|
|
|
- せとか のたけ
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2
3 Fig.1 MICs of penicillins against 24 strains of B. pertussis Fig.2 MICs of cepherns against 24 strains of B. pertussis
4 Fig.3 MICs of macrolides against 24 strains of B. pertussis Fig.4 MICs of nalidixic acid analogs against 24 strains of B. pertuosis Fig.5 Bactericidal activity of ampicillin, piperacillin, and TA- 058 on B. pertussis NNBP 3
5 Fig.6 Bactericidal activity of latamoxef, cefoperazone, and ampicillin on B. pertussis NNBP 3 Fig.7 Comparative bactericidal activity of cefoperazone, latamoxef, ampicillin, minocy- Fig.8 Method of cryopreservation of B. pertussis and the result of viability on 24 strains of B. pertussis by using this methodology
6
7 of phase I Bordetella pertussis. J. Gen. Microbiol. 63: 211 `220, ) NELSON, J. D.; B. M. MATTECK& J. MCNABB: Susceptibility of Bordetella pertussis to am- picillin. J. Pediatr. 68: 222 `226, ) TROLLFORS, B.: Effect of erythromycin and amoxicillin on Bordetella pertussis in the 17) SHISHIDO, H.; K. MATSUMOTO, K. WATANABE& 8) FIELD, L. H.& C. D. PARKER: Differences observed between fresh isolates of Bordetella pertussis and their laboratory passaged derivatives. 3 rd International Symposium on Pertussis. Dhew Publication, pp.124 `132, ) FIELD, L. H.& C. D. PARKER: Antibiotic susceptibility testing of Bordetella pertussis. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 74: 312 `316, ) STAINER, D. W. & M. J. SCHOLTE: A simple chemically defined medium for the production 12) BASS, J. W.: The role of antimicrobial agents in the treatment pertussis. J. Pediatr. 83: 891 `892, ) SIMON, C.; M. BONTEMPS, K. WIESE& R. SCHE- WIOR- ROLAND: Zur Ampicillin- Therapie des Keuch hustens. Dtsch. Med. Wschr. 94: 2435 `4437, ) KURT, T. L.; A. S. YEAGER, S. GUENETTE& S. DUNLOP: Spread of pertussis by hospital staff. JAMA 221: 264 `267, 1972 nasopharynx. Infection 6: 228 `230, 1978 Y. UZUKA: In vitro activity of Ĉ- lactam antibiotics against Bordetella pertussis: Unusually high anti- B. pertussis activity of piperazine 19- lactams. Current chemotherapy and infections disease. Proceedings of the 11 th ICC and the 19 th ICAAC. Amer. Soc.
8 ANTIMICROBIAL SUSCEPTIBILITY OF CLINICALLY ISOLATED BORDETELLA PERTUSSIS, WITH THE SPECIAL REFERENCE TO THE IN VITRO BACTERICIDAL ACTIVITY HARUMI SHISHIDO, AMISHI TAKAHASHI, KIWAO WATANABE, and KEIZO MATSUMOTO Department of Internal Medicine, Institute for Tropical Medicine, Nagasaki University KEISUKE TAZAKI Tazaki Clinic In vitro bactericidal activity testing was performed using BORDET- GENGOU broth (2.5g of soluble starch, 10g of peptone, 5g of NaCl, and 10ml of glycerol per liter supplemented with 15% of defibrinated horse blood), which has been established in our laboratory. The in vitro bactericidal activities of Ĉ- lactam antibiotics against Bordetella pertussis (B. pertussis) were compared, ampicillin showing the highest activity. The comparative in vitro bactericidal activities of the 8 representative antimicrobial agents were in the order: Erythromycin> gentamicin> norfloxacin> chloramphenicol> minocycline> ampicillin> latamoxef> cefoperazone. It has been suggested that in vitro bactericidal activity in our methodology should be consistent with clinical results. The MICs at 106 cfu/ml of 22 antimicrobial agents against 24 strains of clinically isolated B. pertussis were determined by the agar dilution method. Comparison of the MICs of Ĉ- lactam antibiotics against B. pertussis indicated that TA- 058 and cefpiramide were as active as piperacillin and cefoperazone, respectively. DL and norfloxacin were more active against B. pertussis than the older nalidixic acid analogs. The method of cryopreservation and transport of clinical isolates of B. pertussis have been studied, and new methodology was established.
CHEMOTHERAPY
 CHEMOTHERAPY VOL.41 S-2 Laboratory and clinical evaluation of teicoplanin CHEMOTHERAPY AUG. 1993 VOL.41 S-2 Laboratory and clinical evaluation of teicoplanin Table 1. Comparative in vitro activity of teicoplanin
CHEMOTHERAPY VOL.41 S-2 Laboratory and clinical evaluation of teicoplanin CHEMOTHERAPY AUG. 1993 VOL.41 S-2 Laboratory and clinical evaluation of teicoplanin Table 1. Comparative in vitro activity of teicoplanin
CHEMOTHERAPY Table 1 Clinical effect of Sultamicillin
 CHEMOTHERAPY CHEMOTHERAPY Table 1 Clinical effect of Sultamicillin CHEMOTHERAPY Fig. 1 MICs of sultamicillin against respiratory pathogenic Branhamella catarrhalis 62 strains, inoculum size 106CFU/m1 Fig.
CHEMOTHERAPY CHEMOTHERAPY Table 1 Clinical effect of Sultamicillin CHEMOTHERAPY Fig. 1 MICs of sultamicillin against respiratory pathogenic Branhamella catarrhalis 62 strains, inoculum size 106CFU/m1 Fig.
CHEMOTHERAPY FEB Table 1. Activity of cefpirome and others against clinical isolates
 VOL.39 S-1 CHEMOTHERAPY FEB. 1981 Table 1. Activity of cefpirome and others against clinical isolates VOL.39 S-1 CHEMOTHERAPY FEB. 1991 72 M, 55.5 kg 66 F, 53 kg Chronic bronchitis Bronchopneumonia Peak
VOL.39 S-1 CHEMOTHERAPY FEB. 1981 Table 1. Activity of cefpirome and others against clinical isolates VOL.39 S-1 CHEMOTHERAPY FEB. 1991 72 M, 55.5 kg 66 F, 53 kg Chronic bronchitis Bronchopneumonia Peak
Fig. 1 Chemical structure of DL-8280
 Fig. 1 Chemical structure of DL-8280 Fig. 2 Susceptibility of cl in ical isolates to DL4280 Fig. 5 Susceptibility of clinical isolates to DL-8280 Fig. 3 Susceptibility of clinical isolates to DL-8280 Fig.
Fig. 1 Chemical structure of DL-8280 Fig. 2 Susceptibility of cl in ical isolates to DL4280 Fig. 5 Susceptibility of clinical isolates to DL-8280 Fig. 3 Susceptibility of clinical isolates to DL-8280 Fig.
 Table 1 Survival rates of infected mice given antibiotic doses producing peak serum a) S. aurcus Smith Challenge dose :7 ~10 (5% mucin) CFU/mouse. LD50: 1 ~103 (5% mucin) CFU/mouse. Table 2 Survival rates
Table 1 Survival rates of infected mice given antibiotic doses producing peak serum a) S. aurcus Smith Challenge dose :7 ~10 (5% mucin) CFU/mouse. LD50: 1 ~103 (5% mucin) CFU/mouse. Table 2 Survival rates
Clostridium difficile ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, norfloxacin Bifidobacterium Lactobacillus Lactobacillus Bacteroides fragilis B. fragilis C. difficile
 Clostridium difficile ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, norfloxacin Bifidobacterium Lactobacillus Lactobacillus Bacteroides fragilis B. fragilis C. difficile Key words: temafloxacin, TA-167, Bacteroides fragilis,
Clostridium difficile ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, norfloxacin Bifidobacterium Lactobacillus Lactobacillus Bacteroides fragilis B. fragilis C. difficile Key words: temafloxacin, TA-167, Bacteroides fragilis,
 Table 1.Resistance criteria Fig.1.The resistance rates of piperacillin,ceftazidime, cefsulodin,imipenem,aztreonam,gentamicin,tobramycin,amikacin,isepamicin,fosfomycin and ofloxacin against 2,793 strains
Table 1.Resistance criteria Fig.1.The resistance rates of piperacillin,ceftazidime, cefsulodin,imipenem,aztreonam,gentamicin,tobramycin,amikacin,isepamicin,fosfomycin and ofloxacin against 2,793 strains
 Key words : R-plasmid, Urinary tract infection, E. coli Fig. 1. MIC distribution against E. coli isolated from urinary tract (366 strains) and isolation - frequencies of drug-resistant strains Table 1.
Key words : R-plasmid, Urinary tract infection, E. coli Fig. 1. MIC distribution against E. coli isolated from urinary tract (366 strains) and isolation - frequencies of drug-resistant strains Table 1.
 b) Gram-negative bacteria Fig. 2 Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates : E. coli Fig. 3 Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates : Pseudomonas Fig. 1 Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates
b) Gram-negative bacteria Fig. 2 Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates : E. coli Fig. 3 Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates : Pseudomonas Fig. 1 Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates
Table 1. Antibacterial spectrum SBT ABPC ABPC CPZ : sulbactamiampicillin : ampicillin : cefoperazone
 Table 1. Antibacterial spectrum SBT ABPC ABPC CPZ : sulbactamiampicillin : ampicillin : cefoperazone (inoculum size= 106 CFU/ml) (Ĉ-lactamase producer : 2 strains) Fig. 1. Sensitivity distribution of
Table 1. Antibacterial spectrum SBT ABPC ABPC CPZ : sulbactamiampicillin : ampicillin : cefoperazone (inoculum size= 106 CFU/ml) (Ĉ-lactamase producer : 2 strains) Fig. 1. Sensitivity distribution of
988 CHEMOTHERAPY NOV. 1971
 988 CHEMOTHERAPY NOV. 1971 VOL. 19 NO. 8 CHEMOTHERAPY 989 Effect of medium-ph and inoculum size on activity of SB-PC heart infusion agar, mcg/ml Sensitivity distribution of Staphylococci to SB-PC in surgical
988 CHEMOTHERAPY NOV. 1971 VOL. 19 NO. 8 CHEMOTHERAPY 989 Effect of medium-ph and inoculum size on activity of SB-PC heart infusion agar, mcg/ml Sensitivity distribution of Staphylococci to SB-PC in surgical
CHEMOTHERAPY
 CHEMOTHERAPY CHEMOTHERAPY Table 1 Antibacterial activity of Sulbactam/CPZ against standard strains MIC mg/ml Inoculum size 106 CFU/ml * Sulbactam/CPZ= 1: 1 ** Concentration of Sulbactam+ CPZ CHEMOTHERAPY
CHEMOTHERAPY CHEMOTHERAPY Table 1 Antibacterial activity of Sulbactam/CPZ against standard strains MIC mg/ml Inoculum size 106 CFU/ml * Sulbactam/CPZ= 1: 1 ** Concentration of Sulbactam+ CPZ CHEMOTHERAPY
 Table 1 Antibacterial spectra of CPM and other antimicrobials against anaerobes Fig. 1 In vitro activity of CPM and other antibiotics against B. fragilis (136 strains) Fig. 2 In vitro activity of CPM and
Table 1 Antibacterial spectra of CPM and other antimicrobials against anaerobes Fig. 1 In vitro activity of CPM and other antibiotics against B. fragilis (136 strains) Fig. 2 In vitro activity of CPM and
CHEMOTHERAPY JUN Citrobacter freundii 27, Enterobacter aerogenes 26, Enterobacter cloacae 27, Proteus rettgeri 7, Proteus inconstans 20, Proteus
 VOL. 32 S-4 CHEMOTHERAPY Fig. 1 Chemical structure of sodium cefoperazone Fig. 2 Chemical structure of sodium cefoperazone CHEMOTHERAPY JUN. 1984 Citrobacter freundii 27, Enterobacter aerogenes 26, Enterobacter
VOL. 32 S-4 CHEMOTHERAPY Fig. 1 Chemical structure of sodium cefoperazone Fig. 2 Chemical structure of sodium cefoperazone CHEMOTHERAPY JUN. 1984 Citrobacter freundii 27, Enterobacter aerogenes 26, Enterobacter
CHEMOTHERAPY Fig. 1 Chemical structure of CXM-AX
 Fig. 1 Chemical structure of CXM-AX NOV. 1986 Fig. 2 Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates organisms (106 cells/ml) a Smurcus 27 strains d) P.m irabilis 15 strains b Ecol i 27 strains 111.morganii
Fig. 1 Chemical structure of CXM-AX NOV. 1986 Fig. 2 Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates organisms (106 cells/ml) a Smurcus 27 strains d) P.m irabilis 15 strains b Ecol i 27 strains 111.morganii
CHEMOTHERAPY
 CHEMOTHERAPY CHEMOTHERAPY Table 1 Antibacterial activity of BRL 28500 against standard strains of bacteria Fig, 1 Sensitivity distribution of ABPC-resistant E. coli isolated from urinary tract Fig. 2 Sensitivity
CHEMOTHERAPY CHEMOTHERAPY Table 1 Antibacterial activity of BRL 28500 against standard strains of bacteria Fig, 1 Sensitivity distribution of ABPC-resistant E. coli isolated from urinary tract Fig. 2 Sensitivity
CHEMOTHERAPY JUNE 1993 Table 1. Background of patients in pharmacokinetic study
 CHEMOTHERAPY JUNE 1993 Table 1. Background of patients in pharmacokinetic study VOL. 41 S 1 Table 2. Levels (Đg/ml or Đg/g) of S-1006 in serum, bile, and tissue (gallbladder) after oral administration
CHEMOTHERAPY JUNE 1993 Table 1. Background of patients in pharmacokinetic study VOL. 41 S 1 Table 2. Levels (Đg/ml or Đg/g) of S-1006 in serum, bile, and tissue (gallbladder) after oral administration
CHEMOTHERAPY DEC Table 1 Antibacterial spectra of T-1982, CTT, CMZ, CTX, CPZ and CEZ 106 CFU/ml Note: P; Peptococcus, S; Streptococcus, G; Gaffk
 VOL. 30 S-3 CHEMOTHERAPY imeumoniae, Serratia marcescens, Proteus sp, CHEMOTHERAPY DEC. 1982 Table 1 Antibacterial spectra of T-1982, CTT, CMZ, CTX, CPZ and CEZ 106 CFU/ml Note: P; Peptococcus, S; Streptococcus,
VOL. 30 S-3 CHEMOTHERAPY imeumoniae, Serratia marcescens, Proteus sp, CHEMOTHERAPY DEC. 1982 Table 1 Antibacterial spectra of T-1982, CTT, CMZ, CTX, CPZ and CEZ 106 CFU/ml Note: P; Peptococcus, S; Streptococcus,
CHEMOTHERAPY JUNE 1987 Table1 Media used *BHIB, brain heart infusion broth (Difco); /3 -NAD, S -nicotinamidoadeninedinucleotide (Sigma Chemical Co.);
 VOL.35 S-2 CHEMOTHERAPY Fig.1 Chemical structure of carumonam CHEMOTHERAPY JUNE 1987 Table1 Media used *BHIB, brain heart infusion broth (Difco); /3 -NAD, S -nicotinamidoadeninedinucleotide (Sigma Chemical
VOL.35 S-2 CHEMOTHERAPY Fig.1 Chemical structure of carumonam CHEMOTHERAPY JUNE 1987 Table1 Media used *BHIB, brain heart infusion broth (Difco); /3 -NAD, S -nicotinamidoadeninedinucleotide (Sigma Chemical
Key words: Surfactant, Tween, Legionella
 Key words: Surfactant, Tween, Legionella Fig. 1 Inhibitory Activity of Various Tween Against Legionella pneumophila Fig. 2 Inhibitory Activity of Various Tween Against Legionella bozemanii Fig. 3 Inhibitory
Key words: Surfactant, Tween, Legionella Fig. 1 Inhibitory Activity of Various Tween Against Legionella pneumophila Fig. 2 Inhibitory Activity of Various Tween Against Legionella bozemanii Fig. 3 Inhibitory
VOL. 43 NO. 4
 VOL. 43 NO. 4 Fig. 1. Frequency of Enterococcus species from complicated UTI, 1988-1992. the number * of Enterococcus species/the number of cases with complicated UTI. Fig. 3 Epidemiologic characteristics
VOL. 43 NO. 4 Fig. 1. Frequency of Enterococcus species from complicated UTI, 1988-1992. the number * of Enterococcus species/the number of cases with complicated UTI. Fig. 3 Epidemiologic characteristics
CHEMOTHERAPY Table 1 Urinary excretion of mezlocillin Fig. 4 Urinary excretion of mezlocillin Fig. 3 Blood levels of mezlocillin
 CHEMOTHERAPY Fig. 2 Urinary excretion of mezlocillin Fig. 1 Blood levels of mezlocillin CHEMOTHERAPY Table 1 Urinary excretion of mezlocillin Fig. 4 Urinary excretion of mezlocillin Fig. 3 Blood levels
CHEMOTHERAPY Fig. 2 Urinary excretion of mezlocillin Fig. 1 Blood levels of mezlocillin CHEMOTHERAPY Table 1 Urinary excretion of mezlocillin Fig. 4 Urinary excretion of mezlocillin Fig. 3 Blood levels
VOL.42 S-1
 CHEMOTHERAPY APR. 1994 VOL.42 S-1 CHEMOTHERAPY APR. 1994 Table 1. Criteria for evaluation of clinical efficacy by the Japanese Society of Oral and Maxillo-Facial Surgeons Grades of symptoms and numerical
CHEMOTHERAPY APR. 1994 VOL.42 S-1 CHEMOTHERAPY APR. 1994 Table 1. Criteria for evaluation of clinical efficacy by the Japanese Society of Oral and Maxillo-Facial Surgeons Grades of symptoms and numerical
CHEMOTHERAPY JUNE 1986
 VOL. 34 S-3 CHEMOTHERAPY Fig. 1 Structural formula of L-105 CHEMOTHERAPY JUNE 1986 VOL. 34 S-3 CHEMOTHERAPY Table 1 Antibacterial spectra of L-105 against gram negative anaerobic rods Inoculum 106 cells/ml
VOL. 34 S-3 CHEMOTHERAPY Fig. 1 Structural formula of L-105 CHEMOTHERAPY JUNE 1986 VOL. 34 S-3 CHEMOTHERAPY Table 1 Antibacterial spectra of L-105 against gram negative anaerobic rods Inoculum 106 cells/ml
Table1MIC of BAY o 9867 against standard strains
 Table1MIC of BAY o 9867 against standard strains Fig.2Cumulative and Distribution Curves of MIC (S.aureus 54 strains) 106cfu/ml Fig.3Correlogram of MIC (S.aureus 54 strains) CHEMOTHERAPY 451 Fig.4Cumulative
Table1MIC of BAY o 9867 against standard strains Fig.2Cumulative and Distribution Curves of MIC (S.aureus 54 strains) 106cfu/ml Fig.3Correlogram of MIC (S.aureus 54 strains) CHEMOTHERAPY 451 Fig.4Cumulative
 1) i) Barber, M. et al.: Brit. Med J, 2, 565, 19'49. ii) Barber, M.F.G. J. Hayhoe and J. E. M. Whithead: Lancet, 1120 `1125, 1949.-2) Bergey: Bergey's Manual of Determinative Bacteriology 7 th Ed: (1958).-3)
1) i) Barber, M. et al.: Brit. Med J, 2, 565, 19'49. ii) Barber, M.F.G. J. Hayhoe and J. E. M. Whithead: Lancet, 1120 `1125, 1949.-2) Bergey: Bergey's Manual of Determinative Bacteriology 7 th Ed: (1958).-3)
 CHEMOTHERAPY Table 2 Clinical response of 6059-S by infection Table 3 Effect of 6059-S on blood chemistry *Normal range : S-GOT 20 `60 mu/ml, S-GPT 5 `25 IU/L, Al-Pase 30 `85 mu/ml In oilier cases : S-GOT
CHEMOTHERAPY Table 2 Clinical response of 6059-S by infection Table 3 Effect of 6059-S on blood chemistry *Normal range : S-GOT 20 `60 mu/ml, S-GPT 5 `25 IU/L, Al-Pase 30 `85 mu/ml In oilier cases : S-GOT
CHEMOTHERAPY Proteus mirabilis GN-79 Escherichia coli No. 35 Proteus vulgaris GN-76 Pseudomonas aeruginosa No. 11 Escherichia coli ML-1410 RGN-823 Kle
 VOL. 29 NO.8 CHEMOTHERAPY 865 CHEMOTHERAPY Proteus mirabilis GN-79 Escherichia coli No. 35 Proteus vulgaris GN-76 Pseudomonas aeruginosa No. 11 Escherichia coli ML-1410 RGN-823 Klebsiella pneumoniae GN-69
VOL. 29 NO.8 CHEMOTHERAPY 865 CHEMOTHERAPY Proteus mirabilis GN-79 Escherichia coli No. 35 Proteus vulgaris GN-76 Pseudomonas aeruginosa No. 11 Escherichia coli ML-1410 RGN-823 Klebsiella pneumoniae GN-69
Fig. 1 Chemical structure of KW-1070
 Fig. 1 Chemical structure of KW-1070 Fig. 2 Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates Fig. 4 Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates Fig. 3 Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates Fig.
Fig. 1 Chemical structure of KW-1070 Fig. 2 Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates Fig. 4 Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates Fig. 3 Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates Fig.
CHEMOTHERAPY APR Fig. 1 Chemical structure of cefotetan (CTT, YM09330)
 CHEMOTHERAPY APR. 1982 Fig. 1 Chemical structure of cefotetan (CTT, YM09330) VOL.30 S-1 CHEMOTHERAPY Fig. 2 Comparison of standard curves of CTT on various test organisms by cylinder plate method Column
CHEMOTHERAPY APR. 1982 Fig. 1 Chemical structure of cefotetan (CTT, YM09330) VOL.30 S-1 CHEMOTHERAPY Fig. 2 Comparison of standard curves of CTT on various test organisms by cylinder plate method Column
 Table 1.Quality control of MICs for reference strains Table 2.Antimicrobial activity of gatifloxacin against aerobic bacteria Table 4.Antimicrobial activity of gatifloxacin and other quinolones against
Table 1.Quality control of MICs for reference strains Table 2.Antimicrobial activity of gatifloxacin against aerobic bacteria Table 4.Antimicrobial activity of gatifloxacin and other quinolones against
CHEMOTHERAPY MAY. 1988
 CHEMOTHERAPY MAY. 1988 CHEMOTHERAPY Fig. 1 Chemical structure CHEMOTHERAPY MAY. 1988 VOL.36 5-1 CHEMOTHERAPY CHEMOTHERAPY MAY. 1988 VOL.36 S-1 CHEMOTHERAPY CHEMOTHERAPY MAY. 1988 VOL.36 S-1 CHEMOTHERAPY
CHEMOTHERAPY MAY. 1988 CHEMOTHERAPY Fig. 1 Chemical structure CHEMOTHERAPY MAY. 1988 VOL.36 5-1 CHEMOTHERAPY CHEMOTHERAPY MAY. 1988 VOL.36 S-1 CHEMOTHERAPY CHEMOTHERAPY MAY. 1988 VOL.36 S-1 CHEMOTHERAPY
 VOL.32 S-9 CHEMOTHERAPY Table 1 Minimum inhibitory concentrations of AC-1370, CPZ and CAZ Table 2 Efficacy of AC-1370 and CPZ against systemic infections in mice *Inoculum size: 106 cells/ml * 95% confidence
VOL.32 S-9 CHEMOTHERAPY Table 1 Minimum inhibitory concentrations of AC-1370, CPZ and CAZ Table 2 Efficacy of AC-1370 and CPZ against systemic infections in mice *Inoculum size: 106 cells/ml * 95% confidence
VOL.35 S-2 CHEMOTHERAPY Table 1 Sex and age distribution Table 2 Applications of treatment with carumonam Table 3 Concentration of carumonam in human
 CHEMOTHERAPY Fig. 1 Chemical structure of carumonam Disodium(+)-(Z)-CCE1-(2-amino-4-thiazoly1)-2-[[(2S, -(carbamoyloxymethyl)-4-oxo-1-sulfonato-3-azetidinyll -2-oxoethylidene] amino] oxy] acetate 3S)-2
CHEMOTHERAPY Fig. 1 Chemical structure of carumonam Disodium(+)-(Z)-CCE1-(2-amino-4-thiazoly1)-2-[[(2S, -(carbamoyloxymethyl)-4-oxo-1-sulfonato-3-azetidinyll -2-oxoethylidene] amino] oxy] acetate 3S)-2
 VOL.30 NO.10 CHEMOTHERAPY 1123 Fig,1 Group B case 6 hepatolithiasis,e.k.66 y.0.,f.45kg Postoperative wound infection Fig.2 Group B case 15 gastric cancer,k.k.60 y.o.,m. Postoperative peritonitis Fig.3
VOL.30 NO.10 CHEMOTHERAPY 1123 Fig,1 Group B case 6 hepatolithiasis,e.k.66 y.0.,f.45kg Postoperative wound infection Fig.2 Group B case 15 gastric cancer,k.k.60 y.o.,m. Postoperative peritonitis Fig.3
CHEMOTHERAPY FEB Table 1 Background of volunteers
 CHEMOTHERAPY FEB. 1985 Table 1 Background of volunteers Table 3 Reproducibility of saisomicln In the EIA and the RIA Fig.1 Comparison of the EIA with the RIA or bioassay of sisomicin Table 4 Blood levels
CHEMOTHERAPY FEB. 1985 Table 1 Background of volunteers Table 3 Reproducibility of saisomicln In the EIA and the RIA Fig.1 Comparison of the EIA with the RIA or bioassay of sisomicin Table 4 Blood levels
 CHEMOTHERAPY AUG. 1982 VOL. 30 NO. 8 CHEMOTHERAPY Fig.1 Relation between various-closis of cefazolin and detection rate of organisms in heart blood of dying mice with E. coli and P. aeruginosa infection
CHEMOTHERAPY AUG. 1982 VOL. 30 NO. 8 CHEMOTHERAPY Fig.1 Relation between various-closis of cefazolin and detection rate of organisms in heart blood of dying mice with E. coli and P. aeruginosa infection
 2) Goetz, A., Tsuneishi, N.: Application of molecular filter membranes to the bacteriological analysis of water, J. Am. Water Works Assn., 43 (12): 943-969,1951. 3) Clark, H.F. et al.: The membrane filter
2) Goetz, A., Tsuneishi, N.: Application of molecular filter membranes to the bacteriological analysis of water, J. Am. Water Works Assn., 43 (12): 943-969,1951. 3) Clark, H.F. et al.: The membrane filter
400 46 THE JAPANESE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS 65 6 Dec. 2012 LVFX 100 mg 3 / 7 150 mg 2 / 7 2 2006 2008 9 LVFX PK PD 2009 7 100 mg 1 3 500 mg 1 1 AUC/MIC
 Dec. 2012 THE JAPANESE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS 65 6 399 45 2012 11 5 LVFX 500 mg 1 1 20 Chlamydia trachomatis C. trachomatismycoplasma genitalium M. genitalium LVFX 1 500 mg 1 1 7 22 22 C. trachomatis 17
Dec. 2012 THE JAPANESE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS 65 6 399 45 2012 11 5 LVFX 500 mg 1 1 20 Chlamydia trachomatis C. trachomatismycoplasma genitalium M. genitalium LVFX 1 500 mg 1 1 7 22 22 C. trachomatis 17
 Table 1.Concentration of gatifloxacin (Middle-ear) Table 2.Concentration of gatifloxacin (Paranasal sinuses) Table 3.Concentration of gatifloxacin (Tonsil) Table 4.No.of patients studied Table 5.Background
Table 1.Concentration of gatifloxacin (Middle-ear) Table 2.Concentration of gatifloxacin (Paranasal sinuses) Table 3.Concentration of gatifloxacin (Tonsil) Table 4.No.of patients studied Table 5.Background
(ABPC), Carbenicillin (CBPC), Surbenicillin (SBPC), Piperacillin (PIPC), Cephalexin (CEX), Cefaclor (CCL), Cephalothin (CET), Cefazolin (CEZ), Cefotia
 Key words: Blood culture, Trend of bacterial isolation, Increasing of staphylococcus, Use of new cephems (ABPC), Carbenicillin (CBPC), Surbenicillin (SBPC), Piperacillin (PIPC), Cephalexin (CEX), Cefaclor
Key words: Blood culture, Trend of bacterial isolation, Increasing of staphylococcus, Use of new cephems (ABPC), Carbenicillin (CBPC), Surbenicillin (SBPC), Piperacillin (PIPC), Cephalexin (CEX), Cefaclor
 CHEMOTHERAPY 34 T-2588の APR.1986 嫌 気 性 菌 に 対す る抗 菌 作 用 に つ い て 沢 赫 代 神 野 英 毅 青 木 誠 小 林 と よ子 渡 辺 邦 友 上 野 一 恵 岐阜大学医学部附属嫌気性菌実験施設 新 し く 開 発 さ れ た 経 口 用 エ ス テ ル 型 セ フ ェ ム 系 抗 生 剤T-2588の 口 剤 で あ るcephalexin(CEX),cefaclor(CCL)
CHEMOTHERAPY 34 T-2588の APR.1986 嫌 気 性 菌 に 対す る抗 菌 作 用 に つ い て 沢 赫 代 神 野 英 毅 青 木 誠 小 林 と よ子 渡 辺 邦 友 上 野 一 恵 岐阜大学医学部附属嫌気性菌実験施設 新 し く 開 発 さ れ た 経 口 用 エ ス テ ル 型 セ フ ェ ム 系 抗 生 剤T-2588の 口 剤 で あ るcephalexin(CEX),cefaclor(CCL)
Staphylococcus sp. K.pneumoniae P.mirabilis C.freundii E. cloacae Serratia sp. P. aeruginosa ml, Enterococcus avium >100ƒÊg/ml
 CHEMOTHERAPY SEPT. 1992 cefoperazone ceftazidime (CAZ), imipenem (IPM) Staphylococcus sp., Enterococcus (CPZ), faecalis, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Citrobacter freundii, Enterobacter cloacae,
CHEMOTHERAPY SEPT. 1992 cefoperazone ceftazidime (CAZ), imipenem (IPM) Staphylococcus sp., Enterococcus (CPZ), faecalis, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Citrobacter freundii, Enterobacter cloacae,
2 The Bulletin of Meiji University of Integrative Medicine 3, Yamashita 10 11
 1-122013 1 2 1 2 20 2,000 2009 12 1 2 1,362 68.1 2009 1 1 9.5 1 2.2 3.6 0.82.9 1.0 0.2 2 4 3 1 2 4 3 Key words acupuncture and moxibustion Treatment with acupuncture, moxibustion and Anma-Massage-Shiatsu
1-122013 1 2 1 2 20 2,000 2009 12 1 2 1,362 68.1 2009 1 1 9.5 1 2.2 3.6 0.82.9 1.0 0.2 2 4 3 1 2 4 3 Key words acupuncture and moxibustion Treatment with acupuncture, moxibustion and Anma-Massage-Shiatsu
 1) Chemical name: Fig. 1 Chemical structure of TE-031 (-)-(3R,4S,5S,6R,7R,9R,11R,12R,13S,14R)-4-[(2, PYranosyl)oxy]-14-ethyl-12,13-dihydroxy-7-meth 6-dideoxy-3-C-methyl-3-O-methyl-a-L-ribo-hexo- oxy-3,5,7,9,11,13-hexamethy1-6-[[3,4,6-trideoxy-3-
1) Chemical name: Fig. 1 Chemical structure of TE-031 (-)-(3R,4S,5S,6R,7R,9R,11R,12R,13S,14R)-4-[(2, PYranosyl)oxy]-14-ethyl-12,13-dihydroxy-7-meth 6-dideoxy-3-C-methyl-3-O-methyl-a-L-ribo-hexo- oxy-3,5,7,9,11,13-hexamethy1-6-[[3,4,6-trideoxy-3-
epidermidis, Enterococcus faecalis, Enterococcus Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis, indolepositive Proteus spp., Enterobacter spp., Serratia
 epidermidis, Enterococcus faecalis, Enterococcus Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis, indolepositive Proteus spp., Enterobacter spp., Serratia Table 3. Overall clinical efficacy of cefozopran in
epidermidis, Enterococcus faecalis, Enterococcus Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis, indolepositive Proteus spp., Enterobacter spp., Serratia Table 3. Overall clinical efficacy of cefozopran in
 Table 1 Classification of female patients with vealcal irritating symptom by their signs Urination pain with other vesical irritability or not Table 2 Serum levels of DL-8280 after a single oral administration
Table 1 Classification of female patients with vealcal irritating symptom by their signs Urination pain with other vesical irritability or not Table 2 Serum levels of DL-8280 after a single oral administration
Fig.2. Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates of S. epidermidis (24 strains, 106 CFU/ml) Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus epider- midis Ent
 Fig.2. Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates of S. epidermidis (24 strains, 106 CFU/ml) Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus epider- midis Enterococcus faecalis Klebsiella pneumoniae, Morganella
Fig.2. Sensitivity distribution of clinical isolates of S. epidermidis (24 strains, 106 CFU/ml) Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus epider- midis Enterococcus faecalis Klebsiella pneumoniae, Morganella
日本化学療法学会雑誌第53巻第S-3号
 moxifloxacin in vitro moxifloxacin in vitro 17 9 6 17 11 21 moxifloxacinmflx in vitro cefdinir CFDNclavulanic acidamoxicillincvaampcclarithromycincamclindamycincldm levofloxacinlvfx 1MFLX Clostridium clostridiiformeclostridium
moxifloxacin in vitro moxifloxacin in vitro 17 9 6 17 11 21 moxifloxacinmflx in vitro cefdinir CFDNclavulanic acidamoxicillincvaampcclarithromycincamclindamycincldm levofloxacinlvfx 1MFLX Clostridium clostridiiformeclostridium
The Journal of the Japan Academy of Nursing Administration and Policies Vol 7, No 2, pp 19 _ 30, 2004 Survey on Counseling Services Performed by Nursi
 The Journal of the Japan Academy of Nursing Administration and Policies Vol 7, No 2, pp 19 _ 30, 2004 Survey on Counseling Services Performed by Nursing Professionals for Diabetic Outpatients Not Using
The Journal of the Japan Academy of Nursing Administration and Policies Vol 7, No 2, pp 19 _ 30, 2004 Survey on Counseling Services Performed by Nursing Professionals for Diabetic Outpatients Not Using
m m Satoshi SATO 48
 46 22 3 23 REPORT OF HYDROGRAPHIC AND OCEANOGRAPHIC RESEARCHES No.46 March, 2010 Activities on Tides at Hydrographic Department in Meiji Era Satoshi SATO : Environmental and Oceanographic Division Abstract
46 22 3 23 REPORT OF HYDROGRAPHIC AND OCEANOGRAPHIC RESEARCHES No.46 March, 2010 Activities on Tides at Hydrographic Department in Meiji Era Satoshi SATO : Environmental and Oceanographic Division Abstract
CHEMOTHERAPY DEC phvlococcus aureus Staphylococcus Enterococcus faecalis Escherichia Klebsiella pneumoniae Serratia marcescens Pseudomonas cepac
 CHEMOTHERAPY DEC. 1988 phvlococcus aureus Staphylococcus Enterococcus faecalis Escherichia Klebsiella pneumoniae Serratia marcescens Pseudomonas cepacia 1 Bacteroides bivius Propionibacterium granulosum
CHEMOTHERAPY DEC. 1988 phvlococcus aureus Staphylococcus Enterococcus faecalis Escherichia Klebsiella pneumoniae Serratia marcescens Pseudomonas cepacia 1 Bacteroides bivius Propionibacterium granulosum
 Key words: yeast, Etest(R), microdilution method, MIC Table 1 MICs of quality control strains The data shown are the range of MIC performed in triplicate Table 2 Renge of MICs, MIC50s and MIC90s for 81
Key words: yeast, Etest(R), microdilution method, MIC Table 1 MICs of quality control strains The data shown are the range of MIC performed in triplicate Table 2 Renge of MICs, MIC50s and MIC90s for 81
 VOL. 17 NO. 7 CHEMOTHERAPY 1305 1) W. BRumFirr et al. : Clinical and laboratory studies with carbenicillin. Lancet 1: 1289~ 1293, 1967 2) E. T. KNUDSEN et al. : A new semisynthetic penicillin active against
VOL. 17 NO. 7 CHEMOTHERAPY 1305 1) W. BRumFirr et al. : Clinical and laboratory studies with carbenicillin. Lancet 1: 1289~ 1293, 1967 2) E. T. KNUDSEN et al. : A new semisynthetic penicillin active against
Table 1. Antibacterial activitiy of grepafloxacin and other antibiotics against clinical isolates
 Table 1. Antibacterial activitiy of grepafloxacin and other antibiotics against clinical isolates Table 2-1. Summary of patients treated with grepafloxacin for respiratory infection 1) Out: outpatient,
Table 1. Antibacterial activitiy of grepafloxacin and other antibiotics against clinical isolates Table 2-1. Summary of patients treated with grepafloxacin for respiratory infection 1) Out: outpatient,
 Table 1. Antibacterial activity of cefdinir, cefixime, cefteram, cefuroxime, cefaclor and amoxicillin against standard strains Inoculum size: 108 cells/ml CFDN: cefdinir, CFIX: cefixime, CFTM: cefteram,
Table 1. Antibacterial activity of cefdinir, cefixime, cefteram, cefuroxime, cefaclor and amoxicillin against standard strains Inoculum size: 108 cells/ml CFDN: cefdinir, CFIX: cefixime, CFTM: cefteram,
VOL. 34 S-2 CHEMOTH8RAPY 913
 VOL. 34 S-2 CHEMOTH8RAPY 913 914 CHEMOTHERAPY APR. 1986 Fig. 1 Chemical structure of T-2588 and T-2525 T- 2588 pivaloyloxymethyl (+ )- (6 R, 7 R)-7-[(Z)-2- (2-amino- 4-thiazolyl)-2-methox yiminoacetamido]-3-[(
VOL. 34 S-2 CHEMOTH8RAPY 913 914 CHEMOTHERAPY APR. 1986 Fig. 1 Chemical structure of T-2588 and T-2525 T- 2588 pivaloyloxymethyl (+ )- (6 R, 7 R)-7-[(Z)-2- (2-amino- 4-thiazolyl)-2-methox yiminoacetamido]-3-[(
Fig. 1 Chemical structure of norfioxacin (AM-715)
 Fig. 1 Chemical structure of norfioxacin (AM-715) Table 1 Serum and biliary concentration of norfloxacin (AM-715) Table 2 Protocol for clinical evaluation of norfloxacin (AM-715) in the treatment of biliary
Fig. 1 Chemical structure of norfioxacin (AM-715) Table 1 Serum and biliary concentration of norfloxacin (AM-715) Table 2 Protocol for clinical evaluation of norfloxacin (AM-715) in the treatment of biliary
 Table 1. Influence of urine ph on MBCs of new quinolones against Escherichia coli NIHJ JC-2 and Pseudomonas aeruginosa 18S; MBCs in urine were compared with those in Miieller-Hinton broth. Table 2. Influence
Table 1. Influence of urine ph on MBCs of new quinolones against Escherichia coli NIHJ JC-2 and Pseudomonas aeruginosa 18S; MBCs in urine were compared with those in Miieller-Hinton broth. Table 2. Influence
 Table 1.Distribution and number of cases with acute upper respiratory tract infections classified according to antimicrobial agents administered Table 2. Distribution of cases which were enrolled to set
Table 1.Distribution and number of cases with acute upper respiratory tract infections classified according to antimicrobial agents administered Table 2. Distribution of cases which were enrolled to set
 Table 1 Patients with various renal function * Ccr, Creatinine clearance ml/min per 1. 48 m2 ** C.V.D., Cerebral vascular disease ; C.R F., Chronic renal failure ; H.D., Hemoclialysis ; D., Dialyzer ;
Table 1 Patients with various renal function * Ccr, Creatinine clearance ml/min per 1. 48 m2 ** C.V.D., Cerebral vascular disease ; C.R F., Chronic renal failure ; H.D., Hemoclialysis ; D., Dialyzer ;
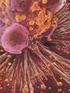
Fig. 1 Clinical findings and extent of inflammation area in female urethrocystitis Fig. 2 Classification and distribution of female patients with blad
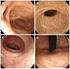 Key words: Female with bladder irritability, Subjective symptoms, Pyuria, Bacteriuria Fig. 1 Clinical findings and extent of inflammation area in female urethrocystitis Fig. 2 Classification and distribution
Key words: Female with bladder irritability, Subjective symptoms, Pyuria, Bacteriuria Fig. 1 Clinical findings and extent of inflammation area in female urethrocystitis Fig. 2 Classification and distribution
Key words : 7432-S, Oral cephem, Urinary tract infection Fig. 1. Chemical structure of 7432-S.
 Key words : 7432-S, Oral cephem, Urinary tract infection Fig. 1. Chemical structure of 7432-S. Table 1. Clinical summary of acute uncomplicated cystitis patients treated with 7432-S UTI : Criteria by the
Key words : 7432-S, Oral cephem, Urinary tract infection Fig. 1. Chemical structure of 7432-S. Table 1. Clinical summary of acute uncomplicated cystitis patients treated with 7432-S UTI : Criteria by the
 A comparison of abdominal versus vaginal hysterectomy for leiomyoma and adenomyosis Kenji ARAHORI, Hisasi KATAYAMA, Suminori NIOKA Department of Obstetrics and Gnecology, National Maizuru Hospital,Kyoto,
A comparison of abdominal versus vaginal hysterectomy for leiomyoma and adenomyosis Kenji ARAHORI, Hisasi KATAYAMA, Suminori NIOKA Department of Obstetrics and Gnecology, National Maizuru Hospital,Kyoto,
