untitled
|
|
|
- しおり みうら
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Infectious Agents Surveillance Report (IASR) : 3, : 5, NESID 6, : 7, : 9, L. pneumophila SG3 ST93 : 0,, ATP 3, 4, 5, Human coronavirus : 6, AH7N9 : 8, A H7N9 : 9, HIV AIDS 9 Vol. 34 No Vol.34 No. 6 No.400 ISSN Tel ,,, :,,, Legionella spp.,,,,, , 7 iasr/34/400/graph/f400aj.gif,, , 7.5, 0 03, , ; MMWR 60: , 0,,, 045, : kenkou/kekkakukansenshou/ html , 3 4, * *
2 56 Vol. 34 No ,, 9, 90, 48, 44, , 9.8, 8.5, 700.5, 3, , 95.3, : 4,08, 3,98 96, 3.8, 69.7, PCR LAMP 6.5, Legionella pneumophila SG, LAMP 0 0, 0 LAMP 5 34, 4,03 9, 4, 5 7, 8,.8, 4., 5.3, : 3,, 7, 6 L. pneumophila SG 6 5, L. feeleii, L. rubrilucens, 3 SG SGSG6, SG, 6, 9, 4 SG L. pneumophila 4 SG, SG3 6, SG6 4, SG5, SG0, SG, SG9, SG5 L. londiniensis, L. longbeachae, 9 : 008, IASR 9: 39330, 008, 008 7, IASR 9: 33033, 008, , IASR 3: 07 09, 00, 0 9 9, 0 3, 5, 0 9, 3, 008 0,, 5 3, 0 3,,, IASR 3: 3333, 00 & 3: 33333, 00,,, 5, IASR 3: 35, 0, IASR 6:, 005 IASR 9: 9394, 008,,, 3, 4,, 4, 00 ml 0 CFU ATP, 3 3 4,, mhlw.go.jp/bunya/kenkou/seikatsueisei09/03. html, 3,,, sequencebased typing 7, 6 :
3 Vol. 34 No , 8,,,, 30,,,,, 8 5,,, 8, 8, 3 Legionella Legionella pneumophila SG,.0 0 CFU/00 ml 0, L. pneumophila SG, L. pneumophila SG PFGE, 8,,, 5, L. pneumophila SG, PFGE, PFGE, 0 5, PFGE, 8 99,,, 7, Table. Methods of diagnosis for legionellosis, 0080 Methods of diagnosis A. A. Isolation and/or identification of Legionella B. B. Fluorescent antibody detection of Legionella antigens (including immunoenzayme method) C. C. Detection of Legionella antigens in urine D. PCRLAMP D. PCR detection of the bacterial genome (including LAMP method) E. E. Detection of serum antibodies by indirect immunofluorescence assay Year Total 6 (7) 3 () (8) (6) 3 () 45 (3) () 3 (3) () () 4 (8) 858 (879) 674 (695) 70 (70) 77 (790) 83 (844) 3,835 (3,98) (9) 6 (0) 9 () 8 () 7 (0) 4 (6) 9 () 4 (7) 7 (8) 9 () 5 (5) 54 (6) F. F. Detection of serum antibodies by microplate agglutination test () () 4 (4) 7 (7) AC Methods A and C ACD Methods A, C, and D 3 ACE Methods A, C, and E AD Methods A and D BC Methods B and C 4 CD Methods C and D CE Methods C and E 6 CDE Methods C, D, and E Total ,08 ( ): ( ): Total number of cases including those diagnosed by more than one method. (National Epidemiological Surveillance of Infectious Diseases: Data based on the reports as of May 5, 03)
4 458 Vol. 34 No (kb) M M. PFGE Sfi I, ,, 6 9, 5080, 6, 3, 004 6, 800,,, 6, 6 4, ph 8.,,,,, 5, 7,,,,,,, L. pneumophila SG, PFGE,,,,,,,,, L. pneumophila SG, PFGE, EWGLI European Working Group for Legionella Infections, org sequence basedtyping: SBT, PFGE 3, 7, 7, 6, 7, 5, 3, 9,, SBT, ST45, PFGE, ST89,, PFGE SBT,,, PFGE,,,,, 4, 53 AmemuraMaekawa J, et al., Appl Environ Microbiol 78: , 0 Vol.34 No.4, p.7 5 9,, GAVI03 4, 04
5 Vol. 34 No ,, 6, 3 5,, ,,,,, 3,,,, 3,,,, 7,,,,,,,,,,,,, 3,. H4..8 CFU/00ml 4,300 5,700 3,500 3,300,, 4,,,, 38, 460,, 8 0 mg/l, 5, Legionella pneumophila, SG, SG6, UT,,,,,,, L. pneumophila SG,,,, 4,, PFGE L. pneumophila SG, SG6, UT SGPFGE Legionella pneumophila
6 660 Vol. 34 No , 6,,,,, L. pneumophila SG, SG,, PFGE,,,,, 8,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,, 0 3,,,,,, ,,,,,,,, 8, ,,, , , 5,, 3 : 37.5, 0 3 4,,, 4 3, ,,,, 4, 3, 3,. n=8
7 Vol. 34 No , 33 3, 75 4, No., No.3 3 3, Legionella pneumophila Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, Burkholderia cepacia, Pseudomonas aeruginosa 33 No., Stenotrophomonas maltophilia 87, 86,,, 4 75, Escherichia coli,,,,, 004,, X,, 5 underreporting,,,,,,,, WHO, 0 3,,,, WHO 3 4,,, 4 4,,,,,,,,,,,, p00,, 0,, Inoue, et al., Tsunami lung, J Anesth 6 : 46 49, 0 4Ebisawa, et al., Internal Medicine 509: 33 36, 0 5Maegele, et al., Critical Care 0: R50, 006 doi:0.86/cc4868, , , 009 8, 00 33, 0 39, ,,,,,, 9 Legionella pneumophila SG 65, SG 4, SG3 8, SG5, SG6 5, SG9, SG0,
8 86 Vol. 34 No L. pneumophila ST0080 ST ( SG) 3 ST3 (S), ST38* (B3) 0 ST0 (S) 8 ST (C), ST93 (SG3) 6 ST384* (S) 5 ST609 (U) 4 ST4 (N), ST89 (S), ST644* (B) 3 ST3* (B), ST3* (S), ST353* (S), ST077 * (U) ST (B), ST39 (SG), ST59 (B), ST68 (SG6, SG), ST (U), ST4 (S3), ST56 (B), ST354* (SG), ST505* (B), ST530* (B), ST537* (SG6), ST550* (S), ST566 * (B), ST679* (S), ST687* (B), ST850* (S), ST876* (S), ST36* (SG9, UT) S, S3:B, B, B3:C: U:N: *03 5 SG, SG5,, Legionella feeleii, Legionella londiniensis, Legionella longbeachae, Legionella rubrilucens L. pneumophila, EWGLI European Working Group of Legionella Infections SBT sequencebased typing, flaa, pile, asd, mip, momps, proa, neua, php/sbt_homepage.php L. pneumophila 9 00 ST, , SBT, ST, ST3 ST38 3, ST0 0, ST ST93 8 ST3, ST ST38 3, ST ST0, 9 ST,, ST, ST93 0 L. pneumophila SG 50, 50, 34 SBT, 8 B, B, B3, C, C, S, S, S3 ST, ST, SG, S 63 ST3, ST0, B 67 ST38, C 0 ST, 5 8 ST, U 0, B 75,,,, S 30, U 7, C 0, ST,,,,, 4 3 ST S,,,,, L. pneumophila SG,,,,,, AmemuraMaekawa J, et al., Appl Environ Microbiol 78: , 0
9 Vol. 34 No , 90 Legionella pneumophila SG, L. pneumophila SG,,,,, 000,, ml, GVPC, L. pneumophila SG,, European Working Group for Legionella Infections EWGLI, sbt_homepage.php sequencebased typing SBT /34, 54, 099 CFU/ 00ml 34, CFU/00ml 8,,000 CFU/00ml 8, , 4/ , 30/74, P0.05, SD log0 CFU/00ml , t, P , 4, 54 40, 90 L. pneumophila SG , 8 L. pneumophila SG, SBT 44 ST, ST48 ST0 8,, ST48 5, 44 ST, ST ST, ST48,, ST0,, EWGLI ST0, ST0 6 ST0, 5.3 7,,, 7, L. pneumophila SG 8, L. pneumophila SG,, ST0 L. pneumophila SG,, Kanatani JI, et al., J Infect Chemother 0 Epub, ahead of print Sakamoto R, et al., Emerg Infect Dis 5:
10 064 Vol. 34 No , 009 3IASR 9: 3738, 008 4IASR 9: 3333, 008 5AmemuraMaekawa J, et al., Appl Environ Microbiol 78: , 0 6Kanatani JI, et al., Appl Environ Microbiol 03 Epub, ahead of print 7Wallensten A, et al., Eur J Epidemiol 5: , 00 8Palmer ME, et al., Eur J Epidemiol 7: 667, 0 Legionella pneumophila 3 sequence type 93, L. pneumophila SG3 sequence type ST93,,., , ,,, L. pneumophila SG3 7, sequencebased typing SBT, ST PFGE, IASR 9: , 008,. : 6 L. pneumophila, SG 6, SG, SG3 8, SG0, SG,,,,,,,, SG3,, SG, SBT SG ST, SG3 8 ST93, PFGE 7 : L. pneumophila SG3 7, SBT 8 7, PFGE 7 7, SBT 7, ST PFGE ST PFGE, ST37, PFGE : b ST38, PFGE : a 3, ST 7 PFGE 5,, PFGE, 7 PFGE, 3., , L.
11 Vol. 34 No L. pneumophila 3 pneumophila SG, 9 L. pneumophila, SG 6, SG3 8, SG SG0 SBT, L. pneumophila SG ST, L. pneumophila SG3 8 ST93 PFGE, L. pneumophila SG3, ST93,,, 0 4, ST93 L. pneumophila SG3 3,,, 8 ST93 ST93,, L. pneumophila SG3, ST93 L. pneumophila SG, ST93 L. pneumophila SG3,,, 3 6, 3, LAMP PCR,,,,,, DNA EMA ethidium monoazide, PCR, DNA EMAqPCR,, EMA,,, 8 PCR Liquid Culture LCRTqPCR LC RT, EMAqPCR EMA LC EMAqPCR LC EMA
12 66 Vol. 34 No RNA60 RTqPCR90 5* 368 EMA30 DNA30 qpcr90 CFU/00ml) LC viable (log y R² = plate count (log CFU/00ml) y = 0.704x R² = CFU/00ml CFU/00ml Plate count Plate count LC RT Viable LC Legionella EMAqPCR ,, , LC RTqPCR 83.3%, 96.6% (a) LC RTqPCR 95.5%, 75.4% (b) LC EMAqPCR,,,,000, MWY 36 8,, 00 total RNA, Diederen qpcr RTqPCR 5S rrna, rrna Acanthamoeba castellanii, Legionella pneumophila S rrna, CFU , 5S rrna CFU rrna Total Legionella, rrna Viable Legionella, Ct, CFU/00 ml Viable Legionella, Ct CFU/00 ml, , LC RT, Total Legionella 90.0, 8.9, 8 Viable Legionella 83.3, 96.6 Viable Legionella R 0.80, a. LC EMAqPCR, EMA, LC RT, EMA 5, 5 DNA EMA DNA, 6S rrna DNA 8 EMA 6S rrna, CFU 00, CFU 4 3 LC EMA, LC EMA 5 CFU/00 ml 95.5, 75.4, b ph 8.8, 0.8 mg/l, 0 CFU/00 ml L. pneumophila SG9LC RT Total Legionella 00 CFU/00 ml, Viable Legionella 0 CFU/00 ml, LC EMA 9 CFU/00 ml, LC RT Total Legionella 00 CFU/00 ml, Viable Legionella 88 CFU/00 ml, LC EMA 47 CFU/00 ml, 40 CFU/00 ml L. pneumophila SG, 9,,, log CFU/00ml) LC EMAqPCR (l 5 )y = 0.957x plate count (log CFU/00ml)
13 Vol. 34 No ,, LC RT, LC EMA,,,, Chang B, et al., Appl Environ Microbiol 75: 47 53, 009 Diederen BM, et al., J Med Microbiol 56: 940, 007 ATP,, ,, HACCP HACCP,,,,, ATP 008 0,,,,,,,, 9, 8 54,,,,, ph, ATP , 5, : , : 43., 5 7,000 CFU/00 ml, Legionella pneumophila, L. dumoffii L. micdadei, L. pneumophila SG SG 39, SG6 3, SG5 6, SG4 0 SG3 8 0 CFU/ml95,000,000 CFU/00 ml 0 CFU/ml40,000,000 CFU/ 00 ml 37, ppm, ph ATP , , 0.3,63. 3 RLU/0. ml,,,,, ph ATP,,,, ph,, 8.4,,,,,, 7,, ATP
14 468 Vol. 34 No , ATP, 7., ATP, ATP 30 RLU,, ATP,, ATP ATP,. ATP, ATP 00 ATP 7. ATP, ATP ATP,, ATP ATP, 0cm,,000 RLU, 3,, 0. mg/l0.4 mg/l,.0 mg/l, 5 7,,,, 7,, /,,,,, 3 6, 3 mg/l, m 3,, ph , mgn/l : 3,,,,, : 3 mg/l,,,, 3 :,,,.94.6g/l
15 Vol. 34 No /00 4 :.94.3 mgn/l,,, DPD, 0. mg/l,,, ph 9.0, 3 mg/l,,,,,, ph,,,, ,,, : 008, 8 Legionella pneumophila,, CFU/l SG, SG3 8, 8 9/3 6 3, 33 3/9L. pneumophila SG ST, Oxford/ OLDASG3 ST93 8/9, 996, IASR 9: 90, ,,,,,.50 3 CFU/l, dental unit waterline CFU/l L. pneumophila SG, ST593, Benidorm,, StokeonTrent spa pool, 3 L. pneumophila SG, ST68,, 00 3
16 670 Vol. 34 No , 3, 3,,.4,.5, 008, 4,00 CFU/00 ml, L. pneumophila SG,,, 0 7 8,, 0, , 3 6 9, 9 L. pneumophila SG 997,,,, ; 53, 48, 3 7 Yiallouros PK, et al., Clin Infect Dis, Epub ahead of print, 03 Ricci ML, et al., Lancet : 684, 0 3Coetzee N, et al., Euro Surveill 7 37: 68, 0 4Haupt TE, et al., Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 33: 859, 0 5Chicago Tribune NEWS, Sep, 0; CNN.com Sep, 0 6CBC News Dec 6, 0; The Montreal Gazette Aug 6, 0; ProMed Sep 9, 0 7McCormick D, et al., Euro Surveill 7 8: 69, 0 Human coronavirus 03 4,, C,, RS,,,, Human coronavirus: HCoV HCoV HCoV, 78 HCoV 4, 5 RTPCR 6, 7 HCoV HCoV HCoV, 8, 3 5, 4 4,, 9E NL63, OC43 HKU SARS 0 Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus MERSCoV 8, 9 HCoV OC43 8, NL63 OC43 RS, MERS CoV HCoV 9 0. HCoV034
17 Vol. 34 No HCoV , , , , , , 6 0.7, 6.9, RS 3.4, /030/3 HCoV 8 0,, 03 4 HCoV ,.8,.8, 5.3 3, 7.5 0, 3.5,.8, , 7.0 4,.8, 8.8 5, 0,, HCoV,, IASR 33: 99, 0. HCoV,, IASR 33: 4445, pref.mie.jp/byougentai/kenshutu.htm 4,, IASR 9: 83, 008 5Kon M, et al., Jpn J Infect Dis 65: 707, 0 6Lau SKP, et al., J Clin Microbiol 44: 06307, 006 7Lam WY, et al., J Clin Microbiol 45: , 007 8Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC html 9,, IASR 33: , 0 0
18 87 Vol. 34 No nesid3g.mhlw.go.jp/byogentai/pdf/data95j.pdf AH7N9, CDC 3 AH7N9, 3 3 IHR WHO ARDS,, : , 4 9 8,, 8, , 0 3, , 7 75, 58 7, 4 PCR rrtpcr 7, , 7 8,689,, ILI, 0 CDC, , AH7N9 : Global Initiative on Sharing All Influenza Data GISAID 9, 5,, H7N3, H7N9, H9N3, WHO CDC,,, PFU BALB/c CDC, H75Y,, H7N9 H7N9, CDC rrtpcr H7 H7, 4 FDAEUA in vitro, : 4 6, 68,060, H7N9, USDA ARS,,, MMWR : H7N9 6, 7,, CDC, MMWR, 6, No. 8, 36637, 03
19 Vol. 34 No AH7N9, AH7N9 5 0 AH7N9, 9 /9 RTPCR,,, 7 60,,, 9 7,, RTPCR AH7N9 RNA 4, 8, 4 30, 4,, 4 60 : 38, n=9 50, 0,,, 9 0 0, ,, 9 AH7N9 RNA 9, 35, 38, AH7N9 RNA 7 75, 3 RNA 339,,, AH7N9 Euro Surveill. 03;8 0:pii=048 :, HIV AIDS HIV 7 57, 46 6,, 46 3,, 5 3. AIDS 07 4, 05 05,, 07, 0, HIV AIDS 334. HIV : 5 HIV HIV 9 35, 9, 030. AIDS : 63 AIDS 59 3 AIDS, 0, HIV,58 6,597, 5,05, 6,769 7,3, 7,7. 3,940 37,3, 39, ,,304,48,35,793. HIV 3 40,.763
20 074 Vol. 34 No , HIV, AIDS. HIV,, 3.,, HIV
21 Vol. 34 No
22 76 Vol. 34 No Verotoxinproducing E.coli ( ) Enterotoxigenic enic E.coli ( ) 9 ( ) 3 5 Enteroinvasive E.coli Enteropathogenic E.coli Enteroaggregative E.coli ( ) 6 ( ) 3 Other diarrheagenic E.coli 5 ( ) 4 0 ( 4) 6 Salmonella Typhi ( ) 3 Salmonella Paratyphi A ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) Salmonella O Salmonella O Salmonella O Salmonella O Salmonella O3,0 ( ) Salmonella O,3,99 Salmonella O Salmonella O3 Salmonella O6 Salmonella O8 Salmonella O35 Salmonella O39 Salmonella group unknown 4 Vibrio cholerae O:El Tor Ogawa awa,ct+ ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) Vibrio cholerae nono&o39 Vibrio parahaemolyticus Vibrio furnissii Aeromonas sobria Plesiomonas shigelloides Campylobacter jejuni ( 4) Campylobacter coli Staphylococcus aureus Clostridium perfringens Clostridium botulinum A Bacillus cereus Listeria monocytogenes Yersinia enterocolitica 3 Shigella dysenteriae 4 Shigella flexneri b ( ) Shigella flexneri a ( ) ( ) Shigella flexneri b Shigella flexneri 3 a ( ) Shigella flexneri 6 ( ) Shigella flexneri other serovars Shigella flexneri untypable Shigella boydii ( ) Shigella boydii 4 Shigella boydii 9 ( ) Shigella sonnei 3 ( 3) 3 ( ) 4 ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) Kudoa septempunctata Streptococcus tococcus group A Streptococcus group B Streptococcus group C Streptococcus tococcus group G Streptococcus tococcus other groups S.dysgalactiae subsp.equisimilis Streptococcus tococcus group unknown Streptococcus pneumoniae Bordetella pertussis Clostridium tetani Legionella pneumophila 4 5 Mycobacterium tuberculosis Mycobacterium bovis MAC Mycoplasma pneumoniae Haemophilus influenzae b Haemophilus influenzae nonb Klebsiella pneumoniae Neisseria meningitidis Enterococcus faecalis 3 Enterococcus faecium Enterococcus gallinarum Enterococcus casseliflavus Pseudomonas aeruginosa Leptospira interogans Cryptococcus neoformans 480 ( 5) 336 ( 3) 37 ( 5) 90 ( 3) 37 ( 4) 6 ( 4) 409 ( 3) 64 ( 7) 595 ( ) 807 ( )
23 Vol. 34 No ( ) 0 6 ( ) ( ) 3 ( ) 85 ( 7) Verotoxinproducing E.coli ( ) 5 73 ( 4) Enterotoxigenic enic E.coli Enteroinvasive E.coli ( ) 63 ( ) Enteropathogenic E.coli ( ) 49 ( 4) Enteroaggregative E.coli ( 6) Other diarrheagenic E.coli ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) 3 ( 8) Salmonella Typhi ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( 9) Salmonella Paratyphi A ( ) 3 6 ( ) Salmonella O4 6 ( ) ( ) 57 ( 3) Salmonella O Salmonella O ( ) 7 ( ) Salmonella O9 3 0 ( ) Salmonella O3,0 Salmonella O,3,99 Salmonella O 4 Salmonella O3 Salmonella O6 6 Salmonella O8 Salmonella O35 Salmonella O39 3 Salmonella group unknown 4 ( 4) Vibrio cholerae O:El Tor Ogawa awa,ct+ Vibrio cholerae nono&o39 3 Vibrio parahaemolyticus Vibrio furnissii Aeromonas sobria Plesiomonas shigelloides ( 4) Campylobacter jejuni 5 65 Campylobacter coli Staphylococcus aureus Clostridium perfringens Clostridium botulinum A 7 0 Bacillus cereus Listeria monocytogenes 4 57 Yersinia enterocolitica ( ) ( ) Shigella dysenteriae 4 ( ) 3 ( ) Shigella flexneri b 3 8 ( 3) Shigella flexneri a ( ) 5 ( ) Shigella flexneri b 3 ( ) Shigella flexneri 3a ( ) Shigella flexneri 6 ( ) 3 ( ) Shigella flexneri other serovars ( ) ( ) Shigella flexneri untypable ( ) Shigella boydii Shigella boydii 4 ( ) Shigella boydii 9 3 ( 8) ( ) 3 ( ) ( ) ( ) 3 ( ) 64 ( 8) Shigella sonnei Kudoa septempunctata Streptococcus tococcus group A 7 44 Streptococcus group B Streptococcus group C 8 Streptococcus tococcus group G 4 Streptococcus tococcus other groups 4 S.dysgalactiae subsp.equisimilis Streptococcus tococcus group unknown Streptococcus pneumoniae Bordetella pertussis Clostridium tetani Legionella pneumophila Mycobacterium tuberculosis Mycobacterium bovis MAC Mycoplasma pneumoniae Haemophilus influenzae b Haemophilus influenzae nonb 0 Klebsiella pneumoniae 4 Neisseria meningitidis 7 Enterococcus faecalis 7 Enterococcus faecium Enterococcus gallinarum Enterococcus casseliflavus Pseudomonas aeruginosa Leptospira interogans Cryptococcus neoformans 6 ( ) 50 ( 4) 344 ( 4) 339 ( 5) 8 ( 5) 6 ( 5) 74 ( 0) 36 ( 3) 7050 ( 05)
24 478 Vol. 34 No Verotoxinproducing E.coli ( ) 3 Enterotoxigenic E.coli 5 Enteroinvasive E.coli Enteropathogenic E.coli ( ) Enteroaggregative E.coli ( ) Other diarrheagenic E.coli Salmonella Typhi Salmonella O4 Salmonella O8 Salmonella O9 Salmonella group unknown Campylobacter jejuni Staphylococcus aureus 6 Clostridium perfringens 4 Yersinia enterocolitica 0 Shigella flexneri Shigella sonnei Streptococcus group A 7 5 Streptococcus group B Streptococcus group G Streptococcus pneumoniae 9 Bordetella pertussis Legionella pneumophila Mycobacterium tuberculosis Mycoplasma pneumoniae Haemophilus influenzae nonb Pseudomonas aeruginosa ( 3) Salmonella O4 Typhimurium O4 Bredeney O4 Saintpaul O8 Kottbus O9 Javiana Shigella Shigella flexneri a Shigella flexneri others Shigella sonnei T T4 T T5 T8 TB364 3 Untypable
25 Vol. 34 No ( ) Verotoxinproducing E.coli 5 Enterotoxigenic E.coli Enteroinvasive E.coli 3 ( ) Enteropathogenic E.coli ( ) Enteroaggregative E.coli 3 Other diarrheagenic E.coli Salmonella Typhi 3 Salmonella O4 Salmonella O8 Salmonella O9 Salmonella group unknown 4 40 Campylobacter jejuni Staphylococcus aureus 4 Clostridium perfringens Yersinia enterocolitica Shigella flexneri Shigella sonnei 3 8 Streptococcus group A Streptococcus group B Streptococcus group G 9 Streptococcus pneumoniae Bordetella pertussis Legionella pneumophila Mycobacterium tuberculosis 4 4 Mycoplasma pneumoniae Haemophilus influenzae nonb 63 Pseudomonas aeruginosa ( 3) Salmonella O4 Typhimurium O4 Bredeney O4 Saintpaul O8 Kottbus O9 Javiana Shigella Shigella flexneri a Shigella flexneri others Shigella sonnei T 4 T4 4 T T5 T8 4 TB364 Untypable
26 680 Vol. 34 No Verotoxinproducing E.coli 3 3 Enteroaggregative E.coli Other diarrheagenic E. coli Salmonella Paratyphi A Salmonella O4 Salmonella O7 Campylobacter jejuni Staphylococcus aureus Shigella flexneri 6 Shigella sonnei Streptococcus pyogenes 3 Streptococcus group G Bordetella pertussis Mycoplasma pneumoniae Salmonella Paratyphi A Shigella flexneri 6 Shigella sonnei Coxsackievirus A4 Influenza virus A Hpdm Influenza virus A H3 5 7 Influenza virus B/Yamagata 3 Measles virus ge B3 Dengue virus NT Dengue virus Dengue virus 3 Dengue virus 4 Chikungunya virus Hepatitis A virus NT Dengue virus NT Dengue virus 3 / NT :
27 Vol. 34 No Picornavirus NT Enterovirus NT Coxsackievirus A NT Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A7 Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A4 0 Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus B 7 3 Coxsackievirus B Coxsackievirus B Coxsackievirus B Coxsackievirus B Coxsackievirus B6 Echovirus Echovirus 3 3 Echovirus Echovirus Echovirus Echovirus 4 6 Echovirus 4 Echovirus 7 Echovirus Echovirus Echovirus 0 Echovirus Echovirus 5 7 Echovirus 30 Poliovirus 5 3 Poliovirus Poliovirus Enterovirus rus 68 Enterovirus Parechovirus NT Parechovirus Rhinovirus Aichivirus 3 Influenza virus A not subtyped Influenza virus A Hpdm Influenza virus A H Influenza virus B NT Influenza virus B/Victoria Influenza virus B/Yamagata Influenza virus C Parainfluenza virus Respiratory syncytial virus Human metapneumovirus Other coronavirus Mumps virus Measles virus ge NT 6 Measles virus ge A Measles virus ge B3 Measles virus ge D4 4 6 Measles virus ge D Measles virus ge D9 5 4 Measles virus ge H 4 9 Rubella virus ge NT Rubella virus ge a Rubella virus ge E Rubella virus ge B Dengue virus Chikungunya virus 7 Rotavirus group unknown Rotavirus group A Rotavirus group C 7 Astrovirus Norovirus genogroup unknown Norovirus genogroup I Norovirus genogroup II Sapovirus genogroup unknown Sapovirus genogroup I Sapovirus genogroup II Sapovirus genogroup III 3 Sapovirus genogroup IV 3 8 Sapovirus genogroup V Adenovirus NT Adenovirus Adenovirus Adenovirus Adenovirus Adenovirus Adenovirus Adenovirus 7 Adenovirus Adenovirus 4 Adenovirus 9 Adenovirus Adenovirus 33 Adenovirus 34 Adenovirus Adenovirus 40/ Adenovirus Adenovirus 53/ 3 8 Adenovirus Adenovirus Herpes simplex virus NT Herpes simplex virus Herpes simplex virus Varicellazoster virus Cytomegalovirus Human herpes virus Human herpes virus EpsteinBarr virus Hepatitis A virus NT Hepatitis A virus IA Hepatitis A virus IB Hepatitis A virus IIIA 3 4 Hepatitis E virus 3 Human papilloma virus B9 virus Human bocavirus Human immunodeficiency virus Virus NT Chlamydophila pneumoniae Orientia tsutsugamushi Rickettsia japonica NT :
28 Picorna N Picorna NT Entero N Entero NT 88 Coxsackie A Coxsackie A 4 Coxsackie A Coxsackie A4 Coxsackie A Coxsackie A5 Coxsackie A Coxsackie A Coxsackie A Coxsackie A8 Coxsackie A Coxsackie A9 Coxsackie A Coxsackie A Coxsackie A Coxsackie A4 Coxsackie A Coxsackie A6 Coxsackie B Coxsackie B Coxsackie B Coxsackie B 5 5 Coxsackie B Coxsackie B3 Coxsackie B Coxsackie B4 Coxsackie B Coxsackie B5 3 cho E cho E 7 cho E cho E cho E 8 cho E 5 cho E Entero 7 Entero Parecho N Parecho NT Parecho Parecho Rhino A chi i Influenza A not subt Influenza A not subtyp yped Influenza A H Influenza A Hpdm0 dm Influenza A H Influenza A H Influenza B N Influenza B NT Influenza B/Victori Influenza B/Victoria Influenza B/Yama Influenza B/Yamagat ata Parainfluenza Parainfluenza Res Respirator iratory sync ncytial tial Human meta Human metapneum neumo Other coron Other corona Mum Mump s 4 Measles Measles genot ype N e NT 3 Measles Measles genot ype A Measles Measles genot ype B e B3 Measles Measles genot ype D e D8 Measles Measles genot ype D e D9 Measles Measles genot ype H e H Rubella Rubella genot ype N e NT Rubella Rubella genot ype e a Rubella Rubella genot ype e E 5 5 Rubella Rubella genot ype e B Den Deng e u Chikungunya Chikungunya Rota Rota grou roup unknow unknown Rota Rota grou roup A A tro s 5 Noro Noro geno enogrou roup unknow unknown Noro Noro geno enogrou roup I Noro Noro geno enogrou roup II Sa Sapo geno enogrou roup unknow unknown Sa Sapo geno enogrou roup I Sa Sapo geno enogrou roup II Sa Sapo geno enogrou roup II III Sapo genogroup IV Sapo genogroup IV Adeno N deno NT 34 5 A eno d 3 A deno A eno d A 4 4 eno d A eno d A 6 eno d A 8 eno d A eno d A 3 eno d A 37 eno d Adeno 40/4 deno 40/4 A 4 eno d A 54 eno d A 56 eno d Her Herpes sim es simplex N lex NT 7 Her Herpes sim es simplex lex 4 Her Herpes sim es simplex lex Varicellazoster aricellazoster Cytome tomegal alo Human her Human herpes es Human her Human herpes es EpsteinBarr steinbarr He Hepatitis A N atitis A NT He Hepatitis A I atitis A IA He Hepatitis E atitis E Human Human papilloma illoma 30 9 B Human boc Human boca 7 3 Orientia tsutsu Orientia tsutsugamush amushi Rickettsia japonica Rickettsia japonica NT : Vol. 34 No
29 Picorna NT Picorna NT Entero NT Entero NT 7 Coxsackie A Coxsackie A 4 Coxsackie A4 Coxsackie A4 5 Coxsackie A5 Coxsackie A Coxsackie A6 Coxsackie A6 3 6 Coxsackie A8 Coxsackie A8 7 Coxsackie A9 Coxsackie A9 Coxsackie A Coxsackie A Coxsackie A4 Coxsackie A4 0 0 Coxsackie A6 Coxsackie A6 Coxsackie B Coxsackie B 6 Coxsackie B Coxsackie B 5 Coxsackie B3 Coxsackie B3 3 3 Coxsackie B4 Coxsackie B Coxsackie B5 Coxsackie B5 Echo 3 Echo Echo 6 Echo 6 6 Echo 7 Echo 7 3 Echo 9 Echo 9 Echo Echo Echo 8 Echo 8 Echo 5 Echo Entero 7 Entero 7 Parecho NT Parecho NT 5 Parecho Parecho Rhino Rhino Aichi ichi 7 Influenza A not subt Influenza A not subtyp yped ed Influenza A H Influenza A Hpdm09 dm Influenza A H3 Influenza A H Influenza B NT Influenza B NT Influenza B/Victoria Influenza B/Victoria Influenza B/Yama Influenza B/Yamagata ata Parainfluenza Parainfluenza Res Respirator iratory sync ncytial tial Human meta Human metapneumo neumo Other corona Other corona 0 46 Mum Mumps 3 Measles Measles genot ype NT e NT Measles Measles genot ype A e A Measles Measles genot ype B3 e B3 Measles Measles genot ype D8 e D8 4 Measles Measles genot ype D9 e D9 Measles Measles genot ype H e H Rubella Rubella genot ype NT e NT Rubella Rubella genot ype a e a 0 0 Rubella Rubella genot ype E e E Rubella Rubella genot ype B e B 4 6 Den Dengue ue Chikungunya Chikungunya Rota Rota grou roup unknown unknown Rota Rota grou roup A Astro stro Noro Noro geno enogrou roup unknown unknown Noro Noro geno enogrou roup I Noro Noro geno enogrou roup II II Sa Sapo geno enogrou roup unknown unknown Sa Sapo geno enogrou roup I Sa Sapo geno enogrou roup II II Sa Sapo geno enogrou roup III III 3 6 Sapo genogroup IV Sapo genogroup IV Adeno NT deno NT Adeno deno Adeno deno Adeno 3 deno Adeno 4 deno Adeno 5 deno 5 9 Adeno 6 deno 6 5 Adeno 8 deno 8 Adeno deno 6 Adeno 3 deno Adeno 37 deno Adeno 40/4 deno 40/ Adeno 4 deno Adeno 54 deno 54 3 Adeno 56 deno 56 9 Her Herpes sim es simplex NT lex NT Her Herpes sim es simplex lex Her Herpes sim es simplex lex 5 5 Varicellazoster aricellazoster 3 66 Cytome tomegalo alo Human her Human herpes 6 es Human her Human herpes 7 es 7 47 EpsteinBarr steinbarr 4 He Hepatitis A NT atitis A NT 5 He Hepatitis A IA atitis A IA He Hepatitis E atitis E Human Human papilloma illoma 4 B9 B Human boca Human boca 4 Orientia tsutsu Orientia tsutsugamush amushi 3 5 Rickettsia japonica Rickettsia japonica NT : Vol. 34 No
30 Picornavirus NT Picornavirus NT Enterovirus NT Enterovirus NT Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A 6 7 Coxsackievirus A4 Coxsackievirus A4 3 4 Coxsackievirus A5 Coxsackievirus A5 4 5 Coxsackievirus A6 Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A8 Coxsackievirus A8 4 6 Coxsackievirus A9 Coxsackievirus A9 3 7 Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus A4 Coxsackievirus A4 Coxsackievirus A6 Coxsackievirus A Coxsackievirus B Coxsackievirus B Coxsackievirus B Coxsackievirus B 5 6 Coxsackievirus B3 Coxsackievirus B3 3 5 Coxsackievirus B4 Coxsackievirus B4 6 Coxsackievirus B5 Coxsackievirus B5 5 5 Echovirus 3 Echovirus 3 Echovirus 6 Echovirus Echovirus 7 Echovirus 7 6 Echovirus 9 Echovirus 9 3 Echovirus Echovirus Echovirus 8 Echovirus Echovirus 5 Echovirus 5 Enterovirus 7 Enterovirus Parechovirus NT Parechovirus NT Parechovirus Parechovirus 3 5 Rhinovirus Rhinovirus Aichivirus Aichivirus Influenza virus A not subtyped Influenza virus A not subtyped Influenza virus A Hpdm09 Influenza virus A Hpdm Influenza virus A H3 Influenza virus A H Influenza virus B NT Influenza virus B NT Influenza virus B/Victoria Influenza virus B/Victoria Influenza virus B/Yamagata Influenza virus B/Yamagata Parainfluenza virus Parainfluenza virus Respiratory syncytial virus Respiratory syncytial virus Human metapneumovirus Human metapneumovirus Other coronavirus Other coronavirus Mumps virus Mumps virus Measles virus ge NT Measles virus ge NT 3 Measles virus ge A Measles virus ge A 8 Measles virus ge B3 Measles virus ge B3 Measles virus ge D8 Measles virus ge D8 Measles virus ge D9 Measles virus ge D9 4 4 Measles virus ge H Measles virus ge H Rubella virus ge NT Rubella virus ge NT Rubella virus ge a Rubella virus ge a Rubella virus ge E Rubella virus ge E Rubella virus ge B Rubella virus ge B Dengue virus Dengue virus Chikungunya virus Chikungunya virus Rotavirus group unknown Rotavirus group unknown Rotavirus group A Rotavirus group A Astrovirus Astrovirus Norovirus genogroup unknown Norovirus genogroup unknown Norovirus genogroup I Norovirus genogroup I Norovirus genogroup II Norovirus genogroup II Sapovirus genogroup unknown Sapovirus genogroup unknown Sapovirus genogroup I Sapovirus genogroup I Sapovirus genogroup II Sapovirus genogroup II Sapovirus genogroup III Sapovirus genogroup III Sapovirus genogroup IV Sapovirus genogroup IV 6 6 Adenovirus NT Adenovirus NT Adenovirus Adenovirus Adenovirus Adenovirus Adenovirus 3 Adenovirus Adenovirus 4 Adenovirus Adenovirus 5 Adenovirus Adenovirus 6 Adenovirus Adenovirus 8 Adenovirus Adenovirus Adenovirus Adenovirus 3 Adenovirus Adenovirus 37 Adenovirus Adenovirus 40/4 Adenovirus 40/ Adenovirus 4 Adenovirus Adenovirus 54 Adenovirus Adenovirus 56 Adenovirus Herpes simplex virus NT Herpes simplex virus NT Herpes simplex virus Herpes simplex virus Herpes simplex virus Herpes simplex virus 0 Varicellazoster virus Varicellazoster virus Cytomegalovirus Cytomegalovirus Human herpes virus 6 Human herpes virus Human herpes virus 7 Human herpes virus EpsteinBarr virus EpsteinBarr virus Hepatitis A virus N Hepatitis A virus NT 4 4 Hepatitis A virus I Hepatitis A virus IA 5 5 Hepatitis E viru Hepatitis E virus Human papilloma virus Human papilloma virus B9 virus B9 virus 4 Human bocavirus Human bocavirus Orientia tsutsugamushi Orientia tsutsugamushi 4 4 Rickettsia japonica Rickettsia japonica NT : Vol. 34 No
31 Vol. 34 No IASR An outbreak of legionellosis attributable to a onedaytrip hot spring Saitama Prefecture An outbreak of legionellosis attributable to a bathing facility in a hotelyamagata Prefecture Legionellosis cases associated with the Great East Japan Earthquake, which were reported to NESID Typing of clinical isolates of Legionellareport from Legionella Reference Center... 6 Detection of Legionella species from puddlestoyama Prefecture Epidemiological studies on clinical isolates of L. pneumophila serogroup 3, sequence type 93Okayama Prefecture Rapid detection of viable Legionella bacilli Assessing Legionella contamination by measuring ATP levels for monitoring hygienic conditions of bathing facilities Disinfection of bathing water by monochloramineshizuoka Prefecture Legionellosisvarious sources identified in the recent infections Human coronavirus isolates from infants with respiratory symptoms (JanuaryApril, 03)Mie Prefecture HIV/AIDS in Japan, JanuaryMarch, Legionellosis is an infectious disease caused by Gramnegative bacteria belonging to the genus Legionella. It is a respiratory tract infection and the bacteria multiply within alveolar macrophages. There are two clinical types, severe form of pneumonia called Legionnaires disease and flulike Pontiac fever. As the symptoms of Legionella pneumonia are not unique, differentiation from other pneumonias by symptoms alone is difficult. The first choices for chemotherapy are quinolones and macrolides. Sudden worsening of the general condition may occur among patients, who were not treated with appropriate antibiotics. Pontiac fever is a less severe form of infection and the symptom is like common cold. Elderlies, newborns and immunocompromised persons constitute highrisk groups of legionellosis. Legionella bacilli live within protozoa (amoeba) that inhabit water, moist soil, etc. Optimum growth temperature is 36 C with permissive range of 045 C. Incidence of legionellosis: Legionellosis is a category IV notifiable infectious disease in the National Epidemiological Surveillance of Infectious Diseases (NESID) under the Infectious Diseases Control Law ( de400.pdf). Physicians who have made diagnosis of legionellosis are obliged to notify all the cases. From January 008 to December 0, 4,08 legionellosis patients (including 3 asymptomatic carriers) were reported (as of May 5, 03) (Table ). The peak season of legionellosis was mostly July (Fig. ). More patients were reported from more populated prefectures as expected ( f400a.gif). Number of patients per 00,000 was high in Toyama, Ishikawa, Okayama and Tottori Prefectures (Fig. ). The average patients age was 67.0 years, 65.7 years in males and 7.5 years in females. While the patients ages were distributed widely from 0 year to 03 years, patients younger than 30 years were few (.0%) (Fig. 3). Males occupied 8% of the patients. According to MMWR 60: , 0, males were 64% of the patients in USA. Occupations at high risk were reported to be mining and construction, manufacturing of metal materials, assembly and/or repair of transportation machines, and car driving, etc. Symptoms are fever (9%), pneumonia (90%), cough (48%), dyspnea (44%), disturbance of consciousness (7%), diarrhea Table. Notified cases of legionellosis, 9990 Year of diagnosis Total Male Female 999* *AprilDecember (National Epidemiological Surveillance of Infectious Diseases: Data based on the reports as of May 5, 03) Vol. 34 No. 6 June 03 Infectious Agents Surveillance Report <THE TOPIC OF THIS MONTH> Legionellosis, January 008December 0 Figure. Monthly incidence of legionellosis cases, January 008December Month* Cases * The day of the first consultation (National Epidemiological Surveillance of Infectious Diseases: Data based on the reports received before May 5, 03) Year Figure. Incidence of legionellosis by prefecture, January 008December 0 Symptomatic and asymptomatic cases per 00,000 population (National Epidemiological Surveillance of Infectious Diseases: Data based on the reports received before May 5, 03) 55 ISSN National Institute of Infectious Diseases and Tuberculosis and Infectious Diseases Control Division, Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare Continued on page 56
32 86 Vol. 34 No THE TOPIC OF THIS MONTHContinued (9.8%), multiple organ failure (8.5%), and abdominal pain (.5%) (percentage in parenthesis indicates percentage among the notified patients having the symptom indicated). As for the location of infection, 3,96 cases (97%) were infected in Japan, 95 cases (.3%) abroad and 4 cases (0.6%) unknown. Methods of diagnosis: Of 4,08 cases, 3,98 (96%) were diagnosed by antigen detection in urine, 3 cases (.8%) by bacterial culture, 69 (.7%) by titration of serum antibody, 6 (.5%) by PCR (including LAMP method), and 8 (0.%) by the indirect fluorescent antibody method or by the enzymelinked antibody method (Table on p.57 of this issue). While antigen detection in urine was used in a great majority, it can detect only Legionella pneumophila serogroup (SG). The LAMP assay that can detect a wide range of genus Legionella started to be covered by the medical insurance since October 0. In 0, 5 cases were diagnosed by this method. The number of deaths among the total cases was 34 (3.3%) for Among 4,03 patients having the record of the first medical consultation, there were 9 deaths. It was noted Figure 3. Age distribution of legionellosis cases, by gender, January 008December 0 00 Females that the longer was the delay from the first consultation to the definitive diagnosis, the higher was the fatality rate, i.e.,.8% for 03 day delay, 4.% for 46 day delay and 5.3% for 7 day delay. Early diagnosis is important for saving lives of the patients. Species of Legionella isolated by culture: In addition to the above 3 culturepositive cases, reported were additional 48 cases that included isolates provided to the Legionella Reference Center after the notification (see p. 6 of this issue). Thus Legionella was isolated from total 6 cases. Among them, there were 6 cases attributable to infection of L. pneumophila SG. Some such cases of infection with L. pneumophila SG were infected additionally with other Legionella species or serogroups, such as, L. feeleii (one case), L. rubrilucens (one case), L. pneumophila SG6 (two cases), and L. pneumophila SG6 and SG9 and untypable (one case). There were 4 cases due to L. pneumophila other than L. pneumophila SG; six cases each due to infection with SG and SG3, four cases due to infection with SG6, two cases each due to infection with SG5, SG0 and SG, and one case each due to infection with SG9 and SG5. Furthermore, there were one case of L. londiniensis, one case of L. longbeachae, and 9 cases of Legionella whose species were not identified. Outbreaks: Outbreaks that occurred in Japan during 0080 involved cases at a public bathing facility in Kobe City in January 008 (IASR 9: 39330, 008); cases at a welfare facility for the elderly in Okayama Prefecture in July 008 (IASR 9: 33033, 008); 8 cases attributable to a bathing facility in a hotel in Gifu Prefecture in October 009 (IASR 3: 0709, 00); 9 cases attributable to a bathing facility of a sports club in Yokohama City in September 0; 3 cases attributable to a bathing facility in a hotel in Yamagata Prefecture in November 0 (see p. 59 of this issue); and 9 cases attributable to a onedaytrip hot spring in Saitama Prefecture in November to December 0 (see p. 57 of this issue). There were 3 suspected clusters, each reporting 5 legionellosis patients that were found among those who used the same facilities or toured together. In addition, after the tsunami associated with the Great East Japan Earthquake, legionellosis was reported among those who were rescued from drowning or engaged in debris processing (see p. 60 of this issue). Control measures: Legionella infection occurs through inhalation of aerosols or dusts contaminated by Legionella. The infection source includes spa pools, cooling towers, showers (IASR 3: 3333, 00 & 3: 33333, 00), hot water supply system, landscaping water, humidifiers (see p.69 of this issue), solar waterheaters (IASR 3: 35, 0) and leaf molds (IASR 6:, 005). Biofilm growing on porous natural stones in a bath sometimes becomes a hotbed of Legionella (IASR 9: 9394, 008). Principles of prevention of legionellosis include ) prevention of microbial growth and biofilm formation, ) removal of biofilm formed on equipments and facilities, 3) minimizing aerosol splash, and 4) minimizing of bacterial contamination from external sources. For this, following measures should be taken. Firstly, water should be disinfected (see p.68 of this issue), which should be checked by culture of microbes or by rapid tests (see p.65 of this issue). The current hygienic standard of bath water that may pose risk of aerosol inhalation is Legionella counts less than 0 cfu per 00 ml (below the detection limit). Secondly, the wall of bath rooms and inner surface of water tanks should be cleaned. Removal of the biofilm can be checked by measuring adenosinetriphosphate (ATP) (see p.67 of this issue). Thirdly, equipments and facilities should be designed so as not to splash aerosols. Fourthly, those who clean the wall of bathrooms or hand leaf molds should wear a dust mask. Hygienic control for prevention of legionellosis should follow guidelines, such as Legionella Control Measures (Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare: MHLW), Building Hygiene (MHLW), Guidelines for prevention of legionellosis (3 rd Ed., Building Management Education Center), Introduction to hygienic maintenance of storagetype hotwater supply equipment ( st Ed., Japan Water Facilities Environmental Hygiene Association). For prevention of legionellosis, infection sources should be identified by analyzing the data obtained from the pulsedfield gel electrophoresis and sequencebased typing using Legionella obtained from both patients and environment (see p.6 of this issue). With such information, disinfection and/or removal of Legionella can be effectively conducted. Cases Males IASR Vol. 34 No. 6 Jun Deaths Age group National Epidemiological Surveillance of Infectious Diseases: Data based on the reports received before May 5, 03 The statistics in this report are based on ) the data concerning patients and laboratory findings obtained by the National Epidemiological Surveillance of Infectious Diseases undertaken in compliance with the Law Concerning the Prevention of Infectious Diseases and Medical Care for Patients of Infections, and ) other data covering various aspects of infectious diseases. The prefectural and municipal health centers and public health institutes (PHIs), the Department of Food Safety, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, and quarantine stations, have provided the above data. Infectious Disease Surveillance Center, National Institute of Infectious Diseases Toyama 3, Shinjukuku, Tokyo 68640, JAPAN Tel (+83)585
untitled
 Infectious Agents Surveillance Report (IASR) http://www.nih.go.jp/niid/ja/iasr.html EHEC 202 3, EHEC O57 : 4 O57 ISprinting system 5, 6, O57 : 20 7, O57 : 8, O26 : 9, O26 : 0, O26 : 2, O03 O : 3, O45 :
Infectious Agents Surveillance Report (IASR) http://www.nih.go.jp/niid/ja/iasr.html EHEC 202 3, EHEC O57 : 4 O57 ISprinting system 5, 6, O57 : 20 7, O57 : 8, O26 : 9, O26 : 0, O26 : 2, O03 O : 3, O45 :
untitled
 Vol. 35 No. 3 204. ISSN 3 63 https://nesid3g.mhlw.go. 200 0 Vol.35 No. 3 No.409 2043 Infectious Agents Surveillance Report (IASR) 095583http://www.nih.go.jp/niid/ja/iasr.html 3, 4, : 5, A ; 6, : 8, 9,,
Vol. 35 No. 3 204. ISSN 3 63 https://nesid3g.mhlw.go. 200 0 Vol.35 No. 3 No.409 2043 Infectious Agents Surveillance Report (IASR) 095583http://www.nih.go.jp/niid/ja/iasr.html 3, 4, : 5, A ; 6, : 8, 9,,
untitled
 Seminal paper Anhalt JP Pioneering paper Claydon MA Kishnamurthy T Enterobacter B. cereus Routine identification paper Eigner U Seng P Cherkaoui A Saureus S. Saureus* S. Vagococcus Haemophilus Mycobacterium
Seminal paper Anhalt JP Pioneering paper Claydon MA Kishnamurthy T Enterobacter B. cereus Routine identification paper Eigner U Seng P Cherkaoui A Saureus S. Saureus* S. Vagococcus Haemophilus Mycobacterium
CHEMOTHERAPY aureus 0.10, Enterococcus faecalis 3.13, Escherichia coli 0.20, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter spp., Serratia marcescens 0.78, Prote
 aureus 0.10, Enterococcus faecalis 3.13, Escherichia coli 0.20, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter spp., Serratia marcescens 0.78, Proteus mirabilis 3.13, Proteus vulgaris 1.56, Citrobacter freundii 0.39,
aureus 0.10, Enterococcus faecalis 3.13, Escherichia coli 0.20, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter spp., Serratia marcescens 0.78, Proteus mirabilis 3.13, Proteus vulgaris 1.56, Citrobacter freundii 0.39,
 2) Goetz, A., Tsuneishi, N.: Application of molecular filter membranes to the bacteriological analysis of water, J. Am. Water Works Assn., 43 (12): 943-969,1951. 3) Clark, H.F. et al.: The membrane filter
2) Goetz, A., Tsuneishi, N.: Application of molecular filter membranes to the bacteriological analysis of water, J. Am. Water Works Assn., 43 (12): 943-969,1951. 3) Clark, H.F. et al.: The membrane filter
untitled
 Infectious Agents Surveillance Report (IASR) http://www.nih.go.jp/niid/ja/iasr.html SFTS 3, SFTS 4, SFTSV 5, SFTSV : 7, 03 SFTS 40 8, SFTS 9, SFTS 0, AHpdm09, 03/4 AHpdm09, 3, Zika fever 5, 6, CA 8, 03
Infectious Agents Surveillance Report (IASR) http://www.nih.go.jp/niid/ja/iasr.html SFTS 3, SFTS 4, SFTSV 5, SFTSV : 7, 03 SFTS 40 8, SFTS 9, SFTS 0, AHpdm09, 03/4 AHpdm09, 3, Zika fever 5, 6, CA 8, 03
Table 1 Profiles of 28 patients with Legionella pneumonia in Japan, 1980-1990 a) Y Taguchi, personal communication b) M. Hayase, personal communicatio
 Key words: Legionella pneumonia, culture-positive, Japanese patients Legionella (L. pneumophila (L. micdadei, L. bozemanii, Table 1 Profiles of 28 patients with Legionella pneumonia in Japan, 1980-1990
Key words: Legionella pneumonia, culture-positive, Japanese patients Legionella (L. pneumophila (L. micdadei, L. bozemanii, Table 1 Profiles of 28 patients with Legionella pneumonia in Japan, 1980-1990
CHEMOTHERAPY FEB Table 1. Activity of cefpirome and others against clinical isolates
 VOL.39 S-1 CHEMOTHERAPY FEB. 1981 Table 1. Activity of cefpirome and others against clinical isolates VOL.39 S-1 CHEMOTHERAPY FEB. 1991 72 M, 55.5 kg 66 F, 53 kg Chronic bronchitis Bronchopneumonia Peak
VOL.39 S-1 CHEMOTHERAPY FEB. 1981 Table 1. Activity of cefpirome and others against clinical isolates VOL.39 S-1 CHEMOTHERAPY FEB. 1991 72 M, 55.5 kg 66 F, 53 kg Chronic bronchitis Bronchopneumonia Peak
CHEMOTHERAPY
 CHEMOTHERAPY VOL.41 S-2 Laboratory and clinical evaluation of teicoplanin CHEMOTHERAPY AUG. 1993 VOL.41 S-2 Laboratory and clinical evaluation of teicoplanin Table 1. Comparative in vitro activity of teicoplanin
CHEMOTHERAPY VOL.41 S-2 Laboratory and clinical evaluation of teicoplanin CHEMOTHERAPY AUG. 1993 VOL.41 S-2 Laboratory and clinical evaluation of teicoplanin Table 1. Comparative in vitro activity of teicoplanin
SARS HIV/AIDS n = 672; % 5% 2% 8% 16% 43% 20%
 SARS HIV/AIDS n = 672; 20074 20108 6% 5% 2% 8% 16% 43% 20% 1999 2008 HIV/AIDS B A 0% 50% 100% 1049 552 17 186 867 431 739 3847 332 7556 102 2420 3648 449 802 2709 31774 1286 13651 1611 207 95 8 162 667
SARS HIV/AIDS n = 672; 20074 20108 6% 5% 2% 8% 16% 43% 20% 1999 2008 HIV/AIDS B A 0% 50% 100% 1049 552 17 186 867 431 739 3847 332 7556 102 2420 3648 449 802 2709 31774 1286 13651 1611 207 95 8 162 667
Fig. 1 Trends of TB incidence rates for all forms and smear-positive pulmonary TB in Kawasaki City and Japan. Incidence=newly notified cases of all fo
 Kekkaku Vol. 79, No. 1: 17-24, 2004 17 (Received 21 Aug. 2003/Accepted 18 Nov. 2003) Fig. 1 Trends of TB incidence rates for all forms and smear-positive pulmonary TB in Kawasaki City and Japan. Incidence=newly
Kekkaku Vol. 79, No. 1: 17-24, 2004 17 (Received 21 Aug. 2003/Accepted 18 Nov. 2003) Fig. 1 Trends of TB incidence rates for all forms and smear-positive pulmonary TB in Kawasaki City and Japan. Incidence=newly
indd
 24 61 1 2011 調査 研究 1 2 1 1 2 4 1 3 4 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 2 1 1 2 3 4 2010 11 11 2011 1 7 Infection Control in an Endoscopy Room Multi - society Guideline and Current Status at Fukushima Medical University
24 61 1 2011 調査 研究 1 2 1 1 2 4 1 3 4 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 2 1 1 2 3 4 2010 11 11 2011 1 7 Infection Control in an Endoscopy Room Multi - society Guideline and Current Status at Fukushima Medical University
VOL. 23 NO. 3 CHEMOTHERAPY 1067 Table 2 Sensitivity of gram positive cocci isolated from various diagnostic materials Table 3 Sensitivity of gram nega
 1066 CHEMOTHERAPY MAR. 1975 Table 1 Sensitivity of standard strains VOL. 23 NO. 3 CHEMOTHERAPY 1067 Table 2 Sensitivity of gram positive cocci isolated from various diagnostic materials Table 3 Sensitivity
1066 CHEMOTHERAPY MAR. 1975 Table 1 Sensitivity of standard strains VOL. 23 NO. 3 CHEMOTHERAPY 1067 Table 2 Sensitivity of gram positive cocci isolated from various diagnostic materials Table 3 Sensitivity
CHEMOTHERAPY JUNE 1993 Table 1. Background of patients in pharmacokinetic study
 CHEMOTHERAPY JUNE 1993 Table 1. Background of patients in pharmacokinetic study VOL. 41 S 1 Table 2. Levels (Đg/ml or Đg/g) of S-1006 in serum, bile, and tissue (gallbladder) after oral administration
CHEMOTHERAPY JUNE 1993 Table 1. Background of patients in pharmacokinetic study VOL. 41 S 1 Table 2. Levels (Đg/ml or Đg/g) of S-1006 in serum, bile, and tissue (gallbladder) after oral administration
Table 1. Antibacterial activitiy of grepafloxacin and other antibiotics against clinical isolates
 Table 1. Antibacterial activitiy of grepafloxacin and other antibiotics against clinical isolates Table 2-1. Summary of patients treated with grepafloxacin for respiratory infection 1) Out: outpatient,
Table 1. Antibacterial activitiy of grepafloxacin and other antibiotics against clinical isolates Table 2-1. Summary of patients treated with grepafloxacin for respiratory infection 1) Out: outpatient,
Key words: Antibodies to Leptospira, Tokyo, Uveitis
 Key words: Antibodies to Leptospira, Tokyo, Uveitis Fig. 1 Distribution of Antibody Titers in Age Decade Fig. 3 Distribution of Antibody Titers in each Strain Fig. 2 Correlation between Antibody Titers
Key words: Antibodies to Leptospira, Tokyo, Uveitis Fig. 1 Distribution of Antibody Titers in Age Decade Fig. 3 Distribution of Antibody Titers in each Strain Fig. 2 Correlation between Antibody Titers
CHEMOTHERAPY Table 1 Clinical effect of Sultamicillin
 CHEMOTHERAPY CHEMOTHERAPY Table 1 Clinical effect of Sultamicillin CHEMOTHERAPY Fig. 1 MICs of sultamicillin against respiratory pathogenic Branhamella catarrhalis 62 strains, inoculum size 106CFU/m1 Fig.
CHEMOTHERAPY CHEMOTHERAPY Table 1 Clinical effect of Sultamicillin CHEMOTHERAPY Fig. 1 MICs of sultamicillin against respiratory pathogenic Branhamella catarrhalis 62 strains, inoculum size 106CFU/m1 Fig.
ñ{ï 01-65
 191252005.2 19 *1 *2 *3 19562000 45 10 10 Abstract A review of annual change in leading rice varieties for the 45 years between 1956 and 2000 in Japan yielded 10 leading varieties of non-glutinous lowland
191252005.2 19 *1 *2 *3 19562000 45 10 10 Abstract A review of annual change in leading rice varieties for the 45 years between 1956 and 2000 in Japan yielded 10 leading varieties of non-glutinous lowland
semen quality or those without WBC in semen. In the patients with azoospermia and normal FSH levels (normogonadotropic azzospermia), the antibody (IgG
 CLINICAL STUDIES OF UROGENITAL INFECTIONS WITH CHLAMYDIA TRACHOMA TIS Report 2. The Epidemiology of Chlamydial Infections in Okayama District in Japan and Detection of Antibodies to Chlamydiae in the Sera
CLINICAL STUDIES OF UROGENITAL INFECTIONS WITH CHLAMYDIA TRACHOMA TIS Report 2. The Epidemiology of Chlamydial Infections in Okayama District in Japan and Detection of Antibodies to Chlamydiae in the Sera
untitled
 Quantitative Risk Assessment on the Public Health Impact of Pathogenic Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Raw Oyster 1 15 5 23 48 2 21 1 16 1 16 1 11 3 1 3 4 23 1 2 16 12 16 5 6 Hazard IdentificationExposure
Quantitative Risk Assessment on the Public Health Impact of Pathogenic Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Raw Oyster 1 15 5 23 48 2 21 1 16 1 16 1 11 3 1 3 4 23 1 2 16 12 16 5 6 Hazard IdentificationExposure
988 CHEMOTHERAPY NOV. 1971
 988 CHEMOTHERAPY NOV. 1971 VOL. 19 NO. 8 CHEMOTHERAPY 989 Effect of medium-ph and inoculum size on activity of SB-PC heart infusion agar, mcg/ml Sensitivity distribution of Staphylococci to SB-PC in surgical
988 CHEMOTHERAPY NOV. 1971 VOL. 19 NO. 8 CHEMOTHERAPY 989 Effect of medium-ph and inoculum size on activity of SB-PC heart infusion agar, mcg/ml Sensitivity distribution of Staphylococci to SB-PC in surgical
Key words: bacterial meningitis, Haemophilus influenzae type b, Streptococcus pneumoniae, rapid diagnosis, childhood
 Key words: bacterial meningitis, Haemophilus influenzae type b, Streptococcus pneumoniae, rapid diagnosis, childhood Fig.1 Distribution of the cases with bacterial meningitis by age and pathogens Chiba
Key words: bacterial meningitis, Haemophilus influenzae type b, Streptococcus pneumoniae, rapid diagnosis, childhood Fig.1 Distribution of the cases with bacterial meningitis by age and pathogens Chiba
coccus aureus Corynebacterium sp, Haemophilus parainfluenzae Klebsiella pneumoniae Pseudornonas aeruginosa Pseudomonas sp., Xanthomonas maltophilia, F
 VOL.43 S-1 coccus aureus Corynebacterium sp, Haemophilus parainfluenzae Klebsiella pneumoniae Pseudornonas aeruginosa Pseudomonas sp., Xanthomonas maltophilia, Flavobacter- Table 1. Concentration of grepafloxacin
VOL.43 S-1 coccus aureus Corynebacterium sp, Haemophilus parainfluenzae Klebsiella pneumoniae Pseudornonas aeruginosa Pseudomonas sp., Xanthomonas maltophilia, Flavobacter- Table 1. Concentration of grepafloxacin
_念3)医療2009_夏.indd
 Evaluation of the Social Benefits of the Regional Medical System Based on Land Price Information -A Hedonic Valuation of the Sense of Relief Provided by Health Care Facilities- Takuma Sugahara Ph.D. Abstract
Evaluation of the Social Benefits of the Regional Medical System Based on Land Price Information -A Hedonic Valuation of the Sense of Relief Provided by Health Care Facilities- Takuma Sugahara Ph.D. Abstract
〈企業特集:検査機器・試薬・技術の新たな展開〉新規マイコプラズマ抗原検査キット—プロラスト®Myco
 New immunochromatographic assay kit for Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection 'PRORAST Myco' Shohei Ohshima, Yasushi Shimada, Atsuko Minagawa, Kazuyuki Sugiyama and Yumiko Hirayama Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection
New immunochromatographic assay kit for Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection 'PRORAST Myco' Shohei Ohshima, Yasushi Shimada, Atsuko Minagawa, Kazuyuki Sugiyama and Yumiko Hirayama Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection
 1) i) Barber, M. et al.: Brit. Med J, 2, 565, 19'49. ii) Barber, M.F.G. J. Hayhoe and J. E. M. Whithead: Lancet, 1120 `1125, 1949.-2) Bergey: Bergey's Manual of Determinative Bacteriology 7 th Ed: (1958).-3)
1) i) Barber, M. et al.: Brit. Med J, 2, 565, 19'49. ii) Barber, M.F.G. J. Hayhoe and J. E. M. Whithead: Lancet, 1120 `1125, 1949.-2) Bergey: Bergey's Manual of Determinative Bacteriology 7 th Ed: (1958).-3)
CHEMOTHERAPY Fig. 1 Chemical structure of CXM-AX
 Fig. 1 Chemical structure of CXM-AX NOV. 1986 Fig. 2 Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates organisms (106 cells/ml) a Smurcus 27 strains d) P.m irabilis 15 strains b Ecol i 27 strains 111.morganii
Fig. 1 Chemical structure of CXM-AX NOV. 1986 Fig. 2 Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates organisms (106 cells/ml) a Smurcus 27 strains d) P.m irabilis 15 strains b Ecol i 27 strains 111.morganii
4月号 学会特集号 122247/16)一般演題目次
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 48 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 49 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 48 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 49 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68
Fig. 1 Chemical structure of DL-8280
 Fig. 1 Chemical structure of DL-8280 Fig. 2 Susceptibility of cl in ical isolates to DL4280 Fig. 5 Susceptibility of clinical isolates to DL-8280 Fig. 3 Susceptibility of clinical isolates to DL-8280 Fig.
Fig. 1 Chemical structure of DL-8280 Fig. 2 Susceptibility of cl in ical isolates to DL4280 Fig. 5 Susceptibility of clinical isolates to DL-8280 Fig. 3 Susceptibility of clinical isolates to DL-8280 Fig.
VOL.32 S-7 CHEMOTHERAPY Table 1 MIC of standard strains of CTRX Fig. 2 Cumulative curves of MIC S. aureus (26 strains )
 CHEMOTHERAPY OCT. 1984 Fig. I Chemical structure of CTRX VOL.32 S-7 CHEMOTHERAPY Table 1 MIC of standard strains of CTRX Fig. 2 Cumulative curves of MIC S. aureus (26 strains ) CHEMOTHERAPY Fig. 3 Cumulative
CHEMOTHERAPY OCT. 1984 Fig. I Chemical structure of CTRX VOL.32 S-7 CHEMOTHERAPY Table 1 MIC of standard strains of CTRX Fig. 2 Cumulative curves of MIC S. aureus (26 strains ) CHEMOTHERAPY Fig. 3 Cumulative
A Nutritional Study of Anemia in Pregnancy Hematologic Characteristics in Pregnancy (Part 1) Keizo Shiraki, Fumiko Hisaoka Department of Nutrition, Sc
 A Nutritional Study of Anemia in Pregnancy Hematologic Characteristics in Pregnancy (Part 1) Keizo Shiraki, Fumiko Hisaoka Department of Nutrition, School of Medicine, Tokushima University, Tokushima Fetal
A Nutritional Study of Anemia in Pregnancy Hematologic Characteristics in Pregnancy (Part 1) Keizo Shiraki, Fumiko Hisaoka Department of Nutrition, School of Medicine, Tokushima University, Tokushima Fetal
 Table 1 Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates 1. Escherichia coli Inoculum size: 106cells/ml 2. Klebsiella pneumoniae 3. Enterobacter cloacae 4. Serratia marcescens Inoculum size: 106cells/nil
Table 1 Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates 1. Escherichia coli Inoculum size: 106cells/ml 2. Klebsiella pneumoniae 3. Enterobacter cloacae 4. Serratia marcescens Inoculum size: 106cells/nil
CHEMOTHERAPY JUN Citrobacter freundii 27, Enterobacter aerogenes 26, Enterobacter cloacae 27, Proteus rettgeri 7, Proteus inconstans 20, Proteus
 VOL. 32 S-4 CHEMOTHERAPY Fig. 1 Chemical structure of sodium cefoperazone Fig. 2 Chemical structure of sodium cefoperazone CHEMOTHERAPY JUN. 1984 Citrobacter freundii 27, Enterobacter aerogenes 26, Enterobacter
VOL. 32 S-4 CHEMOTHERAPY Fig. 1 Chemical structure of sodium cefoperazone Fig. 2 Chemical structure of sodium cefoperazone CHEMOTHERAPY JUN. 1984 Citrobacter freundii 27, Enterobacter aerogenes 26, Enterobacter
13●53頁●6-7▲院内感染対策▲.ppt
 No.610 1 No.121 2 No.128 Nosocomial infection, Hospital-acquired infection CDC nosocomial infection, hospital-acquired infection nosocomial nosokomeion hospital nosocomial infection nosocomial pneumonia
No.610 1 No.121 2 No.128 Nosocomial infection, Hospital-acquired infection CDC nosocomial infection, hospital-acquired infection nosocomial nosokomeion hospital nosocomial infection nosocomial pneumonia
 1) University Group Diabetes Program: A study of hypoglycemic agents on vascular complica- in patients with adult-onset tions diabetes. I. Design, methods and baseline results. Diabetes 19 (suppl. 2):
1) University Group Diabetes Program: A study of hypoglycemic agents on vascular complica- in patients with adult-onset tions diabetes. I. Design, methods and baseline results. Diabetes 19 (suppl. 2):
366 12 THE JAPANESE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS 65 6 Dec. 2012 1 8 DNA 2,3 16 12 20 171 2008 12 2010 11 2 3,558 4.44% 1.65% 1.17% 90% 9 Escherichia coli -
 Dec. 2012 THE JAPANESE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS 65 6 365 11 sita oxacin 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 3 3 1 1 1 2 3 2012 9 14 sita oxacin STFX 50 mg 10% 2008 1 2008 12 2010 11 2 STFX 1,452 91.4% 1,235/1,351 95.9% 466/486
Dec. 2012 THE JAPANESE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS 65 6 365 11 sita oxacin 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 3 3 1 1 1 2 3 2012 9 14 sita oxacin STFX 50 mg 10% 2008 1 2008 12 2010 11 2 STFX 1,452 91.4% 1,235/1,351 95.9% 466/486
Yamagata Journal of Health Sciences, Vol. 16, 2013 Tamio KEITOKU 1 2 Katsuko TANNO 3 Kiyoko ARIMA 4 Noboru CHIBA 1 Abstract The present study aimed to
 Yamagata Journal of Health Sciences, Vol. 16, 2013 Tamio KEITOKU 12Katsuko TANNO 3Kiyoko ARIMA 4Noboru CHIBA 1 Abstract The present study aimed to clarify differences in awareness regarding future residence
Yamagata Journal of Health Sciences, Vol. 16, 2013 Tamio KEITOKU 12Katsuko TANNO 3Kiyoko ARIMA 4Noboru CHIBA 1 Abstract The present study aimed to clarify differences in awareness regarding future residence
1272 CHEMOTHERAPY MAR. 1975
 1272 CHEMOTHERAPY MAR. 1975 VOL. 23 NO. 3 CHEMOTHERAPY 1273 Fig. 2 Minimal inhibitory concentration of aminoglycosides against 50 strains of Klebsiella Fig. 1 Minimal inhibitory concentration of aminoglycosides
1272 CHEMOTHERAPY MAR. 1975 VOL. 23 NO. 3 CHEMOTHERAPY 1273 Fig. 2 Minimal inhibitory concentration of aminoglycosides against 50 strains of Klebsiella Fig. 1 Minimal inhibitory concentration of aminoglycosides
小児感染免疫第30巻第1号
 26 2018 314 1 2 2 2 polymerase chain reaction PCR reverse transcription RT -PCR enzyme immunoassay EIA2009 2015 6 315 144 144 6.1 1 28.9% 1 2 1,2 3 4 1999 22 23 1 2 5 2008 2009 1 2015 12 31 6 315 polymerase
26 2018 314 1 2 2 2 polymerase chain reaction PCR reverse transcription RT -PCR enzyme immunoassay EIA2009 2015 6 315 144 144 6.1 1 28.9% 1 2 1,2 3 4 1999 22 23 1 2 5 2008 2009 1 2015 12 31 6 315 polymerase
 b) Gram-negative bacteria Fig. 2 Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates : E. coli Fig. 3 Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates : Pseudomonas Fig. 1 Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates
b) Gram-negative bacteria Fig. 2 Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates : E. coli Fig. 3 Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates : Pseudomonas Fig. 1 Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates
Table1MIC of BAY o 9867 against standard strains
 Table1MIC of BAY o 9867 against standard strains Fig.2Cumulative and Distribution Curves of MIC (S.aureus 54 strains) 106cfu/ml Fig.3Correlogram of MIC (S.aureus 54 strains) CHEMOTHERAPY 451 Fig.4Cumulative
Table1MIC of BAY o 9867 against standard strains Fig.2Cumulative and Distribution Curves of MIC (S.aureus 54 strains) 106cfu/ml Fig.3Correlogram of MIC (S.aureus 54 strains) CHEMOTHERAPY 451 Fig.4Cumulative
THE JAPANESE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS 48-8 Enterococcus avium 5Š, Corynebacterium xerosis 10Š, Corynebacterium pseudodiphtheriticum 10Š, Corynebacterium
 THE JAPANESE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS 48-8 Enterobacter spp., Serratia spp., Burkholderia cepacia, Flavobacterium spp., Alcaligenes spp. THE JAPANESE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS 48-8 Enterococcus avium 5Š, Corynebacterium
THE JAPANESE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS 48-8 Enterobacter spp., Serratia spp., Burkholderia cepacia, Flavobacterium spp., Alcaligenes spp. THE JAPANESE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS 48-8 Enterococcus avium 5Š, Corynebacterium
 Key words : R-plasmid, Urinary tract infection, E. coli Fig. 1. MIC distribution against E. coli isolated from urinary tract (366 strains) and isolation - frequencies of drug-resistant strains Table 1.
Key words : R-plasmid, Urinary tract infection, E. coli Fig. 1. MIC distribution against E. coli isolated from urinary tract (366 strains) and isolation - frequencies of drug-resistant strains Table 1.
 1) Garner J. S.: The Hospital Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee, CDC, Guidelines for Isolation Precautions in Hospitals, 1996. http://wonder.cdc.gov/wonder/prevguid/ p0000419/p0000419.asp.
1) Garner J. S.: The Hospital Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee, CDC, Guidelines for Isolation Precautions in Hospitals, 1996. http://wonder.cdc.gov/wonder/prevguid/ p0000419/p0000419.asp.
2 The Bulletin of Meiji University of Integrative Medicine 3, Yamashita 10 11
 1-122013 1 2 1 2 20 2,000 2009 12 1 2 1,362 68.1 2009 1 1 9.5 1 2.2 3.6 0.82.9 1.0 0.2 2 4 3 1 2 4 3 Key words acupuncture and moxibustion Treatment with acupuncture, moxibustion and Anma-Massage-Shiatsu
1-122013 1 2 1 2 20 2,000 2009 12 1 2 1,362 68.1 2009 1 1 9.5 1 2.2 3.6 0.82.9 1.0 0.2 2 4 3 1 2 4 3 Key words acupuncture and moxibustion Treatment with acupuncture, moxibustion and Anma-Massage-Shiatsu
 Table 1.Distribution and number of cases with acute upper respiratory tract infections classified according to antimicrobial agents administered Table 2. Distribution of cases which were enrolled to set
Table 1.Distribution and number of cases with acute upper respiratory tract infections classified according to antimicrobial agents administered Table 2. Distribution of cases which were enrolled to set
Fig. 1 Chemical structure of TE-031 Code number: TE-031 Chemical name: (-) (3R, 4S, 5S, 6R, 7R, 9R, 11R, 12R, 13S, 14R)-4-[(2, 6-dideoxy-3-C-methyl-3-
 Fig. 1 Chemical structure of TE-031 Code number: TE-031 Chemical name: (-) (3R, 4S, 5S, 6R, 7R, 9R, 11R, 12R, 13S, 14R)-4-[(2, 6-dideoxy-3-C-methyl-3-O-methyl-a-L-ribo-hexopyranosyl) oxy]-14-ethyl-12,
Fig. 1 Chemical structure of TE-031 Code number: TE-031 Chemical name: (-) (3R, 4S, 5S, 6R, 7R, 9R, 11R, 12R, 13S, 14R)-4-[(2, 6-dideoxy-3-C-methyl-3-O-methyl-a-L-ribo-hexopyranosyl) oxy]-14-ethyl-12,
 2014Vol.63No.4p.342349 New impediment factor to health: biological contamination U YANAGI School of Architecture, Kogakuin University Abstract More than 40 years have passed since the Act on Maintenance
2014Vol.63No.4p.342349 New impediment factor to health: biological contamination U YANAGI School of Architecture, Kogakuin University Abstract More than 40 years have passed since the Act on Maintenance
 The clinical characteristics of Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children younger than 6 years old Nobue Takeda1,2),Tomomichi Kurosaki1),Naruhiko Ishiwada2),Yoichi Kohno2) 1)Department of Pediatrics,Chiba
The clinical characteristics of Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children younger than 6 years old Nobue Takeda1,2),Tomomichi Kurosaki1),Naruhiko Ishiwada2),Yoichi Kohno2) 1)Department of Pediatrics,Chiba
 ON A FEW INFLUENCES OF THE DENTAL CARIES IN THE ELEMENTARY SCHOOL PUPIL BY Teruko KASAKURA, Naonobu IWAI, Sachio TAKADA Department of Hygiene, Nippon Dental College (Director: Prof. T. Niwa) The relationship
ON A FEW INFLUENCES OF THE DENTAL CARIES IN THE ELEMENTARY SCHOOL PUPIL BY Teruko KASAKURA, Naonobu IWAI, Sachio TAKADA Department of Hygiene, Nippon Dental College (Director: Prof. T. Niwa) The relationship
 CHEMOTHERAPY APRIL 1992 Table 2. Concentration of meropenem in human prostatic fluid Table 1. Background of 21 chronic complicated UTI cases * NB + BPH, NB + Kidney tumor, NB + Kidney tuberculosis Table
CHEMOTHERAPY APRIL 1992 Table 2. Concentration of meropenem in human prostatic fluid Table 1. Background of 21 chronic complicated UTI cases * NB + BPH, NB + Kidney tumor, NB + Kidney tuberculosis Table
Fig. 1 Clinical findings and extent of inflammation area in female urethrocystitis Fig. 2 Classification and distribution of female patients with blad
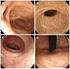 Key words: Female with bladder irritability, Subjective symptoms, Pyuria, Bacteriuria Fig. 1 Clinical findings and extent of inflammation area in female urethrocystitis Fig. 2 Classification and distribution
Key words: Female with bladder irritability, Subjective symptoms, Pyuria, Bacteriuria Fig. 1 Clinical findings and extent of inflammation area in female urethrocystitis Fig. 2 Classification and distribution
 A comparison of abdominal versus vaginal hysterectomy for leiomyoma and adenomyosis Kenji ARAHORI, Hisasi KATAYAMA, Suminori NIOKA Department of Obstetrics and Gnecology, National Maizuru Hospital,Kyoto,
A comparison of abdominal versus vaginal hysterectomy for leiomyoma and adenomyosis Kenji ARAHORI, Hisasi KATAYAMA, Suminori NIOKA Department of Obstetrics and Gnecology, National Maizuru Hospital,Kyoto,
 1) Kojima H: Culture of ejaculate for Neisseria gonorrhoeae, 1st Serually Transmitted Diseases World Congress, San Juan, 11. 19, 1981. 9) Kojima H, Mori C: Clinical studies on Conococcal and Chlamydial
1) Kojima H: Culture of ejaculate for Neisseria gonorrhoeae, 1st Serually Transmitted Diseases World Congress, San Juan, 11. 19, 1981. 9) Kojima H, Mori C: Clinical studies on Conococcal and Chlamydial
2 10 The Bulletin of Meiji University of Integrative Medicine 1,2 II 1 Web PubMed elbow pain baseball elbow little leaguer s elbow acupun
 10 1-14 2014 1 2 3 4 2 1 2 3 4 Web PubMed elbow pain baseball elbow little leaguer s elbow acupuncture electric acupuncture 2003 2012 10 39 32 Web PubMed Key words growth stage elbow pain baseball elbow
10 1-14 2014 1 2 3 4 2 1 2 3 4 Web PubMed elbow pain baseball elbow little leaguer s elbow acupuncture electric acupuncture 2003 2012 10 39 32 Web PubMed Key words growth stage elbow pain baseball elbow
 ;~ (Summary) The Study on the Effects of Foot Bathing on Urination Kumiko Toyoda School of Human Nursing, University of Shiga Prefecture Background Foot bathing is one of the important nursing care for
;~ (Summary) The Study on the Effects of Foot Bathing on Urination Kumiko Toyoda School of Human Nursing, University of Shiga Prefecture Background Foot bathing is one of the important nursing care for
<95DB8C9288E397C389C88A E696E6462>
 2011 Vol.60 No.2 p.138 147 Performance of the Japanese long-term care benefit: An International comparison based on OECD health data Mie MORIKAWA[1] Takako TSUTSUI[2] [1]National Institute of Public Health,
2011 Vol.60 No.2 p.138 147 Performance of the Japanese long-term care benefit: An International comparison based on OECD health data Mie MORIKAWA[1] Takako TSUTSUI[2] [1]National Institute of Public Health,
52-2.indb
 Jpn. J. Health Phys., 52 (2) 55 60 (2017) DOI: 10.5453/jhps.52.55 * 1 * 2 * 2 * 3 * 3 2016 10 28 2017 3 8 Enhancement of Knowledge on Radiation Risk Yukihiko KASAI,* 1 Hiromi KUDO,* 2 Masahiro HOSODA,*
Jpn. J. Health Phys., 52 (2) 55 60 (2017) DOI: 10.5453/jhps.52.55 * 1 * 2 * 2 * 3 * 3 2016 10 28 2017 3 8 Enhancement of Knowledge on Radiation Risk Yukihiko KASAI,* 1 Hiromi KUDO,* 2 Masahiro HOSODA,*
Key words: E. coli O 157: H7, fosfomycin, verotoxin, mouse infection
 Key words: E. coli O 157: H7, fosfomycin, verotoxin, mouse infection Table 1. Bacterial cell counts in feces of mice infected with Esclwrichia coli O 157: H7 NK2 before and during oral dosing with fosfomycin
Key words: E. coli O 157: H7, fosfomycin, verotoxin, mouse infection Table 1. Bacterial cell counts in feces of mice infected with Esclwrichia coli O 157: H7 NK2 before and during oral dosing with fosfomycin
Fig.2. Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates of S. epidermidis (24 strains, 106 CFU/ml) Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus epider- midis Ent
 Fig.2. Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates of S. epidermidis (24 strains, 106 CFU/ml) Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus epider- midis Enterococcus faecalis Klebsiella pneumoniae, Morganella
Fig.2. Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates of S. epidermidis (24 strains, 106 CFU/ml) Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus epider- midis Enterococcus faecalis Klebsiella pneumoniae, Morganella
 VOL.30 NO.12 CHEMOTHERAPY Fig. 1 Effect of temperature on the growth curve of A. calcoaceticus A. calcoaceticits Ac 54 A. calcoacetictts Ac 164 Fig. 2 Effect of medium ph on the growth curve of A. calcoaceticus
VOL.30 NO.12 CHEMOTHERAPY Fig. 1 Effect of temperature on the growth curve of A. calcoaceticus A. calcoaceticits Ac 54 A. calcoacetictts Ac 164 Fig. 2 Effect of medium ph on the growth curve of A. calcoaceticus
 E Societe de Pathologie Infectieuse de Langue Francaise (, 1991) E Spanish Thoracic Society (1992) E American Thoracic Society (ATS : 1993. ü ù2001 ) E British Thoracic Society (1993, ü è2001 ) E Canadian
E Societe de Pathologie Infectieuse de Langue Francaise (, 1991) E Spanish Thoracic Society (1992) E American Thoracic Society (ATS : 1993. ü ù2001 ) E British Thoracic Society (1993, ü è2001 ) E Canadian
 Table 1.Quality control of MICs for reference strains Table 2.Antimicrobial activity of gatifloxacin against aerobic bacteria Table 4.Antimicrobial activity of gatifloxacin and other quinolones against
Table 1.Quality control of MICs for reference strains Table 2.Antimicrobial activity of gatifloxacin against aerobic bacteria Table 4.Antimicrobial activity of gatifloxacin and other quinolones against
Studies of Foot Form for Footwear Design (Part 9) : Characteristics of the Foot Form of Young and Elder Women Based on their Sizes of Ball Joint Girth
 Studies of Foot Form for Footwear Design (Part 9) : Characteristics of the Foot Form of Young and Elder Women Based on their Sizes of Ball Joint Girth and Foot Breadth Akiko Yamamoto Fukuoka Women's University,
Studies of Foot Form for Footwear Design (Part 9) : Characteristics of the Foot Form of Young and Elder Women Based on their Sizes of Ball Joint Girth and Foot Breadth Akiko Yamamoto Fukuoka Women's University,
日本化学療法学会雑誌第59巻第5号
 Streptococcus pneumoniae Haemophilus influenzae Moraxella catarrhalis S. pneumoniae H. influenzae M. catarrhalis S. pneumoniae H. influenzae M. catarrhalis S. pneumoniae H. influenzae M. catarrhalis S.
Streptococcus pneumoniae Haemophilus influenzae Moraxella catarrhalis S. pneumoniae H. influenzae M. catarrhalis S. pneumoniae H. influenzae M. catarrhalis S. pneumoniae H. influenzae M. catarrhalis S.
Table 1 Detection bacterial strains used in this study *1; Methicillin resistant strains(mrsa)
 Key words: PCR, ribosomal RNA, bacterial contamination Table 1 Detection bacterial strains used in this study *1; Methicillin resistant strains(mrsa) PCR法 Fig. 1 Agarose gel ribosomal DNA Amplification
Key words: PCR, ribosomal RNA, bacterial contamination Table 1 Detection bacterial strains used in this study *1; Methicillin resistant strains(mrsa) PCR法 Fig. 1 Agarose gel ribosomal DNA Amplification
udc-2.dvi
 13 0.5 2 0.5 2 1 15 2001 16 2009 12 18 14 No.39, 2010 8 2009b 2009a Web Web Q&A 2006 2007a20082009 2007b200720082009 20072008 2009 2009 15 1 2 2 2.1 18 21 1 4 2 3 1(a) 1(b) 1(c) 1(d) 1) 18 16 17 21 10
13 0.5 2 0.5 2 1 15 2001 16 2009 12 18 14 No.39, 2010 8 2009b 2009a Web Web Q&A 2006 2007a20082009 2007b200720082009 20072008 2009 2009 15 1 2 2 2.1 18 21 1 4 2 3 1(a) 1(b) 1(c) 1(d) 1) 18 16 17 21 10
epidermidis, Enterococcus faecalis, Enterococcus Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis, indolepositive Proteus spp., Enterobacter spp., Serratia
 epidermidis, Enterococcus faecalis, Enterococcus Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis, indolepositive Proteus spp., Enterobacter spp., Serratia Table 3. Overall clinical efficacy of cefozopran in
epidermidis, Enterococcus faecalis, Enterococcus Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis, indolepositive Proteus spp., Enterobacter spp., Serratia Table 3. Overall clinical efficacy of cefozopran in
ec6
 Yamagata Journal of Health Sciences, Vol. 8, 2005 Chikako SAITOU, Miharu NISHIWAKI This study has been undertaken to make clear the relationship of menstruation pattern to self-awareness, premenstrual
Yamagata Journal of Health Sciences, Vol. 8, 2005 Chikako SAITOU, Miharu NISHIWAKI This study has been undertaken to make clear the relationship of menstruation pattern to self-awareness, premenstrual
Table 1 Isolation of legionellae from 24 hr-hot water bath without chlorination 1) Sampling from hot bath water used more than 5 days 2) Samplig from
 Key words : legionella, 24hr-hot water bath, chlorination, hot water contamination Table 1 Isolation of legionellae from 24 hr-hot water bath without chlorination 1) Sampling from hot bath water used more
Key words : legionella, 24hr-hot water bath, chlorination, hot water contamination Table 1 Isolation of legionellae from 24 hr-hot water bath without chlorination 1) Sampling from hot bath water used more
Fig.1 Chemical structure of BAY o 9867
 Fig.1 Chemical structure of BAY o 9867 CHEMOTHERAPY 43 Table 3 Antibacterial spectrum of gram negative bacteria Medium:Heart infusion agar (Nissui) Method:Agar dilution (Streak) CHEMOTHERAPY DEC 1985
Fig.1 Chemical structure of BAY o 9867 CHEMOTHERAPY 43 Table 3 Antibacterial spectrum of gram negative bacteria Medium:Heart infusion agar (Nissui) Method:Agar dilution (Streak) CHEMOTHERAPY DEC 1985
HPV HPV HPV HPV 7 HPV 8 9 HPV 3 HPV HPV HPV , Becker Ajzen H
 3 26 3 Journal of Junshin Gakuen University, HPV Faculty of Health Sciences Vol.3, March 2014 99 HPV Knowledge of and attitudes towards human papillomavirus vaccinations among mothers who have daughters
3 26 3 Journal of Junshin Gakuen University, HPV Faculty of Health Sciences Vol.3, March 2014 99 HPV Knowledge of and attitudes towards human papillomavirus vaccinations among mothers who have daughters
日本職業・災害医学会会誌第51巻第1号
 内野ら 下腿骨骨折におけるハイブリッド創外固定器の有用性 31 図 2 軟部組織損傷程度と機能成績 Gustilo IIIB 以上の開放骨折では Gustilo IIIA 以下の開放骨折 及び皮下骨折よりも明らかに機能低下が認められた 図 1 年齢と機能成績 60 歳未満の若年者の方が明らかに良好な成績を示した a b c 図 3 a Gustilo Type IIIB b, c AO 分類 Type
内野ら 下腿骨骨折におけるハイブリッド創外固定器の有用性 31 図 2 軟部組織損傷程度と機能成績 Gustilo IIIB 以上の開放骨折では Gustilo IIIA 以下の開放骨折 及び皮下骨折よりも明らかに機能低下が認められた 図 1 年齢と機能成績 60 歳未満の若年者の方が明らかに良好な成績を示した a b c 図 3 a Gustilo Type IIIB b, c AO 分類 Type
地域共同体を基盤とした渇水管理システムの持続可能性
 I 1994 1994 1994 1,176 1,377 1995, p.21; 1999 Kazuki Kagohashi / 10 1 1 1991 drought water bank 2013 466-8673 18 E-mail:kagohashi@gmail.com 1 355 10 2 Kondo 2013 136 2015 spring / No.403 2 1 1994 1995,
I 1994 1994 1994 1,176 1,377 1995, p.21; 1999 Kazuki Kagohashi / 10 1 1 1991 drought water bank 2013 466-8673 18 E-mail:kagohashi@gmail.com 1 355 10 2 Kondo 2013 136 2015 spring / No.403 2 1 1994 1995,
The Journal of the Japan Academy of Nursing Administration and Policies Vol 7, No 2, pp 19 _ 30, 2004 Survey on Counseling Services Performed by Nursi
 The Journal of the Japan Academy of Nursing Administration and Policies Vol 7, No 2, pp 19 _ 30, 2004 Survey on Counseling Services Performed by Nursing Professionals for Diabetic Outpatients Not Using
The Journal of the Japan Academy of Nursing Administration and Policies Vol 7, No 2, pp 19 _ 30, 2004 Survey on Counseling Services Performed by Nursing Professionals for Diabetic Outpatients Not Using
日本化学療法学会雑誌第56巻第1号
 β β β β β Streptococcus pneumoniaehaemophilus influenzaemoraxella catarrhalismycoplasma pneumoniaechlamydia pneumoniae β Key wordsβ mys nilc laci ngis Table. Assessmentschedule Parameters Patientcharacteristics
β β β β β Streptococcus pneumoniaehaemophilus influenzaemoraxella catarrhalismycoplasma pneumoniaechlamydia pneumoniae β Key wordsβ mys nilc laci ngis Table. Assessmentschedule Parameters Patientcharacteristics
日本化学療法学会雑誌第58巻第4号
 Escherichia coli Enterococcus faecalisstreptococcus agalactiae Klebsiella pneumoniae Staphylococcus epidermidis E. colie. faecalispseudomonas aeruginosa K. pneumoniae S. agalactiae E. coli E. coli μ p
Escherichia coli Enterococcus faecalisstreptococcus agalactiae Klebsiella pneumoniae Staphylococcus epidermidis E. colie. faecalispseudomonas aeruginosa K. pneumoniae S. agalactiae E. coli E. coli μ p
スライド 1
 1 2006 msv 2 2011 3 CT 2011 10mSv 10 40mSv 4 2012 217mSv 5 (CT) 2012 50 60mSv 6 2012 510mSv BRCA25 310 10mSv3% BRCA60-280% 3 5m Sv 1m Sv 12% . http://www.rea.or.jp/ire/pdf/report4.pdf 1.10 20 SMR 1.00
1 2006 msv 2 2011 3 CT 2011 10mSv 10 40mSv 4 2012 217mSv 5 (CT) 2012 50 60mSv 6 2012 510mSv BRCA25 310 10mSv3% BRCA60-280% 3 5m Sv 1m Sv 12% . http://www.rea.or.jp/ire/pdf/report4.pdf 1.10 20 SMR 1.00
E. coli E. coli é H. influenzae Helicobacter pylori
 é C.pneumoniae C.trachomatis C.trachomatis 1 é Chlamydia pneumoniae Chlamydia psittaci Chlamydia trachomatis 3 E. coli E. coli é H. influenzae Helicobacter pylori K. pneumoniae L. monocytogenes ü l Staphylococcus
é C.pneumoniae C.trachomatis C.trachomatis 1 é Chlamydia pneumoniae Chlamydia psittaci Chlamydia trachomatis 3 E. coli E. coli é H. influenzae Helicobacter pylori K. pneumoniae L. monocytogenes ü l Staphylococcus
過去26年間のスギ花粉飛散パターンのクラスター分析
 117 681 : 2A 2B 2C 2A 2B 2C 2A 2A 2B 2C 2A 2B 2C 2A : DNA Phöbus Blackly 1cm 117 682 2014 1 SYSTAT χ Complete linkage method χ 2A 2B 2C /cm /cm /cm 2A 2B 2C 2A 2B 2C 2A 2B 2C 2 A /cm 2A 2C 117 683 2 2A
117 681 : 2A 2B 2C 2A 2B 2C 2A 2A 2B 2C 2A 2B 2C 2A : DNA Phöbus Blackly 1cm 117 682 2014 1 SYSTAT χ Complete linkage method χ 2A 2B 2C /cm /cm /cm 2A 2B 2C 2A 2B 2C 2A 2B 2C 2 A /cm 2A 2C 117 683 2 2A
Key words: Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis, rapid diagnosis
 Key words: Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis, rapid diagnosis Table 1 Strains evaluated Table 3 Comparison of sensitivity (CFU/mL) of 8 rapid diagnostic kits for detecting
Key words: Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis, rapid diagnosis Table 1 Strains evaluated Table 3 Comparison of sensitivity (CFU/mL) of 8 rapid diagnostic kits for detecting
11_渡辺_紀要_2007
 56 1 19 Bull. Nara Univ. Educ., Vol. 56, No.1 (Cult. & Soc.), 2007 115 19 Why is Kidney Dysfunction Caused by Cadmium (Cadmium Nephropathy) not Officially Recognized as a Pollution-related Disease by the
56 1 19 Bull. Nara Univ. Educ., Vol. 56, No.1 (Cult. & Soc.), 2007 115 19 Why is Kidney Dysfunction Caused by Cadmium (Cadmium Nephropathy) not Officially Recognized as a Pollution-related Disease by the
 Safety Performance of Steel Deck Plate (Flat Decks) Used for Concrete Slab Moulding CONTENTS 1. Introduction ---------------------------------------------------------------- (2) 2. Flat Decks ------------------------------------------------------------------
Safety Performance of Steel Deck Plate (Flat Decks) Used for Concrete Slab Moulding CONTENTS 1. Introduction ---------------------------------------------------------------- (2) 2. Flat Decks ------------------------------------------------------------------
VOL.30 S-1 CHEMOTHERAPY Table 1 Antibacterial activity of CTT against standard strains Table 2 Antibacterial activity of CTT against standard strains
 CHEMOTHERAPY APR. 1982 Fig. 1 Chemical structure of cefotetan (CTT, YM09330) VOL.30 S-1 CHEMOTHERAPY Table 1 Antibacterial activity of CTT against standard strains Table 2 Antibacterial activity of CTT
CHEMOTHERAPY APR. 1982 Fig. 1 Chemical structure of cefotetan (CTT, YM09330) VOL.30 S-1 CHEMOTHERAPY Table 1 Antibacterial activity of CTT against standard strains Table 2 Antibacterial activity of CTT
在日外国人高齢者福祉給付金制度の創設とその課題
 Establishment and Challenges of the Welfare Benefits System for Elderly Foreign Residents In the Case of Higashihiroshima City Naoe KAWAMOTO Graduate School of Integrated Arts and Sciences, Hiroshima University
Establishment and Challenges of the Welfare Benefits System for Elderly Foreign Residents In the Case of Higashihiroshima City Naoe KAWAMOTO Graduate School of Integrated Arts and Sciences, Hiroshima University
400 46 THE JAPANESE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS 65 6 Dec. 2012 LVFX 100 mg 3 / 7 150 mg 2 / 7 2 2006 2008 9 LVFX PK PD 2009 7 100 mg 1 3 500 mg 1 1 AUC/MIC
 Dec. 2012 THE JAPANESE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS 65 6 399 45 2012 11 5 LVFX 500 mg 1 1 20 Chlamydia trachomatis C. trachomatismycoplasma genitalium M. genitalium LVFX 1 500 mg 1 1 7 22 22 C. trachomatis 17
Dec. 2012 THE JAPANESE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS 65 6 399 45 2012 11 5 LVFX 500 mg 1 1 20 Chlamydia trachomatis C. trachomatismycoplasma genitalium M. genitalium LVFX 1 500 mg 1 1 7 22 22 C. trachomatis 17
 VOL.32 S-9 CHEMOTHERAPY Table 1 Minimum inhibitory concentrations of AC-1370, CPZ and CAZ Table 2 Efficacy of AC-1370 and CPZ against systemic infections in mice *Inoculum size: 106 cells/ml * 95% confidence
VOL.32 S-9 CHEMOTHERAPY Table 1 Minimum inhibitory concentrations of AC-1370, CPZ and CAZ Table 2 Efficacy of AC-1370 and CPZ against systemic infections in mice *Inoculum size: 106 cells/ml * 95% confidence
国土技術政策総合研究所 研究資料
 ISSN TECHNICAL NOTE of National Institute for Land and Infrastructure Management No256 September 2005 Experimental Study on Seismic Behavior of Seawalls for Controlled Waste Disposal Shingo KANO, Katsuya
ISSN TECHNICAL NOTE of National Institute for Land and Infrastructure Management No256 September 2005 Experimental Study on Seismic Behavior of Seawalls for Controlled Waste Disposal Shingo KANO, Katsuya
 Table 1 Survival rates of infected mice given antibiotic doses producing peak serum a) S. aurcus Smith Challenge dose :7 ~10 (5% mucin) CFU/mouse. LD50: 1 ~103 (5% mucin) CFU/mouse. Table 2 Survival rates
Table 1 Survival rates of infected mice given antibiotic doses producing peak serum a) S. aurcus Smith Challenge dose :7 ~10 (5% mucin) CFU/mouse. LD50: 1 ~103 (5% mucin) CFU/mouse. Table 2 Survival rates
Microsoft Word - ??? ????????? ????? 2013.docx
 @ィーィェィケィャi@@ @@pbィ 050605a05@07ィ 050605a@070200 pbィ 050605a05@07ィ 050605a@070200@ィーィィu05@0208 1215181418 12 1216121419 171210 1918181811 19181719101411 1513 191815181611 19181319101411 18121819191418 1919151811
@ィーィェィケィャi@@ @@pbィ 050605a05@07ィ 050605a@070200 pbィ 050605a05@07ィ 050605a@070200@ィーィィu05@0208 1215181418 12 1216121419 171210 1918181811 19181719101411 1513 191815181611 19181319101411 18121819191418 1919151811
NINJAL Research Papers No.8
 (NINJAL Research Papers) 8: 177 196 (2014) ISSN: 2186-134X print/2186-1358 online 177 3 3 3 1940 3 late adoption real time 3 apparent time * 1. 1 2 3 1.1 3 1 1953 * 2014 3 18 2014 5 13 109 NINJAL 2012
(NINJAL Research Papers) 8: 177 196 (2014) ISSN: 2186-134X print/2186-1358 online 177 3 3 3 1940 3 late adoption real time 3 apparent time * 1. 1 2 3 1.1 3 1 1953 * 2014 3 18 2014 5 13 109 NINJAL 2012
 The Indirect Support to Faculty Advisers of die Individual Learning Support System for Underachieving Student The Indirect Support to Faculty Advisers of the Individual Learning Support System for Underachieving
The Indirect Support to Faculty Advisers of die Individual Learning Support System for Underachieving Student The Indirect Support to Faculty Advisers of the Individual Learning Support System for Underachieving
Shigella flexneri 2a, Shigella flexneri 3a, Shigella sonnei, Salmonella, Salmonella arizonae, Citorobacter freundii, Enterobacter aerogenes, Enterobac
 Key words: Edwardsiella tarda from Healthy Persons, H2S firoducinr. Escherichia coli Shigella flexneri 2a, Shigella flexneri 3a, Shigella sonnei, Salmonella, Salmonella arizonae, Citorobacter freundii,
Key words: Edwardsiella tarda from Healthy Persons, H2S firoducinr. Escherichia coli Shigella flexneri 2a, Shigella flexneri 3a, Shigella sonnei, Salmonella, Salmonella arizonae, Citorobacter freundii,
 VOL. 17 NO. 7 CHEMOTHERAPY 1305 1) W. BRumFirr et al. : Clinical and laboratory studies with carbenicillin. Lancet 1: 1289~ 1293, 1967 2) E. T. KNUDSEN et al. : A new semisynthetic penicillin active against
VOL. 17 NO. 7 CHEMOTHERAPY 1305 1) W. BRumFirr et al. : Clinical and laboratory studies with carbenicillin. Lancet 1: 1289~ 1293, 1967 2) E. T. KNUDSEN et al. : A new semisynthetic penicillin active against
Title 泌尿器科領域に於ける17-Ketosteroidの研究 17-Ketosteroidの臨床的研究 第 III 篇 : 尿 Author(s) 卜部, 敏入 Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1958), 4(1): 3-31 Issue Date URL
 Title 泌尿器科領域に於ける17-Ketosteroidの研究 17-Ketosteroidの臨床的研究 第 III 篇 : 尿 Author(s) 卜部, 敏入 Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1958), 4(1): 3-31 Issue Date 1958-01 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/111559 Right Type Departmental Bulletin
Title 泌尿器科領域に於ける17-Ketosteroidの研究 17-Ketosteroidの臨床的研究 第 III 篇 : 尿 Author(s) 卜部, 敏入 Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1958), 4(1): 3-31 Issue Date 1958-01 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/111559 Right Type Departmental Bulletin
16_.....E...._.I.v2006
 55 1 18 Bull. Nara Univ. Educ., Vol. 55, No.1 (Cult. & Soc.), 2006 165 2002 * 18 Collaboration Between a School Athletic Club and a Community Sports Club A Case Study of SOLESTRELLA NARA 2002 Rie TAKAMURA
55 1 18 Bull. Nara Univ. Educ., Vol. 55, No.1 (Cult. & Soc.), 2006 165 2002 * 18 Collaboration Between a School Athletic Club and a Community Sports Club A Case Study of SOLESTRELLA NARA 2002 Rie TAKAMURA
 CHEMOTHERAPY AUG. 1982 VOL. 30 NO. 8 CHEMOTHERAPY Fig.1 Relation between various-closis of cefazolin and detection rate of organisms in heart blood of dying mice with E. coli and P. aeruginosa infection
CHEMOTHERAPY AUG. 1982 VOL. 30 NO. 8 CHEMOTHERAPY Fig.1 Relation between various-closis of cefazolin and detection rate of organisms in heart blood of dying mice with E. coli and P. aeruginosa infection
Key words : candidemia, endotoxin, D-arabinitol, Candida antigen, serological examination
 Key words : candidemia, endotoxin, D-arabinitol, Candida antigen, serological examination Fig. 1 The value of fungal index and D- arabinitol/creatinine. Fungal index was mesured by Endotoxin D and Endospecy
Key words : candidemia, endotoxin, D-arabinitol, Candida antigen, serological examination Fig. 1 The value of fungal index and D- arabinitol/creatinine. Fungal index was mesured by Endotoxin D and Endospecy
加藤茂孝先生
 Shigetaka KATOW 2009 4 24 WHO 5 9 1 5 16 1 TV 6 12 6 11 WHO 6 4 5 12 E-mail : modern_media@eiken.co.jp 2009. 4. 28. http:idsc.nih.go.jpidwrkanjaweeklygraph01flu.html 0101-0051 - RIKEN Center of Research
Shigetaka KATOW 2009 4 24 WHO 5 9 1 5 16 1 TV 6 12 6 11 WHO 6 4 5 12 E-mail : modern_media@eiken.co.jp 2009. 4. 28. http:idsc.nih.go.jpidwrkanjaweeklygraph01flu.html 0101-0051 - RIKEN Center of Research
日本化学療法学会雑誌第65巻第4号
 Mycoplasma pneumoniae M. pneumoniae M. pneumoniae M. pneumoniae M. pneumoniae M. pneumoniae Key words Mycoplasma pneumoniae Mycoplasma pneumoniae M. pneumoniae I M. pneumoniae M. pneumoniae M. pneumoniae
Mycoplasma pneumoniae M. pneumoniae M. pneumoniae M. pneumoniae M. pneumoniae M. pneumoniae Key words Mycoplasma pneumoniae Mycoplasma pneumoniae M. pneumoniae I M. pneumoniae M. pneumoniae M. pneumoniae
