3 O7 Infantis O7 Thompson O7 Oranienburg 6 O7 Braenderup O7 Rissen O7 Not typed O8 Corvallis O8 Not typed O9 Enteritidis O9 Not typed O3,0 Weltevreden T 3 T4 T6 5 T T5 T8 5 TB364 3 Untypable
27 Vol. 35 No Verotoxinproducing E.coli Enteropathogenic E.coli Enteroaggregative E.coli 4 4 Salmonella O4 Salmonella O3,0 Campylobacter jejuni Staphylococcus aureus 3 Streptococcus pyogenes 0 Streptococcus agalactiae Streptococcus group C S.dysgalactiae subsp.equisimilis Streptococcus pneumoniae 3 Legionella pneumophila SG Mycoplasma pneumoniae Influenza virus A Hpdm Influenza virus A H3 5 6 Influenza virus B/Victoria Influenza virus B/Yamagat ata Measles virus genotype B3 4 5 Measles virus genotype D8 Measles virus genotype D9 Dengue virus NT Dengue virus Dengue virus Dengue virus 4 Hepatitis A virus IA Hepatitis A virus IIIA Plasmodium falciparum Dengue virus Dengue virus 4 / NT :
28 858 Vol. 35 No Picornavirus NT Enterovirus NT Coxsackievirus A NT Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A7 Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A4 8 Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus B Coxsackievirus B Coxsackievirus B Coxsackievirus B Coxsackievirus B Coxsackievirus B6 NT Poliovirus Poliovirus Poliovirus 3 3 Enterovirus Enterovirus Parechovirus NT Parechovirus Parechovirus 3 3 Rhinovirus Aichivirus Influenza virus A not subtyped Influenza virus A Hpdm Influenza virus A H Influenza virus B NT Influenza virus B/Victoria Influenza virus B/Yamagata Parainfluenza virus Respiratory syncytial virus Human metapneumovirus Other coronavirus Mumps virus Measles virus genotype NT 6 Measles virus genotype A Measles virus genotype B Measles virus genotype D Measles virus genotype D9 9 Measles virus genotype H 6 Rubella virus genotype NT Rubella virus genotype a 3 Rubella virus genotype E Rubella virus genotype B Japanese encephalitis virus Dengue virus Chikungunya virus 5 SFTS virus 4 5 Reovirus Rotavirus group unknown Rotavirus group A Rotavirus group C Astrovirus Norovirus genogroup unknown Norovirus genogroup I Norovirus genogroup II Sapovirus genogroup unknown Sapovirus genogroup I Sapovirus genogroup II Sapovirus genogroup III Sapovirus genogroup IV NT / / Herpes simplex virus NT Herpes simplex virus Herpes simplex virus Varicellazoster virus Cytomegalovirus Human herpes virus Human herpes virus EpsteinBarr virus Hepatitis A virus NT 7 Hepatitis A virus IA Hepatitis A virus IB Hepatitis A virus IIIA Hepatitis E virus 5 Human papilloma virus B9 virus Human bocavirus Virus NT Chlamydia trachomatis Chlamydophila pneumoniae Orientia tsutsugamushi Rickettsia japonica NT :
29 Vol. 35 No Enterovirus NT Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A4 4 5 Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A9 7 3 Coxsackievirus A0 4 7 Coxsackievirus A 4 6 Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus B Coxsackievirus B Coxsackievirus B Coxsackievirus B Coxsackievirus B NT Enterovirus Enterovirus Parechovirus NT 8 4 Parechovirus Parechovirus Rhinovirus Influenza virus A Hpdm0 dm Influenza virus A H Influenza virus B NT Influenza virus B/Victoria Influenza virus B/Yamagat ata Parainfluenza virus Respiratory syncytial virus Human metapneumoviru neumovirus 0 Other coronavirus Mumps virus 7 3 Measles virus genotype NT Measles virus genotype A Measles virus genotype B Measles virus genotype D8 3 6 Measles virus genotype D9 3 Rubella virus genotype NT Rubella virus genotype E Rubella virus genotype B Japanese anese encephalitis virus Dengue virus Chikungunya virus Reovirus Rotavirus group A Astrovirus Norovirus genogroup unknown 7 9 Norovirus genogroup I Norovirus genogroup II Sapovirus genogroup unknown 85 0 Sapovirus genogroup I Sapovirus genogroup II 8 8 NT / / Herpes es simplex virus NT 5 Herpes es simplex virus Herpes es simplex virus 3 7 Varicellazoster virus 6 30 Cytomegalovirus Human herpes es virus Human herpes es virus EpsteinBarr virus Hepatitis A virus NT Hepatitis A virus IA 5 Hepatitis A virus IIIA Hepatitis E virus Human papilloma virus 4 5 B9 virus Human bocavirus 9 9 Orientia tsutsugamush amushi Rickettsia japonica NT :
30 Entero N Entero NT Coxsackie A Coxsackie A Coxsackie A4 Coxsackie A4 Coxsackie A Coxsackie A Coxsackie A Coxsackie A Coxsackie A Coxsackie A8 3 4 Coxsackie A Coxsackie A9 4 3 Coxsackie A0 Coxsackie A0 3 3 Coxsackie A Coxsackie A Coxsackie A6 Coxsackie A6 3 3 Coxsackie A Coxsackie A Coxsackie B Coxsackie B Coxsackie B Coxsackie B Coxsackie B Coxsackie B Coxsackie B4 Coxsackie B4 5 5 Coxsackie B5 Coxsackie B Echo NT Echo NT Echo 3 Echo 3 Echo 6 Echo 6 3 Echo 7 Echo 7 Echo 9 Echo Echo Echo Echo 8 Echo Echo 9 Echo 9 Echo 5 Echo Echo 30 Echo ntero E ntero E Parecho NT Parecho NT arecho P Parecho 3 Parecho Rhino Influenza A Hpdm0 Influenza A Hpdm Influenza A H Influenza A H Influenza B NT Influenza B NT 9 Influenza B/Victori Influenza B/Victoria Influenza B/Yamagat Influenza B/Yamagata Parainfluenza Parainfluenza Respiratory syncytial Respiratory syncytial Human metapneum Human metapneumo 5 Other corona Other corona 9 Mumps Mumps Measles genotype NT Measles genotype NT Measles genotype Measles genotype A Measles genotype B3 Measles genotype B Measles genotype D8 Measles genotype D8 Measles genotype D9 Measles genotype D9 Rubella genotype NT Rubella genotype NT 0 Rubella genotype E Rubella genotype E Rubella genotype B Rubella genotype B Japanese encephalitis Japanese encephalitis Dengue Dengue 3 Chikungunya Chikungunya Reo Reo Rota group A Rota group A Astro Astro Noro genogroup unknown Noro genogroup unknown Noro genogroup Noro genogroup I 3 Noro genogroup I Noro genogroup II Sapo genogroup unknown Sapo genogroup unknown 4 8 Sapo genogroup I Sapo genogroup I Sapo genogroup II Sapo genogroup II Adeno NT Adeno NT Adeno Adeno deno A Adeno 3 Adeno deno A Adeno 5 Adeno 5 Adeno 6 Adeno 6 Adeno 7 Adeno 7 Adeno 8 Adeno 8 4 Adeno 9 Adeno 9 Adeno 3 Adeno 3 Adeno 37 Adeno 37 3 Adeno 40/4 Adeno 40/4 Adeno 4 Adeno 4 4 Adeno 53/ Adeno 53/ Adeno 54 Adeno 54 4 Adeno 56 Adeno 56 Herpes simplex NT Herpes simplex NT 5 Herpes simplex Herpes simplex 5 3 Herpes simplex Herpes simplex 3 3 Varicellazoster Varicellazoster 9 Cytomegalo Cytomegalo Human herpes Human herpes Human herpes Human herpes EpsteinBarr EpsteinBarr 8 4 Hepatitis A NT Hepatitis A NT Hepatitis A IA Hepatitis A IA Hepatitis A IIIA Hepatitis A IIIA Hepatitis E Hepatitis E Human papilloma Human papilloma 5 B9 B9 Human boca Human boca Orientia tsutsugamushi Orientia tsutsugamushi 7 Rickettsia japonica Rickettsia japonica NT : Vol. 35 No
31 Entero NT Entero NT Coxsackie A Coxsackie A 5 Coxsackie A4 Coxsackie A4 3 3 Coxsackie A5 Coxsackie A Coxsackie A6 Coxsackie A Coxsackie A8 Coxsackie A Coxsackie A9 Coxsackie A Coxsackie A0 Coxsackie A0 6 Coxsackie A Coxsackie A Coxsackie A6 Coxsackie A6 Coxsackie A Coxsackie A Coxsackie B Coxsackie B Coxsackie B Coxsackie B Coxsackie B3 Coxsackie B3 3 3 Coxsackie B4 Coxsackie B Coxsackie B5 Coxsackie B5 Echo NT Echo NT Echo 3 Echo Echo 6 Echo 6 Echo 7 Echo 7 3 Echo 9 Echo Echo Echo Echo 8 Echo Echo 9 Echo Echo 5 Echo Echo 30 Echo Entero 68 Entero Entero 7 Entero Parecho NT Parecho NT Parecho Parecho 3 Parecho 3 Parecho Rhino Rhino Influenza A Hpdm09 Influenza A Hpdm Influenza A H3 Influenza A H Influenza B NT Influenza B NT Influenza B/Victoria Influenza B/Victoria Influenza B/Yamagata Influenza B/Yamagata Parainfluenza Parainfluenza Respiratory syncytial Respiratory syncytial 3 Human metapneumo Human metapneumo Other corona Other corona Mumps Mumps Measles genotype NT Measles genotype NT Measles genotype A Measles genotype A 3 3 Measles genotype B3 Measles genotype B3 6 Measles genotype D8 Measles genotype D8 3 Measles genotype D9 Measles genotype D Rubella genotype NT Rubella genotype NT Rubella genotype E Rubella genotype E Rubella genotype B Rubella genotype B Japanese encephalitis Japanese encephalitis Dengue Dengue Chikungunya Chikungunya Reo Reo Rota group A Rota group A 3 3 Astro Astro Noro genogroup unknown Noro genogroup unknown 8 Noro genogroup I Noro genogroup I Noro genogroup II Noro genogroup II Sapo genogroup unknown Sapo genogroup unknown Sapo genogroup I Sapo genogroup I 3 8 Sapo genogroup II Sapo genogroup II Adeno NT Adeno NT Adeno Adeno Adeno Adeno Adeno 3 Adeno Adeno 4 Adeno Adeno 5 Adeno Adeno 6 Adeno 6 Adeno 7 Adeno 7 6 Adeno 8 Adeno 8 Adeno 9 Adeno 9 3 Adeno 3 Adeno 3 5 Adeno 37 Adeno Adeno 40/4 Adeno 40/ Adeno 4 Adeno 4 Adeno 53/ Adeno 53/ 5 Adeno 54 Adeno 54 6 Adeno 56 Adeno 56 5 Herpes simplex NT Herpes simplex NT 3 38 Herpes simplex Herpes simplex 7 7 Herpes simplex Herpes simplex Varicellazoster Varicellazoster Cytomegalo Cytomegalo Human herpes 6 Human herpes Human herpes 7 Human herpes EpsteinBarr EpsteinBarr Hepatitis A NT Hepatitis A NT 5 Hepatitis A IA Hepatitis A IA Hepatitis A IIIA Hepatitis A IIIA Hepatitis E Hepatitis E 5 5 Human papilloma Human papilloma 6 6 B9 B9 9 9 Human boca Human boca Orientia tsutsugamushi Orientia tsutsugamushi Rickettsia japonica Rickettsia japonica NT : Vol. 35 No
32 Enterovirus N Enterovirus NT Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A4 3 5 Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A 4 6 Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus B Coxsackievirus B Coxsackievirus B Coxsackievirus B Coxsackievirus B Coxsackievirus B Coxsackievirus B Coxsackievirus B Coxsackievirus B Coxsackievirus B NT chovirus E 3 chovirus E 6 chovirus E chovirus E 9 chovirus E 6 chovirus E chovirus E chovirus E 4 5 chovirus E chovirus E nterovirus E nterovirus E Parechovirus N Parechovirus NT arechovirus P arechovirus P 3 hinovirus R Influenza virus A Hpdm0 Influenza virus A Hpdm Influenza virus A H Influenza virus A H Influenza virus B N Influenza virus B NT Influenza virus B/Victori Influenza virus B/Victoria Influenza virus B/Yamagat Influenza virus B/Yamagata Parainfluenza viru Parainfluenza virus Respiratory syncytial viru Respiratory syncytial virus Human metapneumoviru Human metapneumovirus 9 Other coronaviru Other coronavirus virus umps M 8 3 Measles virus genotype NT Measles virus genotype NT Measles virus genotype A Measles virus genotype A Measles virus genotype B3 Measles virus genotype B Measles virus genotype D8 Measles virus genotype D8 6 6 Measles virus genotype D9 Measles virus genotype D9 3 Rubella virus genotype NT Rubella virus genotype NT Rubella virus genotype E Rubella virus genotype E Rubella virus genotype B Rubella virus genotype B Japanese encephalitis virus Japanese encephalitis virus Dengue virus Dengue virus Chikungunya viru Chikungunya virus Reovirus Reovirus Rotavirus group Rotavirus group A 9 3 strovirus A Norovirus genogroup unknown Norovirus genogroup unknown Norovirus genogroup I Norovirus genogroup I Norovirus genogroup II Norovirus genogroup II Sapovirus genogroup unknown Sapovirus genogroup unknown Sapovirus genogroup I Sapovirus genogroup I Sapovirus genogroup I Sapovirus genogroup II 7 8 NT NT denovirus A denovirus A denovirus A denovirus A denovirus A denovirus A 4 7 denovirus A 8 denovirus A denovirus A 3 denovirus A denovirus A /4 40/ denovirus A 9 53/ 53/ 54 denovirus A 56 denovirus A 6 6 Herpes simplex virus N Herpes simplex virus NT 5 5 Herpes simplex virus Herpes simplex virus Herpes simplex virus Herpes simplex virus Varicellazoster viru Varicellazoster virus Cytomegaloviru Cytomegalovirus Human herpes virus Human herpes virus Human herpes virus Human herpes virus EpsteinBarr viru EpsteinBarr virus Hepatitis A virus N Hepatitis A virus NT Hepatitis A virus I Hepatitis A virus IA 5 5 Hepatitis A virus III Hepatitis A virus IIIA Hepatitis E viru Hepatitis E virus Human papilloma viru Human papilloma virus virus B Human bocaviru Human bocavirus Orientia tsutsugamushi Orientia tsutsugamushi Rickettsia japonica Rickettsia japonica NT NT : Vol. 35 No
33 Vol. 35 No IASR Vol. 35 No. February 04 Infectious Agents Surveillance Report ISSN National Institute of Infectious Diseases and Tuberculosis and Infectious Diseases Control Division, Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare Epidemiology of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS) in China33 SFTS: its regulation as a newly identified infectious disease Genomic phylogenetic analysis of SFTSV isolated from SFTS patients in Japan Biosafety and other guidelines for prevention of familial and hospital infections of SFTSV Summary report of 40 clinical cases of SFTS in 03National Epidemiological Surveillance of Infectious Diseases A mild SFTS case whose clinical differential diagnosis from rickettsiosis was difficult, April Laboratory tests of SFTS Severe influenza pneumonia encountered in the early 03/4 season in a healthy adult person infected by A(H)pdm09 Sapporo City... 4 Antiinfluenza drugresistant A(HN)pdm09 viruses detected in the early 03/4 season in Sapporo City... 4 Antiinfluenza drugresistant A(HN)pdm09 isolated from a child, who was suspected familial infection but had not been administered with oseltamivir, December Two clinical cases diagnosed as Zika fever after return from Bora Bora Island, French Polynesia, December Epidemiological trends of invasive pneumococcal infections and invasive Haemophilus influenzae infectionsnotification as category V infectious disease since April Isolation of coxsackievirus A from two sporadic cases, AugustSeptember 03Tokyo Coxsackievirus A6 detected from hand, foot and mouth disease cases in 03Sendai City An acute encephalopathy case of one year nine month boy, from whom HHV6 and a number of picornavirus were detected, September <THE TOPIC OF THIS MONTH> Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS) in Japan, 03 Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS) is a tickborne systemic infectious disease. It is caused by SFTS virus (SFTSV), a novel virus belonging to Genus Phlebovirus, Family Bunyaviridae (Fig. ), which was first reported from China in 0 (see p. 33 of this issue). Latency is 63 days and the main symptoms are fever and gastrointestinal symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and melena. Hematuria and proteinuria are frequently observed. Leukopenia and thrombocytopenia are usually seen in peripheral blood, and hemophagocytosis with cellular hypoplasia are also demonstrated in the bone marrow. Blood biochemistry shows elevation of AST, ALT and LDH. Neurological symptoms, such as disturbed consciousness, are often associated with poor prognosis. SFTS has been reported from China since 0 and from Japan and the Republic of Korea since 03. Natural history of SFTSV and transmission to humans: In nature, SFTSV is maintained through vertical transmission from adult ticks to their offspring through transovarial transmission (ticktick cycle) and also by transmission from infected mammals to ticks and vice versa (tickmammal cycle). Two tick species, Haemaphysalis longicornis and Rhipicephalus microplus, frequently found in areas inhabited by humans in China, are considered to be the natural reservoir of SFTSV; 5.0% and 0.6% of these two species, respectively, were found to harbor SFTSV or its genome. In Japan, the ticks responsible for SFTSV transmission to humans are probably H. longicornis and Amblyomma testudinarium (Fig. ), because these ticks were found on the patients body surface. The infection route to humans is mainly tick bite; transmission to family members or to medical providers, mediated by blood and other body fluids, have also been reported from China. No airborne or dropletborne infection has been reported so far. Identification of SFTS patient in Japan and retrospective clinical and epidemiological studies: An adult with no history of travel abroad developed fever, vomiting and bloody diarrhea in autumn of 0, and died of systemic organ failure. SFTSV was isolated from the patient s blood and pathological examinations revealed SFTSV antigens in various affected organs. This was the first patient diagnosed as having SFTS in Japan (IASR 34: 404, 03). The Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW) issued a case definition for the surveillance of SFTS on January 30, 03 ( so as to effectively collect information on SFTS patients in Japan. Retrospective studies using the MHLW s case definition identified 8 patients with severe SFTS in or before 0 (including the first clinical case) (IASR 34: 0, 03). Subsequently, 3 additional severe or fatal cases before 03 were also identified, bringing the total number to. Among the patients, 6 died and all the patients were reported from western Japan. Among 5 patients in whom bone marrow was examined, all exhibited the findings characteristic to the hemophagocytic syndrome, and many of the patients suffered from blood coagulation abnormality and/or systemic organ failure. SFTSV was isolated from 8 patients. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that Japanese strains formed an independent cluster from those of the Chinese strains, indicating that Japanese strains are indigenous to Japan and evolved independently from Chinese strains (see p. 35 of this issue). Fig.. Electron micrograph of SFTSV isolated from an SFTS patient Fig.. Haemaphysalis longicornis (left) and Amblyomma testudinarium (right) 3 Continued on page 3
34 64 THE TOPIC OF THIS MONTHContinued Figure 3. Monthly cases of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS), 03, Japan Onset in 03 (n=40) 0 Onset before 03 (n=8) Jan. Feb. Mar. Apr. May Jun. Jul. Aug. Sep. Oct. Nov. Dec. Onset (National Epidemiological Surveillance of Infectious Diseases: As of December 3, 03) Cases Vol. 35 No. 04. Figure 4. Incidence of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS) by prefecture, 03 IASR Vol. 35 No. Feb Figure 5. Age distribution of SFTS cases, by gender, 03, Japan (n=48) 0 8 Males Deaths 6 (n=) Age group 0 8 Females (n=6) 6 Cases Cases Age group including 8 cases of onset in or before 0 (National Epidemiological Surveillance of Infectious Diseases: As of December 3, 03) Onset in 03 (n=40) Onset before 03 (n=8) (National Epidemiological Surveillance of Infectious Diseases: As of December 3, 03) Japanese SFTS patients reported in 03: On March 4, 03, SFTS was designated as a category IV infectious disease, requiring notification to the designated public health center (see for notification criteria), and SFTSV as a biosafety level group 3 pathogen (IASR 34: 0, 03) (see p. 34 & 37 of this issue). Physicians, who have treated a patient diagnosed virologically as SFTS, must notify the information to the designated public health center within 4 hours. The number of SFTS patients reported in compliance with the Infectious Diseases Control Law under the National Epidemiological Surveillance of Infectious Diseases was 48 until the end of 03; 40 were developed in 03 (see p. 38 of this issue), and 8 in or before 0 ( cases in 005; case in 00; 5 cases in 0; IASR 34: 0, 03). The seasonal peak was in May (Fig. 3). Patients were reported from 3 prefectures in Kyushu, Shikoku and Chugoku regions (Fig. 4). Twentytwo cases were males and 6 females. Patients ages ranged from 48 to 95 years (median 7 years) (Fig. 5). Seventeen of 48 had died. With increased recognition of SFTS, mild SFTS cases were discovered (see p. 39 of this issue; IASR 34: 0708, 03). Tickbites were not always found on the body surface of the patients. It is, therefore, advised to conduct laboratory diagnosis if a patient is suspected of having SFTS, even if the clinical pictures, including presence of bites, do not fit perfectly to the previous case definitions (see p. 38 of this issue). Laboratory diagnosis available in Japan: Virological diagnosis includes detection/isolation of SFTSV from acute phase patients blood and other body fluids (throat swab, urine), and/or the demonstration of a significant rise in IgG antibody titers in paired sera between acute and convalescent phases. Diagnosis using RTPCR detection of SFTSV genome is available within the network of prefectural and municipal public health institutes (PHIs). Furthermore, indirect fluorescent antibody test using the SFTSVinfected cells and IgGELISA using the SFTSV antigen are also available in the National Institute of Infectious Disease (NIID), Department of Virology I (see p. 40 of this issue). Methods for the detection of SFTSV genome in ticks inhabiting Japan and antibody detection methods in mammals have been developed and the surveillance of SFTSV genome prevalence in some species of ticks and antibody levels in wild animals are being conducted (IASR 34: , 03). Measures to be taken: An SFTS patient was first reported in January 03 in Japan. Subsequent retrospective and prospective surveillance has revealed the existence of SFTS in western Japan. PHIs and NIID established a laboratory diagnosis system, which should be maintained and developed further. In 03, an MHLWfunded 3year project Comprehensive research on control of SFTS (chief investigator T. Kurata) started. The project includes ) detailed epidemiological and clinical studies on SFTS to elucidate the clinical and pathological characteristics; ) development of rapid SFTSV detection kit; 3) basic research for vaccine development; 4) assessment of risk of SFTSV infection and risk communication on SFTS; and 5) elucidation of SFTSV prevalence among ticks inhabiting Japan, geographical distribution of SFTSVpositive ticks, seroepidemiology of wild animals, and geographical spread of SFTSV in Japan. The statistics in this report are based on ) the data concerning patients and laboratory findings obtained by the National Epidemiological Surveillance of Infectious Diseases undertaken in compliance with the Law Concerning the Prevention of Infectious Diseases and Medical Care for Patients of Infections, and ) other data covering various aspects of infectious diseases. The prefectural and municipal health centers and public health institutes (PHIs), the Department of Food Safety, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, and quarantine stations, have provided the above data. Infectious Disease Surveillance Center, National Institute of Infectious Diseases Toyama 3, Shinjukuku, Tokyo 68640, JAPAN Tel (+83)585
untitled
 Vol. 35 No. 3 204. ISSN 3 63 https://nesid3g.mhlw.go. 200 0 Vol.35 No. 3 No.409 2043 Infectious Agents Surveillance Report (IASR) 095583http://www.nih.go.jp/niid/ja/iasr.html 3, 4, : 5, A ; 6, : 8, 9,,
Vol. 35 No. 3 204. ISSN 3 63 https://nesid3g.mhlw.go. 200 0 Vol.35 No. 3 No.409 2043 Infectious Agents Surveillance Report (IASR) 095583http://www.nih.go.jp/niid/ja/iasr.html 3, 4, : 5, A ; 6, : 8, 9,,
untitled
 Infectious Agents Surveillance Report (IASR) http://www.nih.go.jp/niid/ja/iasr.html EHEC 202 3, EHEC O57 : 4 O57 ISprinting system 5, 6, O57 : 20 7, O57 : 8, O26 : 9, O26 : 0, O26 : 2, O03 O : 3, O45 :
Infectious Agents Surveillance Report (IASR) http://www.nih.go.jp/niid/ja/iasr.html EHEC 202 3, EHEC O57 : 4 O57 ISprinting system 5, 6, O57 : 20 7, O57 : 8, O26 : 9, O26 : 0, O26 : 2, O03 O : 3, O45 :
untitled
 Infectious Agents Surveillance Report (IASR) http://www.nih.go.jp/niid/ja/iasr.html : 3, : 5, NESID 6, : 7, : 9, L. pneumophila SG3 ST93 : 0,, ATP 3, 4, 5, Human coronavirus : 6, AH7N9 : 8, A H7N9 : 9,
Infectious Agents Surveillance Report (IASR) http://www.nih.go.jp/niid/ja/iasr.html : 3, : 5, NESID 6, : 7, : 9, L. pneumophila SG3 ST93 : 0,, ATP 3, 4, 5, Human coronavirus : 6, AH7N9 : 8, A H7N9 : 9,
SARS HIV/AIDS n = 672; % 5% 2% 8% 16% 43% 20%
 SARS HIV/AIDS n = 672; 20074 20108 6% 5% 2% 8% 16% 43% 20% 1999 2008 HIV/AIDS B A 0% 50% 100% 1049 552 17 186 867 431 739 3847 332 7556 102 2420 3648 449 802 2709 31774 1286 13651 1611 207 95 8 162 667
SARS HIV/AIDS n = 672; 20074 20108 6% 5% 2% 8% 16% 43% 20% 1999 2008 HIV/AIDS B A 0% 50% 100% 1049 552 17 186 867 431 739 3847 332 7556 102 2420 3648 449 802 2709 31774 1286 13651 1611 207 95 8 162 667
Fig. 1 Trends of TB incidence rates for all forms and smear-positive pulmonary TB in Kawasaki City and Japan. Incidence=newly notified cases of all fo
 Kekkaku Vol. 79, No. 1: 17-24, 2004 17 (Received 21 Aug. 2003/Accepted 18 Nov. 2003) Fig. 1 Trends of TB incidence rates for all forms and smear-positive pulmonary TB in Kawasaki City and Japan. Incidence=newly
Kekkaku Vol. 79, No. 1: 17-24, 2004 17 (Received 21 Aug. 2003/Accepted 18 Nov. 2003) Fig. 1 Trends of TB incidence rates for all forms and smear-positive pulmonary TB in Kawasaki City and Japan. Incidence=newly
untitled
 Seminal paper Anhalt JP Pioneering paper Claydon MA Kishnamurthy T Enterobacter B. cereus Routine identification paper Eigner U Seng P Cherkaoui A Saureus S. Saureus* S. Vagococcus Haemophilus Mycobacterium
Seminal paper Anhalt JP Pioneering paper Claydon MA Kishnamurthy T Enterobacter B. cereus Routine identification paper Eigner U Seng P Cherkaoui A Saureus S. Saureus* S. Vagococcus Haemophilus Mycobacterium
CHEMOTHERAPY aureus 0.10, Enterococcus faecalis 3.13, Escherichia coli 0.20, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter spp., Serratia marcescens 0.78, Prote
 aureus 0.10, Enterococcus faecalis 3.13, Escherichia coli 0.20, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter spp., Serratia marcescens 0.78, Proteus mirabilis 3.13, Proteus vulgaris 1.56, Citrobacter freundii 0.39,
aureus 0.10, Enterococcus faecalis 3.13, Escherichia coli 0.20, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter spp., Serratia marcescens 0.78, Proteus mirabilis 3.13, Proteus vulgaris 1.56, Citrobacter freundii 0.39,
Key words: bacterial meningitis, Haemophilus influenzae type b, Streptococcus pneumoniae, rapid diagnosis, childhood
 Key words: bacterial meningitis, Haemophilus influenzae type b, Streptococcus pneumoniae, rapid diagnosis, childhood Fig.1 Distribution of the cases with bacterial meningitis by age and pathogens Chiba
Key words: bacterial meningitis, Haemophilus influenzae type b, Streptococcus pneumoniae, rapid diagnosis, childhood Fig.1 Distribution of the cases with bacterial meningitis by age and pathogens Chiba
CHEMOTHERAPY
 CHEMOTHERAPY VOL.41 S-2 Laboratory and clinical evaluation of teicoplanin CHEMOTHERAPY AUG. 1993 VOL.41 S-2 Laboratory and clinical evaluation of teicoplanin Table 1. Comparative in vitro activity of teicoplanin
CHEMOTHERAPY VOL.41 S-2 Laboratory and clinical evaluation of teicoplanin CHEMOTHERAPY AUG. 1993 VOL.41 S-2 Laboratory and clinical evaluation of teicoplanin Table 1. Comparative in vitro activity of teicoplanin
400 46 THE JAPANESE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS 65 6 Dec. 2012 LVFX 100 mg 3 / 7 150 mg 2 / 7 2 2006 2008 9 LVFX PK PD 2009 7 100 mg 1 3 500 mg 1 1 AUC/MIC
 Dec. 2012 THE JAPANESE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS 65 6 399 45 2012 11 5 LVFX 500 mg 1 1 20 Chlamydia trachomatis C. trachomatismycoplasma genitalium M. genitalium LVFX 1 500 mg 1 1 7 22 22 C. trachomatis 17
Dec. 2012 THE JAPANESE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS 65 6 399 45 2012 11 5 LVFX 500 mg 1 1 20 Chlamydia trachomatis C. trachomatismycoplasma genitalium M. genitalium LVFX 1 500 mg 1 1 7 22 22 C. trachomatis 17
/‚“1/ŒxŒ{‚×›î’æ’¶
 60 1 pp.3-8 2010 1. H1N1 1) 2) 3) 4) ERATO 2009 H1N1 21 H1N1 HA PB2 2009 3 Pandemic H1N1 2009 WHO 6 11 21 2009 11 2010 4 21 H1N1 H1N1 2009 4 15 CDC 108-8639 4-6-1 TEL: 03-5449-5281 FAX: 03-5449-5408 E-mail:
60 1 pp.3-8 2010 1. H1N1 1) 2) 3) 4) ERATO 2009 H1N1 21 H1N1 HA PB2 2009 3 Pandemic H1N1 2009 WHO 6 11 21 2009 11 2010 4 21 H1N1 H1N1 2009 4 15 CDC 108-8639 4-6-1 TEL: 03-5449-5281 FAX: 03-5449-5408 E-mail:
/fiÁ1-1/‹Éfi¡ıæ„[’æ’¶
 59 1 pp.53-58 2009 1. H5N1 3 H5N1 2007 1 2 2008 4 5 2003 H5N1 2005 50 1 429 262 2009 5 22 2 680-8553 4 101 TEL/FAX : 0857-31-5437 E-mail: toshiito@muses.tottori-u.ac.jp 3 H5N1 1 A A A 54 59 1 4 A A 5 1997
59 1 pp.53-58 2009 1. H5N1 3 H5N1 2007 1 2 2008 4 5 2003 H5N1 2005 50 1 429 262 2009 5 22 2 680-8553 4 101 TEL/FAX : 0857-31-5437 E-mail: toshiito@muses.tottori-u.ac.jp 3 H5N1 1 A A A 54 59 1 4 A A 5 1997
Table 1. Antibacterial activitiy of grepafloxacin and other antibiotics against clinical isolates
 Table 1. Antibacterial activitiy of grepafloxacin and other antibiotics against clinical isolates Table 2-1. Summary of patients treated with grepafloxacin for respiratory infection 1) Out: outpatient,
Table 1. Antibacterial activitiy of grepafloxacin and other antibiotics against clinical isolates Table 2-1. Summary of patients treated with grepafloxacin for respiratory infection 1) Out: outpatient,
 2) Goetz, A., Tsuneishi, N.: Application of molecular filter membranes to the bacteriological analysis of water, J. Am. Water Works Assn., 43 (12): 943-969,1951. 3) Clark, H.F. et al.: The membrane filter
2) Goetz, A., Tsuneishi, N.: Application of molecular filter membranes to the bacteriological analysis of water, J. Am. Water Works Assn., 43 (12): 943-969,1951. 3) Clark, H.F. et al.: The membrane filter
37, 9-14, 2017 : cefcapene piperacillin 3 CT Clostridium difficile CD vancomycin CD 7 Clostridium difficile CD CD associate
 37, 9-14, 2017 : 36 2015 8 6 cefcapene piperacillin 3 CT Clostridium difficile CD vancomycin 20 1983 2016 3 CD 7 Clostridium difficile CD CD associated diarrhea : CDAD CD 1,2 PPI 3 1 36 33 2015 8 6 5 5
37, 9-14, 2017 : 36 2015 8 6 cefcapene piperacillin 3 CT Clostridium difficile CD vancomycin 20 1983 2016 3 CD 7 Clostridium difficile CD CD associated diarrhea : CDAD CD 1,2 PPI 3 1 36 33 2015 8 6 5 5
CHEMOTHERAPY FEB Table 1. Activity of cefpirome and others against clinical isolates
 VOL.39 S-1 CHEMOTHERAPY FEB. 1981 Table 1. Activity of cefpirome and others against clinical isolates VOL.39 S-1 CHEMOTHERAPY FEB. 1991 72 M, 55.5 kg 66 F, 53 kg Chronic bronchitis Bronchopneumonia Peak
VOL.39 S-1 CHEMOTHERAPY FEB. 1981 Table 1. Activity of cefpirome and others against clinical isolates VOL.39 S-1 CHEMOTHERAPY FEB. 1991 72 M, 55.5 kg 66 F, 53 kg Chronic bronchitis Bronchopneumonia Peak
日本化学療法学会雑誌第59巻第5号
 Streptococcus pneumoniae Haemophilus influenzae Moraxella catarrhalis S. pneumoniae H. influenzae M. catarrhalis S. pneumoniae H. influenzae M. catarrhalis S. pneumoniae H. influenzae M. catarrhalis S.
Streptococcus pneumoniae Haemophilus influenzae Moraxella catarrhalis S. pneumoniae H. influenzae M. catarrhalis S. pneumoniae H. influenzae M. catarrhalis S. pneumoniae H. influenzae M. catarrhalis S.
Fig. 1 Chemical structure of TE-031 Code number: TE-031 Chemical name: (-) (3R, 4S, 5S, 6R, 7R, 9R, 11R, 12R, 13S, 14R)-4-[(2, 6-dideoxy-3-C-methyl-3-
 Fig. 1 Chemical structure of TE-031 Code number: TE-031 Chemical name: (-) (3R, 4S, 5S, 6R, 7R, 9R, 11R, 12R, 13S, 14R)-4-[(2, 6-dideoxy-3-C-methyl-3-O-methyl-a-L-ribo-hexopyranosyl) oxy]-14-ethyl-12,
Fig. 1 Chemical structure of TE-031 Code number: TE-031 Chemical name: (-) (3R, 4S, 5S, 6R, 7R, 9R, 11R, 12R, 13S, 14R)-4-[(2, 6-dideoxy-3-C-methyl-3-O-methyl-a-L-ribo-hexopyranosyl) oxy]-14-ethyl-12,
BUN, CRP K mg/ cm, 49.6 kg, BMI /72 mmhg, 92/ Hb 6.7 g/dl PT-INR CT 1 MRI 2a, b T1 T2 T1 MRI
 20 2 2015 1 2 3 85 K CT Abstract A case of renal subcapsular hematoma resulting from trigger point injection under excessive effect of anticoagulant YAMANE Tateki, UMEDA Akira and SHIMAO Hitoshi An 85-year-old
20 2 2015 1 2 3 85 K CT Abstract A case of renal subcapsular hematoma resulting from trigger point injection under excessive effect of anticoagulant YAMANE Tateki, UMEDA Akira and SHIMAO Hitoshi An 85-year-old
 1) i) Barber, M. et al.: Brit. Med J, 2, 565, 19'49. ii) Barber, M.F.G. J. Hayhoe and J. E. M. Whithead: Lancet, 1120 `1125, 1949.-2) Bergey: Bergey's Manual of Determinative Bacteriology 7 th Ed: (1958).-3)
1) i) Barber, M. et al.: Brit. Med J, 2, 565, 19'49. ii) Barber, M.F.G. J. Hayhoe and J. E. M. Whithead: Lancet, 1120 `1125, 1949.-2) Bergey: Bergey's Manual of Determinative Bacteriology 7 th Ed: (1958).-3)
_02三浦.indd
 36, 7-11, 2016 IPD PCV 5 3 80% 1 invasive pneumococcal disease ; IPD 2010 7 PCV7 2013 13 PCV13 IPD IPD 2,3 2015 1 2015 12 5 1 IPD 2015 1 12 IPD 5 IPD 1 4 2 5 http://pneumocatch.jp/ 5 Statens Serum Institut
36, 7-11, 2016 IPD PCV 5 3 80% 1 invasive pneumococcal disease ; IPD 2010 7 PCV7 2013 13 PCV13 IPD IPD 2,3 2015 1 2015 12 5 1 IPD 2015 1 12 IPD 5 IPD 1 4 2 5 http://pneumocatch.jp/ 5 Statens Serum Institut
Fig. 1 Chemical structure of DL-8280
 Fig. 1 Chemical structure of DL-8280 Fig. 2 Susceptibility of cl in ical isolates to DL4280 Fig. 5 Susceptibility of clinical isolates to DL-8280 Fig. 3 Susceptibility of clinical isolates to DL-8280 Fig.
Fig. 1 Chemical structure of DL-8280 Fig. 2 Susceptibility of cl in ical isolates to DL4280 Fig. 5 Susceptibility of clinical isolates to DL-8280 Fig. 3 Susceptibility of clinical isolates to DL-8280 Fig.
加藤茂孝先生
 Shigetaka KATOW 2009 4 24 WHO 5 9 1 5 16 1 TV 6 12 6 11 WHO 6 4 5 12 E-mail : modern_media@eiken.co.jp 2009. 4. 28. http:idsc.nih.go.jpidwrkanjaweeklygraph01flu.html 0101-0051 - RIKEN Center of Research
Shigetaka KATOW 2009 4 24 WHO 5 9 1 5 16 1 TV 6 12 6 11 WHO 6 4 5 12 E-mail : modern_media@eiken.co.jp 2009. 4. 28. http:idsc.nih.go.jpidwrkanjaweeklygraph01flu.html 0101-0051 - RIKEN Center of Research
 A comparison of abdominal versus vaginal hysterectomy for leiomyoma and adenomyosis Kenji ARAHORI, Hisasi KATAYAMA, Suminori NIOKA Department of Obstetrics and Gnecology, National Maizuru Hospital,Kyoto,
A comparison of abdominal versus vaginal hysterectomy for leiomyoma and adenomyosis Kenji ARAHORI, Hisasi KATAYAMA, Suminori NIOKA Department of Obstetrics and Gnecology, National Maizuru Hospital,Kyoto,
Key words: Antibodies to Leptospira, Tokyo, Uveitis
 Key words: Antibodies to Leptospira, Tokyo, Uveitis Fig. 1 Distribution of Antibody Titers in Age Decade Fig. 3 Distribution of Antibody Titers in each Strain Fig. 2 Correlation between Antibody Titers
Key words: Antibodies to Leptospira, Tokyo, Uveitis Fig. 1 Distribution of Antibody Titers in Age Decade Fig. 3 Distribution of Antibody Titers in each Strain Fig. 2 Correlation between Antibody Titers
8 The Bulletin of Meiji University of Integrative Medicine API II 61 ASO X 11 7 X-4 6 X m 5 X-2 4 X 3 9 X 11 7 API 0.84 ASO X 1 1 MR-angio
 7-14 2010 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 2 Fontaine II ASO61 3 API ASO ASO ASO API API KKKKKKKKKK ASO Fontaine II API Received April 14, 2009; Accepted July 16, 2009 I arteriosclerosis obliterans: ASO ASO 50 70 1,2 Fontaine
7-14 2010 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 2 Fontaine II ASO61 3 API ASO ASO ASO API API KKKKKKKKKK ASO Fontaine II API Received April 14, 2009; Accepted July 16, 2009 I arteriosclerosis obliterans: ASO ASO 50 70 1,2 Fontaine
Table 1 Profiles of 28 patients with Legionella pneumonia in Japan, 1980-1990 a) Y Taguchi, personal communication b) M. Hayase, personal communicatio
 Key words: Legionella pneumonia, culture-positive, Japanese patients Legionella (L. pneumophila (L. micdadei, L. bozemanii, Table 1 Profiles of 28 patients with Legionella pneumonia in Japan, 1980-1990
Key words: Legionella pneumonia, culture-positive, Japanese patients Legionella (L. pneumophila (L. micdadei, L. bozemanii, Table 1 Profiles of 28 patients with Legionella pneumonia in Japan, 1980-1990
CHEMOTHERAPY JUNE 1993 Table 1. Background of patients in pharmacokinetic study
 CHEMOTHERAPY JUNE 1993 Table 1. Background of patients in pharmacokinetic study VOL. 41 S 1 Table 2. Levels (Đg/ml or Đg/g) of S-1006 in serum, bile, and tissue (gallbladder) after oral administration
CHEMOTHERAPY JUNE 1993 Table 1. Background of patients in pharmacokinetic study VOL. 41 S 1 Table 2. Levels (Đg/ml or Đg/g) of S-1006 in serum, bile, and tissue (gallbladder) after oral administration
VOL. 23 NO. 3 CHEMOTHERAPY 1067 Table 2 Sensitivity of gram positive cocci isolated from various diagnostic materials Table 3 Sensitivity of gram nega
 1066 CHEMOTHERAPY MAR. 1975 Table 1 Sensitivity of standard strains VOL. 23 NO. 3 CHEMOTHERAPY 1067 Table 2 Sensitivity of gram positive cocci isolated from various diagnostic materials Table 3 Sensitivity
1066 CHEMOTHERAPY MAR. 1975 Table 1 Sensitivity of standard strains VOL. 23 NO. 3 CHEMOTHERAPY 1067 Table 2 Sensitivity of gram positive cocci isolated from various diagnostic materials Table 3 Sensitivity
 The clinical characteristics of Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children younger than 6 years old Nobue Takeda1,2),Tomomichi Kurosaki1),Naruhiko Ishiwada2),Yoichi Kohno2) 1)Department of Pediatrics,Chiba
The clinical characteristics of Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children younger than 6 years old Nobue Takeda1,2),Tomomichi Kurosaki1),Naruhiko Ishiwada2),Yoichi Kohno2) 1)Department of Pediatrics,Chiba
indd
 18 61 1 2011 症例報告 2010 5 13 2010 12 20 A Case of Varicella with Severe Back Pain in a Patient with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus RIE SAITO, KIORI YANO, FUMIKO KATSUSHIMA, HARUYO IWADATE, HIROKO KOBAYASHI,
18 61 1 2011 症例報告 2010 5 13 2010 12 20 A Case of Varicella with Severe Back Pain in a Patient with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus RIE SAITO, KIORI YANO, FUMIKO KATSUSHIMA, HARUYO IWADATE, HIROKO KOBAYASHI,
 CHEMOTHERAPY APRIL 1992 Table 2. Concentration of meropenem in human prostatic fluid Table 1. Background of 21 chronic complicated UTI cases * NB + BPH, NB + Kidney tumor, NB + Kidney tuberculosis Table
CHEMOTHERAPY APRIL 1992 Table 2. Concentration of meropenem in human prostatic fluid Table 1. Background of 21 chronic complicated UTI cases * NB + BPH, NB + Kidney tumor, NB + Kidney tuberculosis Table
semen quality or those without WBC in semen. In the patients with azoospermia and normal FSH levels (normogonadotropic azzospermia), the antibody (IgG
 CLINICAL STUDIES OF UROGENITAL INFECTIONS WITH CHLAMYDIA TRACHOMA TIS Report 2. The Epidemiology of Chlamydial Infections in Okayama District in Japan and Detection of Antibodies to Chlamydiae in the Sera
CLINICAL STUDIES OF UROGENITAL INFECTIONS WITH CHLAMYDIA TRACHOMA TIS Report 2. The Epidemiology of Chlamydial Infections in Okayama District in Japan and Detection of Antibodies to Chlamydiae in the Sera
Fig. 1 Clinical findings and extent of inflammation area in female urethrocystitis Fig. 2 Classification and distribution of female patients with blad
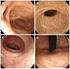 Key words: Female with bladder irritability, Subjective symptoms, Pyuria, Bacteriuria Fig. 1 Clinical findings and extent of inflammation area in female urethrocystitis Fig. 2 Classification and distribution
Key words: Female with bladder irritability, Subjective symptoms, Pyuria, Bacteriuria Fig. 1 Clinical findings and extent of inflammation area in female urethrocystitis Fig. 2 Classification and distribution
 840 Geographical Review of Japan 73A-12 835-854 2000 The Mechanism of Household Reproduction in the Fishing Community on Oro Island Masakazu YAMAUCHI (Graduate Student, Tokyo University) This
840 Geographical Review of Japan 73A-12 835-854 2000 The Mechanism of Household Reproduction in the Fishing Community on Oro Island Masakazu YAMAUCHI (Graduate Student, Tokyo University) This
 1) Garner J. S.: The Hospital Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee, CDC, Guidelines for Isolation Precautions in Hospitals, 1996. http://wonder.cdc.gov/wonder/prevguid/ p0000419/p0000419.asp.
1) Garner J. S.: The Hospital Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee, CDC, Guidelines for Isolation Precautions in Hospitals, 1996. http://wonder.cdc.gov/wonder/prevguid/ p0000419/p0000419.asp.
 1) University Group Diabetes Program: A study of hypoglycemic agents on vascular complica- in patients with adult-onset tions diabetes. I. Design, methods and baseline results. Diabetes 19 (suppl. 2):
1) University Group Diabetes Program: A study of hypoglycemic agents on vascular complica- in patients with adult-onset tions diabetes. I. Design, methods and baseline results. Diabetes 19 (suppl. 2):
CHEMOTHERAPY JUN Citrobacter freundii 27, Enterobacter aerogenes 26, Enterobacter cloacae 27, Proteus rettgeri 7, Proteus inconstans 20, Proteus
 VOL. 32 S-4 CHEMOTHERAPY Fig. 1 Chemical structure of sodium cefoperazone Fig. 2 Chemical structure of sodium cefoperazone CHEMOTHERAPY JUN. 1984 Citrobacter freundii 27, Enterobacter aerogenes 26, Enterobacter
VOL. 32 S-4 CHEMOTHERAPY Fig. 1 Chemical structure of sodium cefoperazone Fig. 2 Chemical structure of sodium cefoperazone CHEMOTHERAPY JUN. 1984 Citrobacter freundii 27, Enterobacter aerogenes 26, Enterobacter
名称未設定-1
 Study on Clinical Factors Affecting the Fungal Culture Test - Relevance of Dry Mouth - Yoshiko YAMAMURA, Yukihiro MOMOTA, Hideyuki TAKANO, Koichi KANI, Katsumi MOTEGI, Fumihiro MATSUMOTO, Masayuki AZUMA
Study on Clinical Factors Affecting the Fungal Culture Test - Relevance of Dry Mouth - Yoshiko YAMAMURA, Yukihiro MOMOTA, Hideyuki TAKANO, Koichi KANI, Katsumi MOTEGI, Fumihiro MATSUMOTO, Masayuki AZUMA
VOL.32 S-7 CHEMOTHERAPY Table 1 MIC of standard strains of CTRX Fig. 2 Cumulative curves of MIC S. aureus (26 strains )
 CHEMOTHERAPY OCT. 1984 Fig. I Chemical structure of CTRX VOL.32 S-7 CHEMOTHERAPY Table 1 MIC of standard strains of CTRX Fig. 2 Cumulative curves of MIC S. aureus (26 strains ) CHEMOTHERAPY Fig. 3 Cumulative
CHEMOTHERAPY OCT. 1984 Fig. I Chemical structure of CTRX VOL.32 S-7 CHEMOTHERAPY Table 1 MIC of standard strains of CTRX Fig. 2 Cumulative curves of MIC S. aureus (26 strains ) CHEMOTHERAPY Fig. 3 Cumulative
untitled
 Quantitative Risk Assessment on the Public Health Impact of Pathogenic Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Raw Oyster 1 15 5 23 48 2 21 1 16 1 16 1 11 3 1 3 4 23 1 2 16 12 16 5 6 Hazard IdentificationExposure
Quantitative Risk Assessment on the Public Health Impact of Pathogenic Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Raw Oyster 1 15 5 23 48 2 21 1 16 1 16 1 11 3 1 3 4 23 1 2 16 12 16 5 6 Hazard IdentificationExposure
coccus aureus Corynebacterium sp, Haemophilus parainfluenzae Klebsiella pneumoniae Pseudornonas aeruginosa Pseudomonas sp., Xanthomonas maltophilia, F
 VOL.43 S-1 coccus aureus Corynebacterium sp, Haemophilus parainfluenzae Klebsiella pneumoniae Pseudornonas aeruginosa Pseudomonas sp., Xanthomonas maltophilia, Flavobacter- Table 1. Concentration of grepafloxacin
VOL.43 S-1 coccus aureus Corynebacterium sp, Haemophilus parainfluenzae Klebsiella pneumoniae Pseudornonas aeruginosa Pseudomonas sp., Xanthomonas maltophilia, Flavobacter- Table 1. Concentration of grepafloxacin
E. coli E. coli é H. influenzae Helicobacter pylori
 é C.pneumoniae C.trachomatis C.trachomatis 1 é Chlamydia pneumoniae Chlamydia psittaci Chlamydia trachomatis 3 E. coli E. coli é H. influenzae Helicobacter pylori K. pneumoniae L. monocytogenes ü l Staphylococcus
é C.pneumoniae C.trachomatis C.trachomatis 1 é Chlamydia pneumoniae Chlamydia psittaci Chlamydia trachomatis 3 E. coli E. coli é H. influenzae Helicobacter pylori K. pneumoniae L. monocytogenes ü l Staphylococcus
indd
 24 61 1 2011 調査 研究 1 2 1 1 2 4 1 3 4 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 2 1 1 2 3 4 2010 11 11 2011 1 7 Infection Control in an Endoscopy Room Multi - society Guideline and Current Status at Fukushima Medical University
24 61 1 2011 調査 研究 1 2 1 1 2 4 1 3 4 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 2 1 1 2 3 4 2010 11 11 2011 1 7 Infection Control in an Endoscopy Room Multi - society Guideline and Current Status at Fukushima Medical University
〈企業特集:検査機器・試薬・技術の新たな展開〉新規マイコプラズマ抗原検査キット—プロラスト®Myco
 New immunochromatographic assay kit for Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection 'PRORAST Myco' Shohei Ohshima, Yasushi Shimada, Atsuko Minagawa, Kazuyuki Sugiyama and Yumiko Hirayama Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection
New immunochromatographic assay kit for Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection 'PRORAST Myco' Shohei Ohshima, Yasushi Shimada, Atsuko Minagawa, Kazuyuki Sugiyama and Yumiko Hirayama Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection
CHEMOTHERAPY Fig. 1 Chemical structure of CXM-AX
 Fig. 1 Chemical structure of CXM-AX NOV. 1986 Fig. 2 Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates organisms (106 cells/ml) a Smurcus 27 strains d) P.m irabilis 15 strains b Ecol i 27 strains 111.morganii
Fig. 1 Chemical structure of CXM-AX NOV. 1986 Fig. 2 Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates organisms (106 cells/ml) a Smurcus 27 strains d) P.m irabilis 15 strains b Ecol i 27 strains 111.morganii
2 The Bulletin of Meiji University of Integrative Medicine 3, Yamashita 10 11
 1-122013 1 2 1 2 20 2,000 2009 12 1 2 1,362 68.1 2009 1 1 9.5 1 2.2 3.6 0.82.9 1.0 0.2 2 4 3 1 2 4 3 Key words acupuncture and moxibustion Treatment with acupuncture, moxibustion and Anma-Massage-Shiatsu
1-122013 1 2 1 2 20 2,000 2009 12 1 2 1,362 68.1 2009 1 1 9.5 1 2.2 3.6 0.82.9 1.0 0.2 2 4 3 1 2 4 3 Key words acupuncture and moxibustion Treatment with acupuncture, moxibustion and Anma-Massage-Shiatsu
988 CHEMOTHERAPY NOV. 1971
 988 CHEMOTHERAPY NOV. 1971 VOL. 19 NO. 8 CHEMOTHERAPY 989 Effect of medium-ph and inoculum size on activity of SB-PC heart infusion agar, mcg/ml Sensitivity distribution of Staphylococci to SB-PC in surgical
988 CHEMOTHERAPY NOV. 1971 VOL. 19 NO. 8 CHEMOTHERAPY 989 Effect of medium-ph and inoculum size on activity of SB-PC heart infusion agar, mcg/ml Sensitivity distribution of Staphylococci to SB-PC in surgical
_念3)医療2009_夏.indd
 Evaluation of the Social Benefits of the Regional Medical System Based on Land Price Information -A Hedonic Valuation of the Sense of Relief Provided by Health Care Facilities- Takuma Sugahara Ph.D. Abstract
Evaluation of the Social Benefits of the Regional Medical System Based on Land Price Information -A Hedonic Valuation of the Sense of Relief Provided by Health Care Facilities- Takuma Sugahara Ph.D. Abstract
東京都微生物検査情報 第32巻 第2号
 ISSN 188-266 東京都微生物検査情報 MONTHLY EPIDEMIOLOGICAL RECORD, TOKYO 第 2 巻第 2 号 2011 年 2 月分月報 http://idsc.tokyo-eiken.go.jp/ 東京都におけるインフルエンザウイルス抗体保有状況 東京都における流行予測調査事業により 2010 年 7 月 ~10 月の間に都民から採取された血清 66 件のうち抗体調査が可能であった
ISSN 188-266 東京都微生物検査情報 MONTHLY EPIDEMIOLOGICAL RECORD, TOKYO 第 2 巻第 2 号 2011 年 2 月分月報 http://idsc.tokyo-eiken.go.jp/ 東京都におけるインフルエンザウイルス抗体保有状況 東京都における流行予測調査事業により 2010 年 7 月 ~10 月の間に都民から採取された血清 66 件のうち抗体調査が可能であった
ñ{ï 01-65
 191252005.2 19 *1 *2 *3 19562000 45 10 10 Abstract A review of annual change in leading rice varieties for the 45 years between 1956 and 2000 in Japan yielded 10 leading varieties of non-glutinous lowland
191252005.2 19 *1 *2 *3 19562000 45 10 10 Abstract A review of annual change in leading rice varieties for the 45 years between 1956 and 2000 in Japan yielded 10 leading varieties of non-glutinous lowland
CHEMOTHERAPY APR. 1984
 VOL.32 S-3 CHEMOTHERAPY dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-1, 8-naphthyridine- CHEMOTHERAPY APR. 1984 VOL.32 S-3 CHEMOTHERAPY Table 1 Implantation rates and post- implantation survival rates in females mated
VOL.32 S-3 CHEMOTHERAPY dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-1, 8-naphthyridine- CHEMOTHERAPY APR. 1984 VOL.32 S-3 CHEMOTHERAPY Table 1 Implantation rates and post- implantation survival rates in females mated
小児感染免疫第30巻第1号
 26 2018 314 1 2 2 2 polymerase chain reaction PCR reverse transcription RT -PCR enzyme immunoassay EIA2009 2015 6 315 144 144 6.1 1 28.9% 1 2 1,2 3 4 1999 22 23 1 2 5 2008 2009 1 2015 12 31 6 315 polymerase
26 2018 314 1 2 2 2 polymerase chain reaction PCR reverse transcription RT -PCR enzyme immunoassay EIA2009 2015 6 315 144 144 6.1 1 28.9% 1 2 1,2 3 4 1999 22 23 1 2 5 2008 2009 1 2015 12 31 6 315 polymerase
 VOL. 17 NO. 7 CHEMOTHERAPY 1305 1) W. BRumFirr et al. : Clinical and laboratory studies with carbenicillin. Lancet 1: 1289~ 1293, 1967 2) E. T. KNUDSEN et al. : A new semisynthetic penicillin active against
VOL. 17 NO. 7 CHEMOTHERAPY 1305 1) W. BRumFirr et al. : Clinical and laboratory studies with carbenicillin. Lancet 1: 1289~ 1293, 1967 2) E. T. KNUDSEN et al. : A new semisynthetic penicillin active against
 ;~ (Summary) The Study on the Effects of Foot Bathing on Urination Kumiko Toyoda School of Human Nursing, University of Shiga Prefecture Background Foot bathing is one of the important nursing care for
;~ (Summary) The Study on the Effects of Foot Bathing on Urination Kumiko Toyoda School of Human Nursing, University of Shiga Prefecture Background Foot bathing is one of the important nursing care for
スライド 1
 1 2006 msv 2 2011 3 CT 2011 10mSv 10 40mSv 4 2012 217mSv 5 (CT) 2012 50 60mSv 6 2012 510mSv BRCA25 310 10mSv3% BRCA60-280% 3 5m Sv 1m Sv 12% . http://www.rea.or.jp/ire/pdf/report4.pdf 1.10 20 SMR 1.00
1 2006 msv 2 2011 3 CT 2011 10mSv 10 40mSv 4 2012 217mSv 5 (CT) 2012 50 60mSv 6 2012 510mSv BRCA25 310 10mSv3% BRCA60-280% 3 5m Sv 1m Sv 12% . http://www.rea.or.jp/ire/pdf/report4.pdf 1.10 20 SMR 1.00
日本化学療法学会雑誌第65巻第4号
 Mycoplasma pneumoniae M. pneumoniae M. pneumoniae M. pneumoniae M. pneumoniae M. pneumoniae Key words Mycoplasma pneumoniae Mycoplasma pneumoniae M. pneumoniae I M. pneumoniae M. pneumoniae M. pneumoniae
Mycoplasma pneumoniae M. pneumoniae M. pneumoniae M. pneumoniae M. pneumoniae M. pneumoniae Key words Mycoplasma pneumoniae Mycoplasma pneumoniae M. pneumoniae I M. pneumoniae M. pneumoniae M. pneumoniae
 ジカ熱の広がり2005 2014 Zika virus: following the path of dengue and chikungunya? globally, similar to dengue (DENV) time and caused an epidemic on Yap Island in the Federated States of and chikungunya (CHIKV)
ジカ熱の広がり2005 2014 Zika virus: following the path of dengue and chikungunya? globally, similar to dengue (DENV) time and caused an epidemic on Yap Island in the Federated States of and chikungunya (CHIKV)
A Nutritional Study of Anemia in Pregnancy Hematologic Characteristics in Pregnancy (Part 1) Keizo Shiraki, Fumiko Hisaoka Department of Nutrition, Sc
 A Nutritional Study of Anemia in Pregnancy Hematologic Characteristics in Pregnancy (Part 1) Keizo Shiraki, Fumiko Hisaoka Department of Nutrition, School of Medicine, Tokushima University, Tokushima Fetal
A Nutritional Study of Anemia in Pregnancy Hematologic Characteristics in Pregnancy (Part 1) Keizo Shiraki, Fumiko Hisaoka Department of Nutrition, School of Medicine, Tokushima University, Tokushima Fetal
1272 CHEMOTHERAPY MAR. 1975
 1272 CHEMOTHERAPY MAR. 1975 VOL. 23 NO. 3 CHEMOTHERAPY 1273 Fig. 2 Minimal inhibitory concentration of aminoglycosides against 50 strains of Klebsiella Fig. 1 Minimal inhibitory concentration of aminoglycosides
1272 CHEMOTHERAPY MAR. 1975 VOL. 23 NO. 3 CHEMOTHERAPY 1273 Fig. 2 Minimal inhibitory concentration of aminoglycosides against 50 strains of Klebsiella Fig. 1 Minimal inhibitory concentration of aminoglycosides
366 12 THE JAPANESE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS 65 6 Dec. 2012 1 8 DNA 2,3 16 12 20 171 2008 12 2010 11 2 3,558 4.44% 1.65% 1.17% 90% 9 Escherichia coli -
 Dec. 2012 THE JAPANESE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS 65 6 365 11 sita oxacin 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 3 3 1 1 1 2 3 2012 9 14 sita oxacin STFX 50 mg 10% 2008 1 2008 12 2010 11 2 STFX 1,452 91.4% 1,235/1,351 95.9% 466/486
Dec. 2012 THE JAPANESE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS 65 6 365 11 sita oxacin 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 3 3 1 1 1 2 3 2012 9 14 sita oxacin STFX 50 mg 10% 2008 1 2008 12 2010 11 2 STFX 1,452 91.4% 1,235/1,351 95.9% 466/486
Table1MIC of BAY o 9867 against standard strains
 Table1MIC of BAY o 9867 against standard strains Fig.2Cumulative and Distribution Curves of MIC (S.aureus 54 strains) 106cfu/ml Fig.3Correlogram of MIC (S.aureus 54 strains) CHEMOTHERAPY 451 Fig.4Cumulative
Table1MIC of BAY o 9867 against standard strains Fig.2Cumulative and Distribution Curves of MIC (S.aureus 54 strains) 106cfu/ml Fig.3Correlogram of MIC (S.aureus 54 strains) CHEMOTHERAPY 451 Fig.4Cumulative
Key words : influenza, nested-pcr, serotype
 Key words : influenza, nested-pcr, serotype Table 1 Sequence of PCR primers used to detect HA gene of influenza virus 524 清水 Fig. 1 Detection of PCR product 英明 他 (lstpcr) Table 2 Results method Fig. 2
Key words : influenza, nested-pcr, serotype Table 1 Sequence of PCR primers used to detect HA gene of influenza virus 524 清水 Fig. 1 Detection of PCR product 英明 他 (lstpcr) Table 2 Results method Fig. 2
日本職業・災害医学会会誌第51巻第5号
 太田ら 同時多発性高血圧性脳葉出血の 1 手術例 図 1 搬入時 CT 上段 単純 CT 下段 造影 CT 図 2 術後の脳血管撮影検査では明らかな出血源は認めない 379 Reprint request: MULTIPLE SIMULTANEOUS HYPERTENSIVE LOBAR HEMORRHAGE Hirotsugu OHTA M.D. 1) and Akira YOKOTA M.D.
太田ら 同時多発性高血圧性脳葉出血の 1 手術例 図 1 搬入時 CT 上段 単純 CT 下段 造影 CT 図 2 術後の脳血管撮影検査では明らかな出血源は認めない 379 Reprint request: MULTIPLE SIMULTANEOUS HYPERTENSIVE LOBAR HEMORRHAGE Hirotsugu OHTA M.D. 1) and Akira YOKOTA M.D.
日本化学療法学会雑誌第59巻第6号
 P P Streptococcus pneumoniae S. pneumoniae Key words Streptococcus pneumoniae Fig. 1. Capsular swelling reaction of S. pneumoniae type 6B. Cells are stained dark blue using a methylene blue. Capsule is
P P Streptococcus pneumoniae S. pneumoniae Key words Streptococcus pneumoniae Fig. 1. Capsular swelling reaction of S. pneumoniae type 6B. Cells are stained dark blue using a methylene blue. Capsule is
Title 泌尿器科領域に於ける17-Ketosteroidの研究 17-Ketosteroidの臨床的研究 第 III 篇 : 尿 Author(s) 卜部, 敏入 Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1958), 4(1): 3-31 Issue Date URL
 Title 泌尿器科領域に於ける17-Ketosteroidの研究 17-Ketosteroidの臨床的研究 第 III 篇 : 尿 Author(s) 卜部, 敏入 Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1958), 4(1): 3-31 Issue Date 1958-01 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/111559 Right Type Departmental Bulletin
Title 泌尿器科領域に於ける17-Ketosteroidの研究 17-Ketosteroidの臨床的研究 第 III 篇 : 尿 Author(s) 卜部, 敏入 Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1958), 4(1): 3-31 Issue Date 1958-01 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/111559 Right Type Departmental Bulletin
 E Societe de Pathologie Infectieuse de Langue Francaise (, 1991) E Spanish Thoracic Society (1992) E American Thoracic Society (ATS : 1993. ü ù2001 ) E British Thoracic Society (1993, ü è2001 ) E Canadian
E Societe de Pathologie Infectieuse de Langue Francaise (, 1991) E Spanish Thoracic Society (1992) E American Thoracic Society (ATS : 1993. ü ù2001 ) E British Thoracic Society (1993, ü è2001 ) E Canadian
VOL.35 S-2 CHEMOTHERAPY Table 1 Sex and age distribution Table 2 Applications of treatment with carumonam Table 3 Concentration of carumonam in human
 CHEMOTHERAPY Fig. 1 Chemical structure of carumonam Disodium(+)-(Z)-CCE1-(2-amino-4-thiazoly1)-2-[[(2S, -(carbamoyloxymethyl)-4-oxo-1-sulfonato-3-azetidinyll -2-oxoethylidene] amino] oxy] acetate 3S)-2
CHEMOTHERAPY Fig. 1 Chemical structure of carumonam Disodium(+)-(Z)-CCE1-(2-amino-4-thiazoly1)-2-[[(2S, -(carbamoyloxymethyl)-4-oxo-1-sulfonato-3-azetidinyll -2-oxoethylidene] amino] oxy] acetate 3S)-2
CHEMOTHERAPY Table 1 Clinical effect of Sultamicillin
 CHEMOTHERAPY CHEMOTHERAPY Table 1 Clinical effect of Sultamicillin CHEMOTHERAPY Fig. 1 MICs of sultamicillin against respiratory pathogenic Branhamella catarrhalis 62 strains, inoculum size 106CFU/m1 Fig.
CHEMOTHERAPY CHEMOTHERAPY Table 1 Clinical effect of Sultamicillin CHEMOTHERAPY Fig. 1 MICs of sultamicillin against respiratory pathogenic Branhamella catarrhalis 62 strains, inoculum size 106CFU/m1 Fig.
28 1 1a 1b 2 MRI T2 3 CT C3 N95 N95 6ml 90
 2015 28 1 89 93 CT C3 Tb PCR XP WBC 7 600/mm 3 CRP 4 08mg/dl MRI MRI CT MRI WBC 9 700/mm 3 CRP 6 09mg/dl CT C3 C2 C7 low density area CT 89 28 1 1a 1b 2 MRI T2 3 CT C3 N95 N95 6ml 90 28 1 4 CT C2 C7 low
2015 28 1 89 93 CT C3 Tb PCR XP WBC 7 600/mm 3 CRP 4 08mg/dl MRI MRI CT MRI WBC 9 700/mm 3 CRP 6 09mg/dl CT C3 C2 C7 low density area CT 89 28 1 1a 1b 2 MRI T2 3 CT C3 N95 N95 6ml 90 28 1 4 CT C2 C7 low
日本消化器外科学会雑誌第29巻第9号
 Table 1 Oligonucleotide primers used for RT-PCR and internal probes used for Southern blot hybridization Cytokine Primer Sequence (5'-3') 5' 3' Internal probe s' 3' Internal probe 5' 3' Internal probe
Table 1 Oligonucleotide primers used for RT-PCR and internal probes used for Southern blot hybridization Cytokine Primer Sequence (5'-3') 5' 3' Internal probe s' 3' Internal probe 5' 3' Internal probe
untitled
 2005 10 13 Dr. RGA 19602000 10 Australian Institute of of Health and and Welfare 2004 ABS Cat. Cat. No. No. 3201.0; AIHW National Population Database 1875 2 211997 8 122164 http://www.wowzone.com/calment.htm
2005 10 13 Dr. RGA 19602000 10 Australian Institute of of Health and and Welfare 2004 ABS Cat. Cat. No. No. 3201.0; AIHW National Population Database 1875 2 211997 8 122164 http://www.wowzone.com/calment.htm
VOL.39 S-3
 VOL.39 S-3 CHEMOTHERAPY SEPT.1991 Table 1. Background of characteristics and allocation of 5 healthy male volunteers in a multiple-dose study on panipenem/betamipron Day 1 Fig. 1. Schedule of multiple-dose
VOL.39 S-3 CHEMOTHERAPY SEPT.1991 Table 1. Background of characteristics and allocation of 5 healthy male volunteers in a multiple-dose study on panipenem/betamipron Day 1 Fig. 1. Schedule of multiple-dose
<4244CDDED8C0B0BCBDC3D1466C752E696E6464>
 111-5605-N-09 400AMX00064000 01778 01597 BD TM Flu 1 1 3 4 5 BD TM BD TM 6 1Processing Reagent A FluA B FluB A FluA B FluB 3A B 4B A BD TM CF BD TM CF C B A N 1. A B 1 A B A A A C A B N BD TM BD TM 1 1..
111-5605-N-09 400AMX00064000 01778 01597 BD TM Flu 1 1 3 4 5 BD TM BD TM 6 1Processing Reagent A FluA B FluB A FluA B FluB 3A B 4B A BD TM CF BD TM CF C B A N 1. A B 1 A B A A A C A B N BD TM BD TM 1 1..
 CHEMOTHERAPY APRIL 1992 VOL. 40 S- 1 Table 1-1. Comparative in vitro activity of meropenem against clinical isolates CNS: coagulase-negative staphylococci CHEMOTHERAPY APRIL 1992 Table 1-2. Comparative
CHEMOTHERAPY APRIL 1992 VOL. 40 S- 1 Table 1-1. Comparative in vitro activity of meropenem against clinical isolates CNS: coagulase-negative staphylococci CHEMOTHERAPY APRIL 1992 Table 1-2. Comparative
16_.....E...._.I.v2006
 55 1 18 Bull. Nara Univ. Educ., Vol. 55, No.1 (Cult. & Soc.), 2006 165 2002 * 18 Collaboration Between a School Athletic Club and a Community Sports Club A Case Study of SOLESTRELLA NARA 2002 Rie TAKAMURA
55 1 18 Bull. Nara Univ. Educ., Vol. 55, No.1 (Cult. & Soc.), 2006 165 2002 * 18 Collaboration Between a School Athletic Club and a Community Sports Club A Case Study of SOLESTRELLA NARA 2002 Rie TAKAMURA
IR0036_62-3.indb
 62 3 2016 253 272 1921 25 : 27 8 19 : 28 6 3 1921 25 1921 25 1952 27 1954 291960 35 1921 25 Ⅰ 0 5 1 5 10 14 21 25 34 36 59 61 6 8 9 11 12 16 1921 25 4 8 1 5 254 62 3 2016 1 1938.8 1926 30 1938.6.23 1939.9
62 3 2016 253 272 1921 25 : 27 8 19 : 28 6 3 1921 25 1921 25 1952 27 1954 291960 35 1921 25 Ⅰ 0 5 1 5 10 14 21 25 34 36 59 61 6 8 9 11 12 16 1921 25 4 8 1 5 254 62 3 2016 1 1938.8 1926 30 1938.6.23 1939.9
untitled
 1988 2000 2002 2004 2006 2008 IFN Lamivudine Adefovir Entecavir 1 Total number 560 Sex (male/female) 424/136 Age (years)* 38 (15-68) Duration of treatment (weeks)* 26 (1-592) Follow-up time (years) 75(05-21
1988 2000 2002 2004 2006 2008 IFN Lamivudine Adefovir Entecavir 1 Total number 560 Sex (male/female) 424/136 Age (years)* 38 (15-68) Duration of treatment (weeks)* 26 (1-592) Follow-up time (years) 75(05-21
過去26年間のスギ花粉飛散パターンのクラスター分析
 117 681 : 2A 2B 2C 2A 2B 2C 2A 2A 2B 2C 2A 2B 2C 2A : DNA Phöbus Blackly 1cm 117 682 2014 1 SYSTAT χ Complete linkage method χ 2A 2B 2C /cm /cm /cm 2A 2B 2C 2A 2B 2C 2A 2B 2C 2 A /cm 2A 2C 117 683 2 2A
117 681 : 2A 2B 2C 2A 2B 2C 2A 2A 2B 2C 2A 2B 2C 2A : DNA Phöbus Blackly 1cm 117 682 2014 1 SYSTAT χ Complete linkage method χ 2A 2B 2C /cm /cm /cm 2A 2B 2C 2A 2B 2C 2A 2B 2C 2 A /cm 2A 2C 117 683 2 2A
明海大学歯学雑誌 37‐2/1.秦泉寺
 J Meikai Dent Med 37, 153 158, 8 153 1 7 5ml /1 min Wong-Baker Face Rating Scale FS 5 1 9. g 3 5ml /1 min, FS 1 66 6ml /1 min FS 5 1 9. g 3 6ml /1 min, FS 3 Two Cases of Xerostomia that Showed an Improvement
J Meikai Dent Med 37, 153 158, 8 153 1 7 5ml /1 min Wong-Baker Face Rating Scale FS 5 1 9. g 3 5ml /1 min, FS 1 66 6ml /1 min FS 5 1 9. g 3 6ml /1 min, FS 3 Two Cases of Xerostomia that Showed an Improvement
_??_ Fig. 1. Annual number of subjects who were bitten by possibly rabid animals in the rabies endemic regions and thereafter visited our vaccine clin
 _??_ Fig. 1. Annual number of subjects who were bitten by possibly rabid animals in the rabies endemic regions and thereafter visited our vaccine clinic to receive the rabies post-exposure prophylaxis.
_??_ Fig. 1. Annual number of subjects who were bitten by possibly rabid animals in the rabies endemic regions and thereafter visited our vaccine clinic to receive the rabies post-exposure prophylaxis.
11_渡辺_紀要_2007
 56 1 19 Bull. Nara Univ. Educ., Vol. 56, No.1 (Cult. & Soc.), 2007 115 19 Why is Kidney Dysfunction Caused by Cadmium (Cadmium Nephropathy) not Officially Recognized as a Pollution-related Disease by the
56 1 19 Bull. Nara Univ. Educ., Vol. 56, No.1 (Cult. & Soc.), 2007 115 19 Why is Kidney Dysfunction Caused by Cadmium (Cadmium Nephropathy) not Officially Recognized as a Pollution-related Disease by the
THE JAPANESE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS 48-8 Enterococcus avium 5Š, Corynebacterium xerosis 10Š, Corynebacterium pseudodiphtheriticum 10Š, Corynebacterium
 THE JAPANESE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS 48-8 Enterobacter spp., Serratia spp., Burkholderia cepacia, Flavobacterium spp., Alcaligenes spp. THE JAPANESE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS 48-8 Enterococcus avium 5Š, Corynebacterium
THE JAPANESE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS 48-8 Enterobacter spp., Serratia spp., Burkholderia cepacia, Flavobacterium spp., Alcaligenes spp. THE JAPANESE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS 48-8 Enterococcus avium 5Š, Corynebacterium
 Table 1.Distribution and number of cases with acute upper respiratory tract infections classified according to antimicrobial agents administered Table 2. Distribution of cases which were enrolled to set
Table 1.Distribution and number of cases with acute upper respiratory tract infections classified according to antimicrobial agents administered Table 2. Distribution of cases which were enrolled to set
Clinical Observation and Etiological Aspect on the Thrombocytopenic Purpura after Rubella Toyoji SODA, Masashi KAWANO, Toshihiko KATO*, and Takeshi SH
 Clinical Observation and Etiological Aspect on the Thrombocytopenic Purpura after Rubella Toyoji SODA, Masashi KAWANO, Toshihiko KATO*, and Takeshi SHIGEMATSU**, Rubella is an acute viral infectious disease
Clinical Observation and Etiological Aspect on the Thrombocytopenic Purpura after Rubella Toyoji SODA, Masashi KAWANO, Toshihiko KATO*, and Takeshi SHIGEMATSU**, Rubella is an acute viral infectious disease
在日外国人高齢者福祉給付金制度の創設とその課題
 Establishment and Challenges of the Welfare Benefits System for Elderly Foreign Residents In the Case of Higashihiroshima City Naoe KAWAMOTO Graduate School of Integrated Arts and Sciences, Hiroshima University
Establishment and Challenges of the Welfare Benefits System for Elderly Foreign Residents In the Case of Higashihiroshima City Naoe KAWAMOTO Graduate School of Integrated Arts and Sciences, Hiroshima University
Microsoft Word - 「黄砂とその健康影響について」小冊子180323版
 ...1...1...1...2...4...4...4...6...7...7...7...7...8...8...9...9...10... 11... 11... 11... 11...12...12...13...16...18...20 1 1-1 1-2 1 1 km 24.5 m/s 10 50 m 1 1-3 μm 1-4 1-5 2 8 http://www.jma-net.go.jp/sat/himawari/obsimg/image_dust.html
...1...1...1...2...4...4...4...6...7...7...7...7...8...8...9...9...10... 11... 11... 11... 11...12...12...13...16...18...20 1 1-1 1-2 1 1 km 24.5 m/s 10 50 m 1 1-3 μm 1-4 1-5 2 8 http://www.jma-net.go.jp/sat/himawari/obsimg/image_dust.html
untitled
 Infectious Agents Surveillance Report (IASR) https://www.niid.go.jp/niid/ja/iasr.html / : 3, 5, 6, 7, 1317 CV-A6 8, 9, EV-D68 : 1, 17 EV- A71 11, EV-A71 1, EV-A7113, CV-B : 1, : 16, B : 17, 18 Vol. 38
Infectious Agents Surveillance Report (IASR) https://www.niid.go.jp/niid/ja/iasr.html / : 3, 5, 6, 7, 1317 CV-A6 8, 9, EV-D68 : 1, 17 EV- A71 11, EV-A71 1, EV-A7113, CV-B : 1, : 16, B : 17, 18 Vol. 38
日本化学療法学会雑誌第56巻第1号
 β β β β β Streptococcus pneumoniaehaemophilus influenzaemoraxella catarrhalismycoplasma pneumoniaechlamydia pneumoniae β Key wordsβ mys nilc laci ngis Table. Assessmentschedule Parameters Patientcharacteristics
β β β β β Streptococcus pneumoniaehaemophilus influenzaemoraxella catarrhalismycoplasma pneumoniaechlamydia pneumoniae β Key wordsβ mys nilc laci ngis Table. Assessmentschedule Parameters Patientcharacteristics
 2014Vol.63No.4p.342349 New impediment factor to health: biological contamination U YANAGI School of Architecture, Kogakuin University Abstract More than 40 years have passed since the Act on Maintenance
2014Vol.63No.4p.342349 New impediment factor to health: biological contamination U YANAGI School of Architecture, Kogakuin University Abstract More than 40 years have passed since the Act on Maintenance
48 皮 膚 第29巻 第1号 昭 和62年2月 第1-b図 第1-a図 第1図Micro Trak法 アッ 皮 細 胞 中あ るいは細 pin point sizeの による 胞 外に,アッ 粒子と 直 接 塗 抹 標本から プル グ リ ー ン に光 プル し てelelnentary る 粒子
 Chlamydia trachomatis-syphilis-micro Trak Mariko SEISHIMA, M. D., Satoshi OKUMURA, M. D. and Michihiro OHTANI, M. D. Megumi WATANABE, Ph. D., Ryo MATSUMOTO, Ph. D., Masayoshi TSUTSUMI, Ph. D. and Kazumasa
Chlamydia trachomatis-syphilis-micro Trak Mariko SEISHIMA, M. D., Satoshi OKUMURA, M. D. and Michihiro OHTANI, M. D. Megumi WATANABE, Ph. D., Ryo MATSUMOTO, Ph. D., Masayoshi TSUTSUMI, Ph. D. and Kazumasa
 2014Vol.63No.4p.383393 Thermal environment for health and safety Hirohumi HAYAMA Masaya SAITO Haruka MIKAMI Faculty of Engineering, Hokkaido University School of Design, Sapporo City University Graduate
2014Vol.63No.4p.383393 Thermal environment for health and safety Hirohumi HAYAMA Masaya SAITO Haruka MIKAMI Faculty of Engineering, Hokkaido University School of Design, Sapporo City University Graduate
ABSTRACT The movement to increase the adult literacy rate in Nepal has been growing since democratization in 1990. In recent years, about 300,000 peop
 Case Study Adult Literacy Education as an Entry Point for Community Empowerment The Evolution of Self-Help Group Activities in Rural Nepal Chizu SATO Masamine JIMBA, MD, PhD, MPH Izumi MURAKAMI, MPH Massachusetts
Case Study Adult Literacy Education as an Entry Point for Community Empowerment The Evolution of Self-Help Group Activities in Rural Nepal Chizu SATO Masamine JIMBA, MD, PhD, MPH Izumi MURAKAMI, MPH Massachusetts
40B: 43-54 2010 43 2010 1 27 Satoshi Shimai 1 and Shigehiro Fujimoto 2 1 Center for Liberal Arts and Education, Minami-Kyushu University, Miyakonojo,
 40B: 43-54 2010 2010 1 27 Satoshi Shimai 1 and Shigehiro Fujimoto 2 1 Center for Liberal Arts and Education, Minami-Kyushu University, Miyakonojo, Miyazaki 885-0035, Japan; 2 Miyakonojo Public Health Institute,
40B: 43-54 2010 2010 1 27 Satoshi Shimai 1 and Shigehiro Fujimoto 2 1 Center for Liberal Arts and Education, Minami-Kyushu University, Miyakonojo, Miyazaki 885-0035, Japan; 2 Miyakonojo Public Health Institute,
Key words : 7432-S, Oral cephem, Urinary tract infection Fig. 1. Chemical structure of 7432-S.
 Key words : 7432-S, Oral cephem, Urinary tract infection Fig. 1. Chemical structure of 7432-S. Table 1. Clinical summary of acute uncomplicated cystitis patients treated with 7432-S UTI : Criteria by the
Key words : 7432-S, Oral cephem, Urinary tract infection Fig. 1. Chemical structure of 7432-S. Table 1. Clinical summary of acute uncomplicated cystitis patients treated with 7432-S UTI : Criteria by the
Table 1 Distribution,by type and classroom,of group B hemolytic streptococcal strains isolated from throat of pupils in A elementary school in Nishime
 Key words: Group B hemolytic streptococci, Types, Elementary & Junior high school pupils, 7 prefectures Table 1 Distribution,by type and classroom,of group B hemolytic streptococcal strains isolated from
Key words: Group B hemolytic streptococci, Types, Elementary & Junior high school pupils, 7 prefectures Table 1 Distribution,by type and classroom,of group B hemolytic streptococcal strains isolated from
VOL. 34 S-2 CHEMOTH8RAPY 913
 VOL. 34 S-2 CHEMOTH8RAPY 913 914 CHEMOTHERAPY APR. 1986 Fig. 1 Chemical structure of T-2588 and T-2525 T- 2588 pivaloyloxymethyl (+ )- (6 R, 7 R)-7-[(Z)-2- (2-amino- 4-thiazolyl)-2-methox yiminoacetamido]-3-[(
VOL. 34 S-2 CHEMOTH8RAPY 913 914 CHEMOTHERAPY APR. 1986 Fig. 1 Chemical structure of T-2588 and T-2525 T- 2588 pivaloyloxymethyl (+ )- (6 R, 7 R)-7-[(Z)-2- (2-amino- 4-thiazolyl)-2-methox yiminoacetamido]-3-[(
CHEMOTHERAPY FEB Table 1 Background of volunteers
 CHEMOTHERAPY FEB. 1985 Table 1 Background of volunteers Table 3 Reproducibility of saisomicln In the EIA and the RIA Fig.1 Comparison of the EIA with the RIA or bioassay of sisomicin Table 4 Blood levels
CHEMOTHERAPY FEB. 1985 Table 1 Background of volunteers Table 3 Reproducibility of saisomicln In the EIA and the RIA Fig.1 Comparison of the EIA with the RIA or bioassay of sisomicin Table 4 Blood levels
HHV-6に Table EB-VCA: HA: EB-viral-capsid-antigen hepatitis Fig. 1 A virus EBNA: HSV: herpes Atypical lymphocyte EB virus simplex 1 Laboratory nuclear
 Key words: infectious mononucleosis-like syndrome, human herpes virus-6 HHV-6に Table EB-VCA: HA: EB-viral-capsid-antigen hepatitis Fig. 1 A virus EBNA: HSV: herpes Atypical lymphocyte EB virus simplex
Key words: infectious mononucleosis-like syndrome, human herpes virus-6 HHV-6に Table EB-VCA: HA: EB-viral-capsid-antigen hepatitis Fig. 1 A virus EBNA: HSV: herpes Atypical lymphocyte EB virus simplex
大学論集第42号本文.indb
 42 2010 2011 3 279 295 COSO 281 COSO 1990 1 internal control 1 19962007, Internal Control Integrated Framework COSO COSO 282 42 2 2) the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway committee
42 2010 2011 3 279 295 COSO 281 COSO 1990 1 internal control 1 19962007, Internal Control Integrated Framework COSO COSO 282 42 2 2) the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway committee
