最小2乗法
|
|
|
- くにひと こやぎ
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ( ) / 42
2 X Y Y = f (X ; Z) linear regression model X Y slope X 1 Y (X, Y ) 1 (X, Y ) ( ) / 42
3 1 β = β = β (4.2) = β 0 + β (4.3) ( ) / 42
4 = β 0 + β + (4.4) ( ) / 42
5 1 Y i = β 0 + β 1 X i + u i, i = 1, 2,..., n (4.5) Y i dependent variable X i explanatory variable, regressor independent variable β 0 + β 1 X population regression line (function) X Y β 0 intercept X = 0 Y β 1 slope β 0 parameter coefficient u i error term β 0 + β 1 X i Y i X i ( ) / 42
6 Y i = β 0 + β 1 X i + u i, i = 1, 2,..., n (4.5) β 0 β 1 X i u i Y i Figure 4.1 (X i, Y i ) β 0 β 1 1 u i (X i, Y i, u i ) (X, Y, u) β 0 β 1 β 0 β 1 ( ) / 42
7 Figure 4.1 Scatter plot of test score vs. student-teacher ratio (hypothetical data)
8 β 0 β 1 Table 4.1. Figure 4.2. u i ( ) / 42
9 Table 4.1 Summary statistics of California school district data (Eviews output) TESTSCR STR Mean Median Maximum Minimum Std. Dev Skewness Kurtosis Jarque-Bera Probability Sum Sum Sq. Dev Observations
10 Figure 4.2 Scatter plot of Test score vs. student-teacher ratio (California school district data)
11 1 X Y 2 Y E[Y ] Y = argmin m n (Y i m) 2 (β 0, β 1 ) i=1 ( ) / 42
12 (β 0, β 1 ) (b 0, b 1 ) b 0 + b 1 X X = X i Y b 0 + b 1 X i Y i (b 0 + b 1 X i ) n (Y i b 0 b 1 X i ) 2 (4.6) i=1 (b 0, b 1 ) ( ) / 42
13 b 0 b 1 n (Y i b 0 b 1 X i ) 2 = 0 i=1 n (Y i b 0 b 1 X i ) 2 = 0 i=1 (b 0, b 1 ) ˆβ 1 = b 1 = n i=1 (X i X )(Y i Y ) n i=1 (X = s XY i X ) 2 sx 2 = ˆβ 0 = b 0 = Y b 1 X ( ) / 42
14 OLS Ordinary Least Squares estimators ( ˆβ 0, ˆβ 1 ) OLS regression line OLS Y = ˆβ 0 + ˆβ 1 X fitted value X i X i Y X i Y i Ŷ i = ˆβ 0 + ˆβ 1 X i (4.9) ( ) / 42
15 residual Y i Ŷ i û i = Y i Ŷi (4.10) error OLS OLS ( ) / 42
16 Figure 4.3 The estimated regression line for the California data
17 (β 0, β 1 ) OLS OLS OLS OLS ( ) / 42
18 OLS MS-Excel ( ) / 42
19 OLS OLS OLS i.i.d. 3 4 OLS ( ) / 42
20 1 E[u i X i ] = 0 X i u i u i X i Y i Figure 4.4 Randomized experiment E[u X = 0] = 0 E[u X = 1] = 0 ( ) / 42
21 Figure 4.4 The conditional probability distributions and the population regression line
22 1 E[u i X i ] = 0 E[u i X i ] = 0 = corr(x i, u i ) = 0 orthogonality condition exogenous endogenous ( ) / 42
23 2 (X i, Y i ) i.i.d. X i Oversampling ( ) / 42
24 3 0 < E[X 4 i ], E[u 4 i ] < X i u i 4 OLS 4 Figure 4.5 ( ) / 42
25 Figure 4.5 The sensitivity of OLS to large outliers
26 OLS OLS OLS ( ) / 42
27 OLS OLS OLS OLS ( ) / 42
28 n OLS E[Y ] = µ y Y d N ( µ y, σ 2 Y E[ ˆβ 0 ] = β 0, E[ ˆβ 1 ] = β 1 (4.20) ) ( ) / 42
29 OLS OLS ˆβ 1 = n i=1 (X i X )(Y i Y ) n i=1 (X i X ) 2, ˆβ 0 = Y ˆβ 1 X Y i = β 0 + β 1 X i + u i Y i Y = β 1 (X i X ) + u i u ˆβ 1 ˆβ 1 = n i=1 (X i X )(β 1 (X i X ) + u i u) n i=1 (X i X ) 2 = β 1 + n i=1 (X i X )u i n i=1 (X i X ) 2 E[ ˆβ 1 ] = β 1 + E = β 1 + E [ [ n i=1 E (X ]] i X )u i n i=1 (X X i X ) 2 i [ n i=1 (X i X )E [u i X i ] n i=1 (X i X ) 2 ] = β 1 Q.E.D. ( ) / 42
30 OLS n OLS 2 OLS ˆβ 1 = β 1 + P n i=1 (X i X )u i P n i=1 (X i X ) 2 X µ X v i (X i X )u i E[u i X i ] = 0 E[v i ] = 0 i.i.d. var(v i ) = var[(x i X )u i ] < v d N(0, σ 2 v /n) var(x ) ˆβ 1 β 1 = v/var(x ) d ˆβ 1 N β 1, var((x µ «X )u) Q.E.D. n(var(x )) 2 ( ) / 42
31 n > 100 OLS X i OLS ˆβ 1 Fig 4.6 ( ) / 42
32 Figure 4.6 The variance of beta and the variance of X
33 β = 0 1 H 0 : E[Y ] = µ Y,0 v.s. H 1 : E[Y ] µ Y,0 2 Y SE(Y ) 3 t t = (Y µ Y,0 )/SE(Y ) 4 p H 0 H 0 n t d N(0, 1) p = 2Φ( t act ) ( ) / 42
34 OLS ˆβ d N [1 ] H 0 : β 1 = β 1,0 v.s. H 1 : β 1 β 1,0 (5.2) [2 ] OLS ˆβ 1 SE( ˆβ 1 ) SE( ˆβ 1 ) = ˆσ 2ˆβ1 = 1 1 n n 2 i=1 (X i X ) 2 ûi 2 n [ 1 n n i=1 (X (5.3) i X ) 2 ] 2 σ 2ˆβ 1 = 1 n var[(x i µ X )u i ] (var[x i ]) 2 (5.4) ( ) / 42
35 OLS [3 ] t t = = ˆβ 1 β 1,0 SE( ˆβ 1 ) (5.5) [4 ] p H 0 [ p = Pr H0 ˆβ ] 1 β 1,0 > ˆβ act 1 β 1,0 = Pr H0 ( t > t act ) ˆβ d N (5.6) p = Pr H0 ( Z > t act ) = 2Φ( t act ) (5.7) H 0 ( ) / 42
36 OLS t p H 0 : β 1 = β 1,0 v.s. H 1 : β 1 < β 1,0 (5.9) p = Pr H0 (Z < t act ) = Φ(t act ) (5.10) ( ) / 42
37 (β 0, β 1 ) β 1 95% 5% β 95% 95% 5% H 0 : β 1 = β 1,0 β 1,0 ( ˆβ 1 ± 1.96SE( ˆβ 1 )) ( ˆβ SE( ˆβ 1 ), ˆβ SE( ˆβ 1 )) ( ) / 42
38 X x Y y = β 1 x x ˆβ 1 ˆβ 1 ( ) ( ˆβ SE( ˆβ 1 )) x, ( ˆβ SE( ˆβ 1 )) x (5.13) ( ) / 42
39 2 2 D i = 0, 1 indicator variable, dummy variable β 1 OLS D i = 0 Y i = β 0 + u i D i = 1 Y i = β 0 + β 1 + u i E[Y i D i = 0] = β 0, E[Y i D i = 1] = β 0 + β 1 (5.16, 17) ( ) / 42
40 2 β 1 2 H 0 : β 1 = 0 β 1 OLS 2 ( ) / 42
41 OLS OLS R 2 Y i X i Y i Standard Error of the Regression Y i ( ) / 42
42 R 2 Y i X i Y i = Ŷi + û i R 2 = Ŷi Y i = ESS n TSS = i=1 (Ŷi Y ) 2 n i=1 (Y (4.16) i Y ) 2 ESS (explained sum of squares) TSS (total sum of squares) SSR: sum of squared residuals R 2 = ESS TSS SSR = = 1 SSR n TSS TSS TSS = 1 i=1 û2 i n i=1 (Y i Y ) 2 (4.18) ( ) / 42
43 R 2 [0, 1] ˆβ 1 = 0 X i Y i Ŷ i = Y, i ESS Ŷ i = Y i, i û i = 0, i ESS TSS R 2 = 1 R 2 1 Y i ( ) / 42
44 SER u i {u 1, u 2,..., u n } {û 1, û 2,..., û n } SER = sû, s 2 û = 1 n 2 n i=1 û 2 i = SSR n 2 (4.19) n 2 2 n ( ) / 42
45 E[u i X i ] = 0 X i E[u 2 i X i] i X i homoskedasticity X i E[u 2 i X i] heteroskedasticity (X i, Y i ) i.i.d. Fig4.4. Fig 5.2. ( ) / 42
46 Figure 5.2 An example of homoskedasticity
47 Figure 5.2 An example of heteroskedasticity
48 Earnings i = β 0 + β 1 Male i + u i (5.19) Male i β 1 var(u i Male i ) Male i u i D i = 0, 1 ( ) / 42
49 Figure 5.3 Scatter plot of hourly earnings and years of education Heteroskedastic or homoskedastic?
50 OLS Gauss-Markov OLS {Y 1, Y 2,..., Y n } efficient OLS BLUE Best Linear Unbiased Estimator OLS ( ) / 42
51 OLS Homoskedasticity-only var( ˆβ 1 ) var( ˆβ 1 ) = var[(x µ X )u] n(var(x )) 2 = var(u i) nvar(x i ) (5.22) Homoskedasticity-only var( ˆβ 1 ) var( ˆβ 1 ) t Heteroskedasticity-robust Eicker-Huber-White robust ( ) / 42
52 WLS Weighted Least Squares OLS BLUE OLS WLS var(u i /X i ) OLS var(u i /X i ) WLS ( ) / 42
第11回:線形回帰モデルのOLS推定
 11 OLS 2018 7 13 1 / 45 1. 2. 3. 2 / 45 n 2 ((y 1, x 1 ), (y 2, x 2 ),, (y n, x n )) linear regression model y i = β 0 + β 1 x i + u i, E(u i x i ) = 0, E(u i u j x i ) = 0 (i j), V(u i x i ) = σ 2, i
11 OLS 2018 7 13 1 / 45 1. 2. 3. 2 / 45 n 2 ((y 1, x 1 ), (y 2, x 2 ),, (y n, x n )) linear regression model y i = β 0 + β 1 x i + u i, E(u i x i ) = 0, E(u i u j x i ) = 0 (i j), V(u i x i ) = σ 2, i
4 OLS 4 OLS 4.1 nurseries dual c dual i = c + βnurseries i + ε i (1) 1. OLS Workfile Quick - Estimate Equation OK Equation specification dual c nurser
 1 EViews 2 2007/5/17 2007/5/21 4 OLS 2 4.1.............................................. 2 4.2................................................ 9 4.3.............................................. 11 4.4
1 EViews 2 2007/5/17 2007/5/21 4 OLS 2 4.1.............................................. 2 4.2................................................ 9 4.3.............................................. 11 4.4
Stata11 whitepapers mwp-037 regress - regress regress. regress mpg weight foreign Source SS df MS Number of obs = 74 F(
 mwp-037 regress - regress 1. 1.1 1.2 1.3 2. 3. 4. 5. 1. regress. regress mpg weight foreign Source SS df MS Number of obs = 74 F( 2, 71) = 69.75 Model 1619.2877 2 809.643849 Prob > F = 0.0000 Residual
mwp-037 regress - regress 1. 1.1 1.2 1.3 2. 3. 4. 5. 1. regress. regress mpg weight foreign Source SS df MS Number of obs = 74 F( 2, 71) = 69.75 Model 1619.2877 2 809.643849 Prob > F = 0.0000 Residual
第13回:交差項を含む回帰・弾力性の推定
 13 2018 7 27 1 / 31 1. 2. 2 / 31 y i = β 0 + β X x i + β Z z i + β XZ x i z i + u i, E(u i x i, z i ) = 0, E(u i u j x i, z i ) = 0 (i j), V(u i x i, z i ) = σ 2, i = 1, 2,, n x i z i 1 3 / 31 y i = β
13 2018 7 27 1 / 31 1. 2. 2 / 31 y i = β 0 + β X x i + β Z z i + β XZ x i z i + u i, E(u i x i, z i ) = 0, E(u i u j x i, z i ) = 0 (i j), V(u i x i, z i ) = σ 2, i = 1, 2,, n x i z i 1 3 / 31 y i = β
k2 ( :35 ) ( k2) (GLM) web web 1 :
 2012 11 01 k2 (2012-10-26 16:35 ) 1 6 2 (2012 11 01 k2) (GLM) kubo@ees.hokudai.ac.jp web http://goo.gl/wijx2 web http://goo.gl/ufq2 1 : 2 2 4 3 7 4 9 5 : 11 5.1................... 13 6 14 6.1......................
2012 11 01 k2 (2012-10-26 16:35 ) 1 6 2 (2012 11 01 k2) (GLM) kubo@ees.hokudai.ac.jp web http://goo.gl/wijx2 web http://goo.gl/ufq2 1 : 2 2 4 3 7 4 9 5 : 11 5.1................... 13 6 14 6.1......................
4.9 Hausman Test Time Fixed Effects Model vs Time Random Effects Model Two-way Fixed Effects Model
 1 EViews 5 2007 7 11 2010 5 17 1 ( ) 3 1.1........................................... 4 1.2................................... 9 2 11 3 14 3.1 Pooled OLS.............................................. 14
1 EViews 5 2007 7 11 2010 5 17 1 ( ) 3 1.1........................................... 4 1.2................................... 9 2 11 3 14 3.1 Pooled OLS.............................................. 14
80 X 1, X 2,, X n ( λ ) λ P(X = x) = f (x; λ) = λx e λ, x = 0, 1, 2, x! l(λ) = n f (x i ; λ) = i=1 i=1 n λ x i e λ i=1 x i! = λ n i=1 x i e nλ n i=1 x
 80 X 1, X 2,, X n ( λ ) λ P(X = x) = f (x; λ) = λx e λ, x = 0, 1, 2, x! l(λ) = n f (x i ; λ) = n λ x i e λ x i! = λ n x i e nλ n x i! n n log l(λ) = log(λ) x i nλ log( x i!) log l(λ) λ = 1 λ n x i n =
80 X 1, X 2,, X n ( λ ) λ P(X = x) = f (x; λ) = λx e λ, x = 0, 1, 2, x! l(λ) = n f (x i ; λ) = n λ x i e λ x i! = λ n x i e nλ n x i! n n log l(λ) = log(λ) x i nλ log( x i!) log l(λ) λ = 1 λ n x i n =
AR(1) y t = φy t 1 + ɛ t, ɛ t N(0, σ 2 ) 1. Mean of y t given y t 1, y t 2, E(y t y t 1, y t 2, ) = φy t 1 2. Variance of y t given y t 1, y t
 87 6.1 AR(1) y t = φy t 1 + ɛ t, ɛ t N(0, σ 2 ) 1. Mean of y t given y t 1, y t 2, E(y t y t 1, y t 2, ) = φy t 1 2. Variance of y t given y t 1, y t 2, V(y t y t 1, y t 2, ) = σ 2 3. Thus, y t y t 1,
87 6.1 AR(1) y t = φy t 1 + ɛ t, ɛ t N(0, σ 2 ) 1. Mean of y t given y t 1, y t 2, E(y t y t 1, y t 2, ) = φy t 1 2. Variance of y t given y t 1, y t 2, V(y t y t 1, y t 2, ) = σ 2 3. Thus, y t y t 1,
(lm) lm AIC 2 / 1
 W707 s-taiji@is.titech.ac.jp 1 / 1 (lm) lm AIC 2 / 1 : y = β 1 x 1 + β 2 x 2 + + β d x d + β d+1 + ϵ (ϵ N(0, σ 2 )) y R: x R d : β i (i = 1,..., d):, β d+1 : ( ) (d = 1) y = β 1 x 1 + β 2 + ϵ (d > 1) y
W707 s-taiji@is.titech.ac.jp 1 / 1 (lm) lm AIC 2 / 1 : y = β 1 x 1 + β 2 x 2 + + β d x d + β d+1 + ϵ (ϵ N(0, σ 2 )) y R: x R d : β i (i = 1,..., d):, β d+1 : ( ) (d = 1) y = β 1 x 1 + β 2 + ϵ (d > 1) y
<4D F736F F D20939D8C7689F090CD985F93C18EEA8D758B E646F63>
 Gretl OLS omitted variable omitted variable AIC,BIC a) gretl gretl sample file Greene greene8_3 Add Define new variable l_g_percapita=log(g/pop) Pg,Y,Pnc,Puc,Ppt,Pd,Pn,Ps Add logs of selected variables
Gretl OLS omitted variable omitted variable AIC,BIC a) gretl gretl sample file Greene greene8_3 Add Define new variable l_g_percapita=log(g/pop) Pg,Y,Pnc,Puc,Ppt,Pd,Pn,Ps Add logs of selected variables
 ( 30 ) 30 4 5 1 4 1.1............................................... 4 1.............................................. 4 1..1.................................. 4 1.......................................
( 30 ) 30 4 5 1 4 1.1............................................... 4 1.............................................. 4 1..1.................................. 4 1.......................................
28
 y i = Z i δ i +ε i ε i δ X y i = X Z i δ i + X ε i [ ] 1 δ ˆ i = Z i X( X X) 1 X Z i [ ] 1 σ ˆ 2 Z i X( X X) 1 X Z i Z i X( X X) 1 X y i σ ˆ 2 ˆ σ 2 = [ ] y i Z ˆ [ i δ i ] 1 y N p i Z i δ ˆ i i RSTAT
y i = Z i δ i +ε i ε i δ X y i = X Z i δ i + X ε i [ ] 1 δ ˆ i = Z i X( X X) 1 X Z i [ ] 1 σ ˆ 2 Z i X( X X) 1 X Z i Z i X( X X) 1 X y i σ ˆ 2 ˆ σ 2 = [ ] y i Z ˆ [ i δ i ] 1 y N p i Z i δ ˆ i i RSTAT
Microsoft Word - 計量研修テキスト_第5版).doc
 Q10-2 テキスト P191 1. 記述統計量 ( 変数 :YY95) 表示変数として 平均 中央値 最大値 最小値 標準偏差 観測値 を選択 A. 都道府県別 Descriptive Statistics for YY95 Categorized by values of PREFNUM Date: 05/11/06 Time: 14:36 Sample: 1990 2002 Included
Q10-2 テキスト P191 1. 記述統計量 ( 変数 :YY95) 表示変数として 平均 中央値 最大値 最小値 標準偏差 観測値 を選択 A. 都道府県別 Descriptive Statistics for YY95 Categorized by values of PREFNUM Date: 05/11/06 Time: 14:36 Sample: 1990 2002 Included
Part 1 GARCH () ( ) /24, p.2/93
 基盤研究 A 統計科学における数理的手法の理論と応用 ( 研究代表者 : 谷口正信 ) によるシンポジウム 計量ファイナンスと時系列解析法の新たな展開 平成 20 年 1 月 24 日 ~26 日香川大学 Realized Volatility の長期記憶性について 1 研究代表者 : 前川功一 ( 広島経済大学 ) 共同研究者 : 得津康義 ( 広島経済大学 ) 河合研一 ( 統計数理研究所リスク解析戦略研究センター
基盤研究 A 統計科学における数理的手法の理論と応用 ( 研究代表者 : 谷口正信 ) によるシンポジウム 計量ファイナンスと時系列解析法の新たな展開 平成 20 年 1 月 24 日 ~26 日香川大学 Realized Volatility の長期記憶性について 1 研究代表者 : 前川功一 ( 広島経済大学 ) 共同研究者 : 得津康義 ( 広島経済大学 ) 河合研一 ( 統計数理研究所リスク解析戦略研究センター
1 15 R Part : website:
 1 15 R Part 4 2017 7 24 4 : website: email: http://www3.u-toyama.ac.jp/kkarato/ kkarato@eco.u-toyama.ac.jp 1 2 2 3 2.1............................... 3 2.2 2................................. 4 2.3................................
1 15 R Part 4 2017 7 24 4 : website: email: http://www3.u-toyama.ac.jp/kkarato/ kkarato@eco.u-toyama.ac.jp 1 2 2 3 2.1............................... 3 2.2 2................................. 4 2.3................................
BR001
 BR001 Stata 11 Stata Stata11 whitepaper mwp 3 mwp-027 22 mwp-028 / 40 mwp-001 logistic/logit 50 mwp-039 logistic/logit postestimation 60 mwp-040 margins 74 mwp-029 regress 90 mwp-037 regress postestimation
BR001 Stata 11 Stata Stata11 whitepaper mwp 3 mwp-027 22 mwp-028 / 40 mwp-001 logistic/logit 50 mwp-039 logistic/logit postestimation 60 mwp-040 margins 74 mwp-029 regress 90 mwp-037 regress postestimation
untitled
 2011/6/22 M2 1*1+2*2 79 2F Y YY 0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 0.000 0.002 0.004 0.006 0.008 0.010 0.012 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 Y 0 50 100 150 200 250 YY A (Y = X + e A ) B (YY = X + e B ) X 0.00 0.05 0.10
2011/6/22 M2 1*1+2*2 79 2F Y YY 0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 0.000 0.002 0.004 0.006 0.008 0.010 0.012 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 Y 0 50 100 150 200 250 YY A (Y = X + e A ) B (YY = X + e B ) X 0.00 0.05 0.10
1 Stata SEM LightStone 4 SEM 4.. Alan C. Acock, Discovering Structural Equation Modeling Using Stata, Revised Edition, Stata Press 3.
 1 Stata SEM LightStone 4 SEM 4.. Alan C. Acock, 2013. Discovering Structural Equation Modeling Using Stata, Revised Edition, Stata Press 3. 2 4, 2. 1 2 2 Depress Conservative. 3., 3,. SES66 Alien67 Alien71,
1 Stata SEM LightStone 4 SEM 4.. Alan C. Acock, 2013. Discovering Structural Equation Modeling Using Stata, Revised Edition, Stata Press 3. 2 4, 2. 1 2 2 Depress Conservative. 3., 3,. SES66 Alien67 Alien71,
y i OLS [0, 1] OLS x i = (1, x 1,i,, x k,i ) β = (β 0, β 1,, β k ) G ( x i β) 1 G i 1 π i π i P {y i = 1 x i } = G (
![y i OLS [0, 1] OLS x i = (1, x 1,i,, x k,i ) β = (β 0, β 1,, β k ) G ( x i β) 1 G i 1 π i π i P {y i = 1 x i } = G ( y i OLS [0, 1] OLS x i = (1, x 1,i,, x k,i ) β = (β 0, β 1,, β k ) G ( x i β) 1 G i 1 π i π i P {y i = 1 x i } = G (](/thumbs/82/85163103.jpg) 7 2 2008 7 10 1 2 2 1.1 2............................................. 2 1.2 2.......................................... 2 1.3 2........................................ 3 1.4................................................
7 2 2008 7 10 1 2 2 1.1 2............................................. 2 1.2 2.......................................... 2 1.3 2........................................ 3 1.4................................................
計量経済分析 2011 年度夏学期期末試験 担当 : 別所俊一郎 以下のすべてに答えなさい. 回答は日本語か英語でおこなうこと. 1. 次のそれぞれの記述が正しいかどうか判定し, 誤りである場合には理由, あるいはより適切な 記述はどのようなものかを述べなさい. (1) You have to wo
 計量経済分析 2011 年度夏学期期末試験 担当 : 別所俊一郎 以下のすべてに答えなさい. 回答は日本語か英語でおこなうこと. 1. 次のそれぞれの記述が正しいかどうか判定し, 誤りである場合には理由, あるいはより適切な 記述はどのようなものかを述べなさい. (1) You have to worry about perfect multicollinearity in the multiple
計量経済分析 2011 年度夏学期期末試験 担当 : 別所俊一郎 以下のすべてに答えなさい. 回答は日本語か英語でおこなうこと. 1. 次のそれぞれの記述が正しいかどうか判定し, 誤りである場合には理由, あるいはより適切な 記述はどのようなものかを述べなさい. (1) You have to worry about perfect multicollinearity in the multiple
σ t σ t σt nikkei HP nikkei4csv H R nikkei4<-readcsv("h:=y=ynikkei4csv",header=t) (1) nikkei header=t nikkei4csv 4 4 nikkei nikkei4<-dataframe(n
 R 1 R R R tseries fseries 1 tseries fseries R Japan(Tokyo) R library(tseries) library(fseries) 2 t r t t 1 Ω t 1 E[r t Ω t 1 ] ɛ t r t = E[r t Ω t 1 ] + ɛ t ɛ t 2 iid (independently, identically distributed)
R 1 R R R tseries fseries 1 tseries fseries R Japan(Tokyo) R library(tseries) library(fseries) 2 t r t t 1 Ω t 1 E[r t Ω t 1 ] ɛ t r t = E[r t Ω t 1 ] + ɛ t ɛ t 2 iid (independently, identically distributed)
Rによる計量分析:データ解析と可視化 - 第3回 Rの基礎とデータ操作・管理
 R 3 R 2017 Email: gito@eco.u-toyama.ac.jp October 23, 2017 (Toyama/NIHU) R ( 3 ) October 23, 2017 1 / 34 Agenda 1 2 3 4 R 5 RStudio (Toyama/NIHU) R ( 3 ) October 23, 2017 2 / 34 10/30 (Mon.) 12/11 (Mon.)
R 3 R 2017 Email: gito@eco.u-toyama.ac.jp October 23, 2017 (Toyama/NIHU) R ( 3 ) October 23, 2017 1 / 34 Agenda 1 2 3 4 R 5 RStudio (Toyama/NIHU) R ( 3 ) October 23, 2017 2 / 34 10/30 (Mon.) 12/11 (Mon.)
kubostat2017c p (c) Poisson regression, a generalized linear model (GLM) : :
 kubostat2017c p.1 2017 (c), a generalized linear model (GLM) : kubo@ees.hokudai.ac.jp http://goo.gl/76c4i 2017 11 14 : 2017 11 07 15:43 kubostat2017c (http://goo.gl/76c4i) 2017 (c) 2017 11 14 1 / 47 agenda
kubostat2017c p.1 2017 (c), a generalized linear model (GLM) : kubo@ees.hokudai.ac.jp http://goo.gl/76c4i 2017 11 14 : 2017 11 07 15:43 kubostat2017c (http://goo.gl/76c4i) 2017 (c) 2017 11 14 1 / 47 agenda
Stata 11 Stata ts (ARMA) ARCH/GARCH whitepaper mwp 3 mwp-083 arch ARCH 11 mwp-051 arch postestimation 27 mwp-056 arima ARMA 35 mwp-003 arima postestim
 TS001 Stata 11 Stata ts (ARMA) ARCH/GARCH whitepaper mwp 3 mwp-083 arch ARCH 11 mwp-051 arch postestimation 27 mwp-056 arima ARMA 35 mwp-003 arima postestimation 49 mwp-055 corrgram/ac/pac 56 mwp-009 dfgls
TS001 Stata 11 Stata ts (ARMA) ARCH/GARCH whitepaper mwp 3 mwp-083 arch ARCH 11 mwp-051 arch postestimation 27 mwp-056 arima ARMA 35 mwp-003 arima postestimation 49 mwp-055 corrgram/ac/pac 56 mwp-009 dfgls
¥¤¥ó¥¿¡¼¥Í¥Ã¥È·×¬¤È¥Ç¡¼¥¿²òÀÏ Âè2²ó
 2 2015 4 20 1 (4/13) : ruby 2 / 49 2 ( ) : gnuplot 3 / 49 1 1 2014 6 IIJ / 4 / 49 1 ( ) / 5 / 49 ( ) 6 / 49 (summary statistics) : (mean) (median) (mode) : (range) (variance) (standard deviation) 7 / 49
2 2015 4 20 1 (4/13) : ruby 2 / 49 2 ( ) : gnuplot 3 / 49 1 1 2014 6 IIJ / 4 / 49 1 ( ) / 5 / 49 ( ) 6 / 49 (summary statistics) : (mean) (median) (mode) : (range) (variance) (standard deviation) 7 / 49
151021slide.dvi
 : Mac I 1 ( 5 Windows (Mac Excel : Excel 2007 9 10 1 4 http://asakura.co.jp/ books/isbn/978-4-254-12172-8/ (1 1 9 1/29 (,,... (,,,... (,,, (3 3/29 (, (F7, Ctrl + i, (Shift +, Shift + Ctrl (, a i (, Enter,
: Mac I 1 ( 5 Windows (Mac Excel : Excel 2007 9 10 1 4 http://asakura.co.jp/ books/isbn/978-4-254-12172-8/ (1 1 9 1/29 (,,... (,,,... (,,, (3 3/29 (, (F7, Ctrl + i, (Shift +, Shift + Ctrl (, a i (, Enter,
2 1 Introduction
 1 24 11 26 1 E-mail: toyoizumi@waseda.jp 2 1 Introduction 5 1.1...................... 7 2 8 2.1................ 8 2.2....................... 8 2.3............................ 9 3 10 3.1.........................
1 24 11 26 1 E-mail: toyoizumi@waseda.jp 2 1 Introduction 5 1.1...................... 7 2 8 2.1................ 8 2.2....................... 8 2.3............................ 9 3 10 3.1.........................
H22 BioS (i) I treat1 II treat2 data d1; input group patno treat1 treat2; cards; ; run; I
 H BioS (i) I treat II treat data d; input group patno treat treat; cards; 8 7 4 8 8 5 5 6 ; run; I II sum data d; set d; sum treat + treat; run; sum proc gplot data d; plot sum * group ; symbol c black
H BioS (i) I treat II treat data d; input group patno treat treat; cards; 8 7 4 8 8 5 5 6 ; run; I II sum data d; set d; sum treat + treat; run; sum proc gplot data d; plot sum * group ; symbol c black
(p.2 ( ) 1 2 ( ) Fisher, Ronald A.1932, 1971, 1973a, 1973b) treatment group controll group (error function) 2 (Legendre, Adrian
 2004 1 1 1.1 Maddala(1993) Mátyás and Sevestre (1996) Hsiao(2003) Baltagi(2001) Lee(2002) Woolridge(2002a), Arellano(2003) Journal of Econometrics Econometrica Greene(2000) Maddala(2001) Johnston and Di-
2004 1 1 1.1 Maddala(1993) Mátyás and Sevestre (1996) Hsiao(2003) Baltagi(2001) Lee(2002) Woolridge(2002a), Arellano(2003) Journal of Econometrics Econometrica Greene(2000) Maddala(2001) Johnston and Di-
I L01( Wed) : Time-stamp: Wed 07:38 JST hig e, ( ) L01 I(2017) 1 / 19
 I L01(2017-09-20 Wed) : Time-stamp: 2017-09-20 Wed 07:38 JST hig e, http://hig3.net ( ) L01 I(2017) 1 / 19 ? 1? 2? ( ) L01 I(2017) 2 / 19 ?,,.,., 1..,. 1,2,.,.,. ( ) L01 I(2017) 3 / 19 ? I. M (3 ) II,
I L01(2017-09-20 Wed) : Time-stamp: 2017-09-20 Wed 07:38 JST hig e, http://hig3.net ( ) L01 I(2017) 1 / 19 ? 1? 2? ( ) L01 I(2017) 2 / 19 ?,,.,., 1..,. 1,2,.,.,. ( ) L01 I(2017) 3 / 19 ? I. M (3 ) II,
DAA09
 > summary(dat.lm1) Call: lm(formula = sales ~ price, data = dat) Residuals: Min 1Q Median 3Q Max -55.719-19.270 4.212 16.143 73.454 Coefficients: Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(> t ) (Intercept) 237.1326
> summary(dat.lm1) Call: lm(formula = sales ~ price, data = dat) Residuals: Min 1Q Median 3Q Max -55.719-19.270 4.212 16.143 73.454 Coefficients: Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(> t ) (Intercept) 237.1326
201711grade2.pdf
 2017 11 26 1 2 28 3 90 4 5 A 1 2 3 4 Web Web 6 B 10 3 10 3 7 34 8 23 9 10 1 2 3 1 (A) 3 32.14 0.65 2.82 0.93 7.48 (B) 4 6 61.30 54.68 34.86 5.25 19.07 (C) 7 13 5.89 42.18 56.51 35.80 50.28 (D) 14 20 0.35
2017 11 26 1 2 28 3 90 4 5 A 1 2 3 4 Web Web 6 B 10 3 10 3 7 34 8 23 9 10 1 2 3 1 (A) 3 32.14 0.65 2.82 0.93 7.48 (B) 4 6 61.30 54.68 34.86 5.25 19.07 (C) 7 13 5.89 42.18 56.51 35.80 50.28 (D) 14 20 0.35
Stata 11 Stata ROC whitepaper mwp anova/oneway 3 mwp-042 kwallis Kruskal Wallis 28 mwp-045 ranksum/median / 31 mwp-047 roctab/roccomp ROC 34 mwp-050 s
 BR003 Stata 11 Stata ROC whitepaper mwp anova/oneway 3 mwp-042 kwallis Kruskal Wallis 28 mwp-045 ranksum/median / 31 mwp-047 roctab/roccomp ROC 34 mwp-050 sampsi 47 mwp-044 sdtest 54 mwp-043 signrank/signtest
BR003 Stata 11 Stata ROC whitepaper mwp anova/oneway 3 mwp-042 kwallis Kruskal Wallis 28 mwp-045 ranksum/median / 31 mwp-047 roctab/roccomp ROC 34 mwp-050 sampsi 47 mwp-044 sdtest 54 mwp-043 signrank/signtest
講義のーと : データ解析のための統計モデリング. 第3回
 Title 講義のーと : データ解析のための統計モデリング Author(s) 久保, 拓弥 Issue Date 2008 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/49477 Type learningobject Note この講義資料は, 著者のホームページ http://hosho.ees.hokudai.ac.jp/~kub ードできます Note(URL)http://hosho.ees.hokudai.ac.jp/~kubo/ce/EesLecture20
Title 講義のーと : データ解析のための統計モデリング Author(s) 久保, 拓弥 Issue Date 2008 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/49477 Type learningobject Note この講義資料は, 著者のホームページ http://hosho.ees.hokudai.ac.jp/~kub ードできます Note(URL)http://hosho.ees.hokudai.ac.jp/~kubo/ce/EesLecture20
1 Stata SEM LightStone 3 2 SEM. 2., 2,. Alan C. Acock, Discovering Structural Equation Modeling Using Stata, Revised Edition, Stata Press.
 1 Stata SEM LightStone 3 2 SEM. 2., 2,. Alan C. Acock, 2013. Discovering Structural Equation Modeling Using Stata, Revised Edition, Stata Press. 2 3 2 Conservative Depress. 3.1 2. SEM. 1. x SEM. Depress.
1 Stata SEM LightStone 3 2 SEM. 2., 2,. Alan C. Acock, 2013. Discovering Structural Equation Modeling Using Stata, Revised Edition, Stata Press. 2 3 2 Conservative Depress. 3.1 2. SEM. 1. x SEM. Depress.
Microsoft Word - 計量研修テキスト_第5版).doc
 Q4-1 テキスト P83 多重共線性が発生する回帰 320000 280000 240000 200000 6000 4000 160000 120000 2000 0-2000 -4000 74 76 78 80 82 84 86 88 90 92 94 96 98 R e s i dual A c tual Fi tted Dependent Variable: C90 Date: 10/27/05
Q4-1 テキスト P83 多重共線性が発生する回帰 320000 280000 240000 200000 6000 4000 160000 120000 2000 0-2000 -4000 74 76 78 80 82 84 86 88 90 92 94 96 98 R e s i dual A c tual Fi tted Dependent Variable: C90 Date: 10/27/05
Microsoft PowerPoint - ch03j
 Ch.3 重回帰分析 : 推定 重回帰分析 ( 複数要因のモデル ) y = + x + x +... + k x k + u. 推定. 重回帰分析の必要性. OLSE の計算と解釈 3. OLSE の期待値 4. OLSE の分散 5. OLS の効率性 :Gauss-Markov 定理 6. 重回帰の用語 入門計量経済学 入門計量経済学 ( 線形 ) 重回帰モデルの定義 変数 yを変数 x, x,,
Ch.3 重回帰分析 : 推定 重回帰分析 ( 複数要因のモデル ) y = + x + x +... + k x k + u. 推定. 重回帰分析の必要性. OLSE の計算と解釈 3. OLSE の期待値 4. OLSE の分散 5. OLS の効率性 :Gauss-Markov 定理 6. 重回帰の用語 入門計量経済学 入門計量経済学 ( 線形 ) 重回帰モデルの定義 変数 yを変数 x, x,,
tokei01.dvi
 2. :,,,. :.... Apr. - Jul., 26FY Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Saga Univ., JAPAN 4 3. (probability),, 1. : : n, α A, A a/n. :, p, p Apr. - Jul., 26FY Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Saga Univ., JAPAN
2. :,,,. :.... Apr. - Jul., 26FY Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Saga Univ., JAPAN 4 3. (probability),, 1. : : n, α A, A a/n. :, p, p Apr. - Jul., 26FY Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Saga Univ., JAPAN
% 10%, 35%( 1029 ) p (a) 1 p 95% (b) 1 Std. Err. (c) p 40% 5% (d) p 1: STATA (1). prtesti One-sample test of pr
 1 1. 2014 6 2014 6 10 10% 10%, 35%( 1029 ) p (a) 1 p 95% (b) 1 Std. Err. (c) p 40% 5% (d) p 1: STATA (1). prtesti 1029 0.35 0.40 One-sample test of proportion x: Number of obs = 1029 Variable Mean Std.
1 1. 2014 6 2014 6 10 10% 10%, 35%( 1029 ) p (a) 1 p 95% (b) 1 Std. Err. (c) p 40% 5% (d) p 1: STATA (1). prtesti 1029 0.35 0.40 One-sample test of proportion x: Number of obs = 1029 Variable Mean Std.
untitled
 2 : n =1, 2,, 10000 0.5125 0.51 0.5075 0.505 0.5025 0.5 0.4975 0.495 0 2000 4000 6000 8000 10000 2 weak law of large numbers 1. X 1,X 2,,X n 2. µ = E(X i ),i=1, 2,,n 3. σi 2 = V (X i ) σ 2,i=1, 2,,n ɛ>0
2 : n =1, 2,, 10000 0.5125 0.51 0.5075 0.505 0.5025 0.5 0.4975 0.495 0 2000 4000 6000 8000 10000 2 weak law of large numbers 1. X 1,X 2,,X n 2. µ = E(X i ),i=1, 2,,n 3. σi 2 = V (X i ) σ 2,i=1, 2,,n ɛ>0
こんにちは由美子です
 Analysis of Variance 2 two sample t test analysis of variance (ANOVA) CO 3 3 1 EFV1 µ 1 µ 2 µ 3 H 0 H 0 : µ 1 = µ 2 = µ 3 H A : Group 1 Group 2.. Group k population mean µ 1 µ µ κ SD σ 1 σ σ κ sample mean
Analysis of Variance 2 two sample t test analysis of variance (ANOVA) CO 3 3 1 EFV1 µ 1 µ 2 µ 3 H 0 H 0 : µ 1 = µ 2 = µ 3 H A : Group 1 Group 2.. Group k population mean µ 1 µ µ κ SD σ 1 σ σ κ sample mean
Stata 11 whitepaper mwp 4 mwp mwp-028 / 41 mwp mwp mwp-079 functions 72 mwp-076 insheet 89 mwp-030 recode 94 mwp-033 reshape wide
 PS001 Stata 11 whitepaper mwp 4 mwp-027 23 mwp-028 / 41 mwp-001 51 mwp-078 62 mwp-079 functions 72 mwp-076 insheet 89 mwp-030 recode 94 mwp-033 reshape wide/long 100 mwp-036 ivregress 110 mwp-082 logistic/logit
PS001 Stata 11 whitepaper mwp 4 mwp-027 23 mwp-028 / 41 mwp-001 51 mwp-078 62 mwp-079 functions 72 mwp-076 insheet 89 mwp-030 recode 94 mwp-033 reshape wide/long 100 mwp-036 ivregress 110 mwp-082 logistic/logit
waseda2010a-jukaiki1-main.dvi
 November, 2 Contents 6 2 8 3 3 3 32 32 33 5 34 34 6 35 35 7 4 R 2 7 4 4 9 42 42 2 43 44 2 5 : 2 5 5 23 52 52 23 53 53 23 54 24 6 24 6 6 26 62 62 26 63 t 27 7 27 7 7 28 72 72 28 73 36) 29 8 29 8 29 82 3
November, 2 Contents 6 2 8 3 3 3 32 32 33 5 34 34 6 35 35 7 4 R 2 7 4 4 9 42 42 2 43 44 2 5 : 2 5 5 23 52 52 23 53 53 23 54 24 6 24 6 6 26 62 62 26 63 t 27 7 27 7 7 28 72 72 28 73 36) 29 8 29 8 29 82 3
¥¤¥ó¥¿¡¼¥Í¥Ã¥È·×¬¤È¥Ç¡¼¥¿²òÀÏ Âè2²ó
 2 212 4 13 1 (4/6) : ruby 2 / 35 ( ) : gnuplot 3 / 35 ( ) 4 / 35 (summary statistics) : (mean) (median) (mode) : (range) (variance) (standard deviation) 5 / 35 (mean): x = 1 n (median): { xr+1 m, m = 2r
2 212 4 13 1 (4/6) : ruby 2 / 35 ( ) : gnuplot 3 / 35 ( ) 4 / 35 (summary statistics) : (mean) (median) (mode) : (range) (variance) (standard deviation) 5 / 35 (mean): x = 1 n (median): { xr+1 m, m = 2r
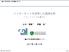
回帰分析 単回帰
 回帰分析 単回帰 麻生良文 単回帰モデル simple regression model = α + β + u 従属変数 (dependent variable) 被説明変数 (eplained variable) 独立変数 (independent variable) 説明変数 (eplanator variable) u 誤差項 (error term) 撹乱項 (disturbance term)
回帰分析 単回帰 麻生良文 単回帰モデル simple regression model = α + β + u 従属変数 (dependent variable) 被説明変数 (eplained variable) 独立変数 (independent variable) 説明変数 (eplanator variable) u 誤差項 (error term) 撹乱項 (disturbance term)
第9回 日経STOCKリーグレポート 審査委員特別賞<地域の元気がでるで賞>
 1/21 1 2 3 1 2 3 4 5 4 5 6 2/21 2 3 2 4 5 6 3/21 38 38 4 2007 10 471 10 10 () () () OKI () () () () () 1989 2008 4 13 10 10 1 2 3 4 1 3 1 4/21 2 3 3 2 5/21 3 100 1.5 1/2 4 () 1991 2002 10 3 1 6/21 10 6
1/21 1 2 3 1 2 3 4 5 4 5 6 2/21 2 3 2 4 5 6 3/21 38 38 4 2007 10 471 10 10 () () () OKI () () () () () 1989 2008 4 13 10 10 1 2 3 4 1 3 1 4/21 2 3 3 2 5/21 3 100 1.5 1/2 4 () 1991 2002 10 3 1 6/21 10 6
.3 ˆβ1 = S, S ˆβ0 = ȳ ˆβ1 S = (β0 + β1i i) β0 β1 S = (i β0 β1i) = 0 β0 S = (i β0 β1i)i = 0 β1 β0, β1 ȳ β0 β1 = 0, (i ȳ β1(i ))i = 0 {(i ȳ)(i ) β1(i ))
 Copright (c) 004,005 Hidetoshi Shimodaira 1.. 3. 4. 004-10-01 16:15:07 shimo cat(" 1: "); c(mea(), mea()) cat(" : "); mmea
Copright (c) 004,005 Hidetoshi Shimodaira 1.. 3. 4. 004-10-01 16:15:07 shimo cat(" 1: "); c(mea(), mea()) cat(" : "); mmea
1 y x y = α + x β+ε (1) x y (2) x y (1) (2) (1) y (2) x y (1) (2) y x y ε x 12 x y 3 3 β x β x 1 1 β 3 1
 1 y x y = α + x β+ε (1) x y (2) x y (1) (2) (1) y (2) x y (1) (2) y x y ε x 12 x y 3 3 β x β x 1 1 β 3 1 2 2 N y(n 1 ) x(n K ) y = E(y x) + u E(y x) y u(n 1 ) y = x β + u β Ordinary Least Squares:OLS (min
1 y x y = α + x β+ε (1) x y (2) x y (1) (2) (1) y (2) x y (1) (2) y x y ε x 12 x y 3 3 β x β x 1 1 β 3 1 2 2 N y(n 1 ) x(n K ) y = E(y x) + u E(y x) y u(n 1 ) y = x β + u β Ordinary Least Squares:OLS (min
(pdf) (cdf) Matlab χ ( ) F t
 (, ) (univariate) (bivariate) (multi-variate) Matlab Octave Matlab Matlab/Octave --...............3. (pdf) (cdf)...3.4....4.5....4.6....7.7. Matlab...8.7.....9.7.. χ ( )...0.7.3.....7.4. F....7.5. t-...3.8....4.8.....4.8.....5.8.3....6.8.4....8.8.5....8.8.6....8.9....9.9.....9.9.....0.9.3....0.9.4.....9.5.....0....3
(, ) (univariate) (bivariate) (multi-variate) Matlab Octave Matlab Matlab/Octave --...............3. (pdf) (cdf)...3.4....4.5....4.6....7.7. Matlab...8.7.....9.7.. χ ( )...0.7.3.....7.4. F....7.5. t-...3.8....4.8.....4.8.....5.8.3....6.8.4....8.8.5....8.8.6....8.9....9.9.....9.9.....0.9.3....0.9.4.....9.5.....0....3
 June 2016 i (statistics) F Excel Numbers, OpenOffice/LibreOffice Calc ii *1 VAR STDEV 1 SPSS SAS R *2 R R R R *1 Excel, Numbers, Microsoft Office, Apple iwork, *2 R GNU GNU R iii URL http://ruby.kyoto-wu.ac.jp/statistics/training/
June 2016 i (statistics) F Excel Numbers, OpenOffice/LibreOffice Calc ii *1 VAR STDEV 1 SPSS SAS R *2 R R R R *1 Excel, Numbers, Microsoft Office, Apple iwork, *2 R GNU GNU R iii URL http://ruby.kyoto-wu.ac.jp/statistics/training/
kubostat2018d p.2 :? bod size x and fertilization f change seed number? : a statistical model for this example? i response variable seed number : { i
 kubostat2018d p.1 I 2018 (d) model selection and kubo@ees.hokudai.ac.jp http://goo.gl/76c4i 2018 06 25 : 2018 06 21 17:45 1 2 3 4 :? AIC : deviance model selection misunderstanding kubostat2018d (http://goo.gl/76c4i)
kubostat2018d p.1 I 2018 (d) model selection and kubo@ees.hokudai.ac.jp http://goo.gl/76c4i 2018 06 25 : 2018 06 21 17:45 1 2 3 4 :? AIC : deviance model selection misunderstanding kubostat2018d (http://goo.gl/76c4i)
10
 z c j = N 1 N t= j1 [ ( z t z ) ( )] z t j z q 2 1 2 r j /N j=1 1/ N J Q = N(N 2) 1 N j j=1 r j 2 2 χ J B d z t = z t d (1 B) 2 z t = (z t z t 1 ) (z t 1 z t 2 ) (1 B s )z t = z t z t s _ARIMA CONSUME
z c j = N 1 N t= j1 [ ( z t z ) ( )] z t j z q 2 1 2 r j /N j=1 1/ N J Q = N(N 2) 1 N j j=1 r j 2 2 χ J B d z t = z t d (1 B) 2 z t = (z t z t 1 ) (z t 1 z t 2 ) (1 B s )z t = z t z t s _ARIMA CONSUME
untitled
 17 5 16 1 2 2 2 3 4 4 5 5 7 5.1... 8 5.2... 9 6 10 1 1 (sample survey metod) 1981 4 27 28 51.5% 48.5% 5 10 51.75% 48.24% (complete survey ( ) ) (populatio) (sample) (parameter) (estimator) 1936 200 2 N
17 5 16 1 2 2 2 3 4 4 5 5 7 5.1... 8 5.2... 9 6 10 1 1 (sample survey metod) 1981 4 27 28 51.5% 48.5% 5 10 51.75% 48.24% (complete survey ( ) ) (populatio) (sample) (parameter) (estimator) 1936 200 2 N
: (EQS) /EQUATIONS V1 = 30*V F1 + E1; V2 = 25*V *F1 + E2; V3 = 16*V *F1 + E3; V4 = 10*V F2 + E4; V5 = 19*V99
 218 6 219 6.11: (EQS) /EQUATIONS V1 = 30*V999 + 1F1 + E1; V2 = 25*V999 +.54*F1 + E2; V3 = 16*V999 + 1.46*F1 + E3; V4 = 10*V999 + 1F2 + E4; V5 = 19*V999 + 1.29*F2 + E5; V6 = 17*V999 + 2.22*F2 + E6; CALIS.
218 6 219 6.11: (EQS) /EQUATIONS V1 = 30*V999 + 1F1 + E1; V2 = 25*V999 +.54*F1 + E2; V3 = 16*V999 + 1.46*F1 + E3; V4 = 10*V999 + 1F2 + E4; V5 = 19*V999 + 1.29*F2 + E5; V6 = 17*V999 + 2.22*F2 + E6; CALIS.
Microsoft Word - 表紙.docx
 黒住英司 [ 著 ] サピエンティア 計量経済学 訂正および練習問題解答 (206/2/2 版 ) 訂正 練習問題解答 3 .69, 3.8 4 (X i X)U i i i (X i μ x )U i ( X μx ) U i. i E [ ] (X i μ x )U i i E[(X i μ x )]E[U i ]0. i V [ ] (X i μ x )U i i 2 i j E [(X i
黒住英司 [ 著 ] サピエンティア 計量経済学 訂正および練習問題解答 (206/2/2 版 ) 訂正 練習問題解答 3 .69, 3.8 4 (X i X)U i i i (X i μ x )U i ( X μx ) U i. i E [ ] (X i μ x )U i i E[(X i μ x )]E[U i ]0. i V [ ] (X i μ x )U i i 2 i j E [(X i
Microsoft Word - 計量研修テキスト_第5版).doc
 Q9-1 テキスト P166 2)VAR の推定 注 ) 各変数について ADF 検定を行った結果 和文の次数はすべて 1 である 作業手順 4 情報量基準 (AIC) によるラグ次数の選択 VAR Lag Order Selection Criteria Endogenous variables: D(IG9S) D(IP9S) D(CP9S) Exogenous variables: C Date:
Q9-1 テキスト P166 2)VAR の推定 注 ) 各変数について ADF 検定を行った結果 和文の次数はすべて 1 である 作業手順 4 情報量基準 (AIC) によるラグ次数の選択 VAR Lag Order Selection Criteria Endogenous variables: D(IG9S) D(IP9S) D(CP9S) Exogenous variables: C Date:
10:30 12:00 P.G. vs vs vs 2
 1 10:30 12:00 P.G. vs vs vs 2 LOGIT PROBIT TOBIT mean median mode CV 3 4 5 0.5 1000 6 45 7 P(A B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A B) P(B A)=P(A B)/P(A) P(A B)=P(B A) P(A) P(A B) P(A) P(B A) P(B) P(A B) P(A) P(B) P(B
1 10:30 12:00 P.G. vs vs vs 2 LOGIT PROBIT TOBIT mean median mode CV 3 4 5 0.5 1000 6 45 7 P(A B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A B) P(B A)=P(A B)/P(A) P(A B)=P(B A) P(A) P(A B) P(A) P(B A) P(B) P(A B) P(A) P(B) P(B
1 Tokyo Daily Rainfall (mm) Days (mm)
 ( ) r-taka@maritime.kobe-u.ac.jp 1 Tokyo Daily Rainfall (mm) 0 100 200 300 0 10000 20000 30000 40000 50000 Days (mm) 1876 1 1 2013 12 31 Tokyo, 1876 Daily Rainfall (mm) 0 50 100 150 0 100 200 300 Tokyo,
( ) r-taka@maritime.kobe-u.ac.jp 1 Tokyo Daily Rainfall (mm) 0 100 200 300 0 10000 20000 30000 40000 50000 Days (mm) 1876 1 1 2013 12 31 Tokyo, 1876 Daily Rainfall (mm) 0 50 100 150 0 100 200 300 Tokyo,
TS002
 TS002 Stata 12 Stata VAR VEC whitepaper mwp 4 mwp-084 var VAR 14 mwp-004 varbasic VAR 26 mwp-005 svar VAR 33 mwp-007 vec intro VEC 51 mwp-008 vec VEC 80 mwp-063 VAR vargranger Granger 93 mwp-062 varlmar
TS002 Stata 12 Stata VAR VEC whitepaper mwp 4 mwp-084 var VAR 14 mwp-004 varbasic VAR 26 mwp-005 svar VAR 33 mwp-007 vec intro VEC 51 mwp-008 vec VEC 80 mwp-063 VAR vargranger Granger 93 mwp-062 varlmar
Stata 11 Stata VAR VEC whitepaper mwp 4 mwp-084 var VAR 14 mwp-004 varbasic VAR 25 mwp-005 svar VAR 31 mwp-007 vec intro VEC 47 mwp-008 vec VEC 75 mwp
 TS002 Stata 11 Stata VAR VEC whitepaper mwp 4 mwp-084 var VAR 14 mwp-004 varbasic VAR 25 mwp-005 svar VAR 31 mwp-007 vec intro VEC 47 mwp-008 vec VEC 75 mwp-063 VAR postestimation vargranger Granger 86
TS002 Stata 11 Stata VAR VEC whitepaper mwp 4 mwp-084 var VAR 14 mwp-004 varbasic VAR 25 mwp-005 svar VAR 31 mwp-007 vec intro VEC 47 mwp-008 vec VEC 75 mwp-063 VAR postestimation vargranger Granger 86
Microsoft Word - 計量研修テキスト_第5版).doc
 Q3-1-1 テキスト P59 10.8.3.2.1.0 -.1 -.2 10.4 10.0 9.6 9.2 8.8 -.3 76 78 80 82 84 86 88 90 92 94 96 98 R e s i d u al A c tual Fi tte d Dependent Variable: LOG(TAXH) Date: 10/26/05 Time: 15:42 Sample: 1975
Q3-1-1 テキスト P59 10.8.3.2.1.0 -.1 -.2 10.4 10.0 9.6 9.2 8.8 -.3 76 78 80 82 84 86 88 90 92 94 96 98 R e s i d u al A c tual Fi tte d Dependent Variable: LOG(TAXH) Date: 10/26/05 Time: 15:42 Sample: 1975
インターネットを活用した経済分析 - フリーソフト Rを使おう
 R 1 1 1 2017 2 15 2017 2 15 1/64 2 R 3 R R RESAS 2017 2 15 2/64 2 R 3 R R RESAS 2017 2 15 3/64 2-4 ( ) ( (80%) (20%) 2017 2 15 4/64 PC LAN R 2017 2 15 5/64 R R 2017 2 15 6/64 3-4 R 15 + 2017 2 15 7/64
R 1 1 1 2017 2 15 2017 2 15 1/64 2 R 3 R R RESAS 2017 2 15 2/64 2 R 3 R R RESAS 2017 2 15 3/64 2-4 ( ) ( (80%) (20%) 2017 2 15 4/64 PC LAN R 2017 2 15 5/64 R R 2017 2 15 6/64 3-4 R 15 + 2017 2 15 7/64
Use R
 Use R! 2008/05/23( ) Index Introduction (GLM) ( ) R. Introduction R,, PLS,,, etc. 2. Correlation coefficient (Pearson s product moment correlation) r = Sxy Sxx Syy :, Sxy, Sxx= X, Syy Y 1.96 95% R cor(x,
Use R! 2008/05/23( ) Index Introduction (GLM) ( ) R. Introduction R,, PLS,,, etc. 2. Correlation coefficient (Pearson s product moment correlation) r = Sxy Sxx Syy :, Sxy, Sxx= X, Syy Y 1.96 95% R cor(x,
Microsoft Word - 研究デザインと統計学.doc
 Study design and the statistical basics Originality Accuracy Objectivity Verifiability Readability perfect Interdisciplinary Sciences Health Science 2014.12.25 2 1. 7 2. 7 3. Bias8 4. random sampling8
Study design and the statistical basics Originality Accuracy Objectivity Verifiability Readability perfect Interdisciplinary Sciences Health Science 2014.12.25 2 1. 7 2. 7 3. Bias8 4. random sampling8
A B P (A B) = P (A)P (B) (3) A B A B P (B A) A B A B P (A B) = P (B A)P (A) (4) P (B A) = P (A B) P (A) (5) P (A B) P (B A) P (A B) A B P
 1 1.1 (population) (sample) (event) (trial) Ω () 1 1 Ω 1.2 P 1. A A P (A) 0 1 0 P (A) 1 (1) 2. P 1 P 0 1 6 1 1 6 0 3. A B P (A B) = P (A) + P (B) (2) A B A B A 1 B 2 A B 1 2 1 2 1 1 2 2 3 1.3 A B P (A
1 1.1 (population) (sample) (event) (trial) Ω () 1 1 Ω 1.2 P 1. A A P (A) 0 1 0 P (A) 1 (1) 2. P 1 P 0 1 6 1 1 6 0 3. A B P (A B) = P (A) + P (B) (2) A B A B A 1 B 2 A B 1 2 1 2 1 1 2 2 3 1.3 A B P (A
ECCS. ECCS,. ( 2. Mac Do-file Editor. Mac Do-file Editor Windows Do-file Editor Top Do-file e
 1 1 2015 4 6 1. ECCS. ECCS,. (https://ras.ecc.u-tokyo.ac.jp/guacamole/) 2. Mac Do-file Editor. Mac Do-file Editor Windows Do-file Editor Top Do-file editor, Do View Do-file Editor Execute(do). 3. Mac System
1 1 2015 4 6 1. ECCS. ECCS,. (https://ras.ecc.u-tokyo.ac.jp/guacamole/) 2. Mac Do-file Editor. Mac Do-file Editor Windows Do-file Editor Top Do-file editor, Do View Do-file Editor Execute(do). 3. Mac System
solutionJIS.dvi
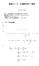 May 0, 006 6 morimune@econ.kyoto-u.ac.jp /9/005 (7 0/5/006 1 1.1 (a) (b) (c) c + c + + c = nc (x 1 x)+(x x)+ +(x n x) =(x 1 + x + + x n ) nx = nx nx =0 c(x 1 x)+c(x x)+ + c(x n x) =c (x i x) =0 y i (x
May 0, 006 6 morimune@econ.kyoto-u.ac.jp /9/005 (7 0/5/006 1 1.1 (a) (b) (c) c + c + + c = nc (x 1 x)+(x x)+ +(x n x) =(x 1 + x + + x n ) nx = nx nx =0 c(x 1 x)+c(x x)+ + c(x n x) =c (x i x) =0 y i (x
H22 BioS t (i) treat1 treat2 data d1; input patno treat1 treat2; cards; ; run; 1 (i) treat = 1 treat =
 H BioS t (i) treat treat data d; input patno treat treat; cards; 3 8 7 4 8 8 5 5 6 3 ; run; (i) treat treat data d; input group patno period treat y; label group patno period ; cards; 3 8 3 7 4 8 4 8 5
H BioS t (i) treat treat data d; input patno treat treat; cards; 3 8 7 4 8 8 5 5 6 3 ; run; (i) treat treat data d; input group patno period treat y; label group patno period ; cards; 3 8 3 7 4 8 4 8 5
yamadaiR(cEFA).pdf
 R 2012/10/05 Kosugi,E.Koji (Yamadai.R) Categorical Factor Analysis by using R 2012/10/05 1 / 9 Why we use... 3 5 Kosugi,E.Koji (Yamadai.R) Categorical Factor Analysis by using R 2012/10/05 2 / 9 FA vs
R 2012/10/05 Kosugi,E.Koji (Yamadai.R) Categorical Factor Analysis by using R 2012/10/05 1 / 9 Why we use... 3 5 Kosugi,E.Koji (Yamadai.R) Categorical Factor Analysis by using R 2012/10/05 2 / 9 FA vs
7. フィリップス曲線 経済統計分析 (2014 年度秋学期 ) フィリップス曲線の推定 ( 経済理論との関連 ) フィリップス曲線とは何か? 物価と失業の関係 トレード オフ 政策運営 ( 財政 金融政策 ) への含意 ( 計量分析の手法 ) 関数形の選択 ( 関係が直線的でない場合の推定 ) 推
 7. フィリップス曲線 経済統計分析 ( 年度秋学期 ) フィリップス曲線の推定 ( 経済理論との関連 ) フィリップス曲線とは何か? 物価と失業の関係 トレード オフ 政策運営 ( 財政 金融政策 ) への含意 ( 計量分析の手法 ) 関数形の選択 ( 関係が直線的でない場合の推定 ) 推定結果に基づく予測シミュレーション 物価と失業の関係......... -. -. -........ 失業率
7. フィリップス曲線 経済統計分析 ( 年度秋学期 ) フィリップス曲線の推定 ( 経済理論との関連 ) フィリップス曲線とは何か? 物価と失業の関係 トレード オフ 政策運営 ( 財政 金融政策 ) への含意 ( 計量分析の手法 ) 関数形の選択 ( 関係が直線的でない場合の推定 ) 推定結果に基づく予測シミュレーション 物価と失業の関係......... -. -. -........ 失業率
Statistics for finance Part II
 Statistics for nance - 2018-2019 Part II Fabio Bacchini University Rome 3 . 1 Financial time series: prices and returns 2 Normality conditions 3 ARCH-GARCH Extension of GARCH: TGARCH EGARCH Bacchini (Univ.
Statistics for nance - 2018-2019 Part II Fabio Bacchini University Rome 3 . 1 Financial time series: prices and returns 2 Normality conditions 3 ARCH-GARCH Extension of GARCH: TGARCH EGARCH Bacchini (Univ.
untitled
 WinLD R (16) WinLD https://www.biostat.wisc.edu/content/lan-demets-method-statistical-programs-clinical-trials WinLD.zip 2 2 1 α = 5% Type I error rate 1 5.0 % 2 9.8 % 3 14.3 % 5 22.6 % 10 40.1 % 3 Type
WinLD R (16) WinLD https://www.biostat.wisc.edu/content/lan-demets-method-statistical-programs-clinical-trials WinLD.zip 2 2 1 α = 5% Type I error rate 1 5.0 % 2 9.8 % 3 14.3 % 5 22.6 % 10 40.1 % 3 Type
untitled
 17 5 13 1 2 1.1... 2 1.2... 2 1.3... 3 2 3 2.1... 3 2.2... 5 3 6 3.1... 6 3.2... 7 3.3 t... 7 3.4 BC a... 9 3.5... 10 4 11 1 1 θ n ˆθ. ˆθ, ˆθ, ˆθ.,, ˆθ.,.,,,. 1.1 ˆθ σ 2 = E(ˆθ E ˆθ) 2 b = E(ˆθ θ). Y 1,,Y
17 5 13 1 2 1.1... 2 1.2... 2 1.3... 3 2 3 2.1... 3 2.2... 5 3 6 3.1... 6 3.2... 7 3.3 t... 7 3.4 BC a... 9 3.5... 10 4 11 1 1 θ n ˆθ. ˆθ, ˆθ, ˆθ.,, ˆθ.,.,,,. 1.1 ˆθ σ 2 = E(ˆθ E ˆθ) 2 b = E(ˆθ θ). Y 1,,Y
k3 ( :07 ) 2 (A) k = 1 (B) k = 7 y x x 1 (k2)?? x y (A) GLM (k
 2012 11 01 k3 (2012-10-24 14:07 ) 1 6 3 (2012 11 01 k3) kubo@ees.hokudai.ac.jp web http://goo.gl/wijx2 web http://goo.gl/ufq2 1 3 2 : 4 3 AIC 6 4 7 5 8 6 : 9 7 11 8 12 8.1 (1)........ 13 8.2 (2) χ 2....................
2012 11 01 k3 (2012-10-24 14:07 ) 1 6 3 (2012 11 01 k3) kubo@ees.hokudai.ac.jp web http://goo.gl/wijx2 web http://goo.gl/ufq2 1 3 2 : 4 3 AIC 6 4 7 5 8 6 : 9 7 11 8 12 8.1 (1)........ 13 8.2 (2) χ 2....................
1 kawaguchi p.1/81
 1 kawaguchi atsushi@kurume-u.ac.jp 2005 7 2 p.1/81 2.1 2.2 2.2.3 2.3 AUC 4.4 p.2/81 X Z X = α + βz + e α : Z = 0 X ( ) β : Z X ( ) e : 0 σ 2 p.3/81 2.1 Z X 1 0.045 2 0.114 4 0.215 6 0.346 7 0.41 8 0.52
1 kawaguchi atsushi@kurume-u.ac.jp 2005 7 2 p.1/81 2.1 2.2 2.2.3 2.3 AUC 4.4 p.2/81 X Z X = α + βz + e α : Z = 0 X ( ) β : Z X ( ) e : 0 σ 2 p.3/81 2.1 Z X 1 0.045 2 0.114 4 0.215 6 0.346 7 0.41 8 0.52
Isogai, T., Building a dynamic correlation network for fat-tailed financial asset returns, Applied Network Science (7):-24, 206,
 H28. (TMU) 206 8 29 / 34 2 3 4 5 6 Isogai, T., Building a dynamic correlation network for fat-tailed financial asset returns, Applied Network Science (7):-24, 206, http://link.springer.com/article/0.007/s409-06-0008-x
H28. (TMU) 206 8 29 / 34 2 3 4 5 6 Isogai, T., Building a dynamic correlation network for fat-tailed financial asset returns, Applied Network Science (7):-24, 206, http://link.springer.com/article/0.007/s409-06-0008-x
卒業論文
 Y = ax 1 b1 X 2 b2...x k bk e u InY = Ina + b 1 InX 1 + b 2 InX 2 +...+ b k InX k + u X 1 Y b = ab 1 X 1 1 b 1 X 2 2...X bk k e u = b 1 (ax b1 1 X b2 2...X bk k e u ) / X 1 = b 1 Y / X 1 X 1 X 1 q YX1
Y = ax 1 b1 X 2 b2...x k bk e u InY = Ina + b 1 InX 1 + b 2 InX 2 +...+ b k InX k + u X 1 Y b = ab 1 X 1 1 b 1 X 2 2...X bk k e u = b 1 (ax b1 1 X b2 2...X bk k e u ) / X 1 = b 1 Y / X 1 X 1 X 1 q YX1
R John Fox R R R Console library(rcmdr) Rcmdr R GUI Windows R R SDI *1 R Console R 1 2 Windows XP Windows * 2 R R Console R ˆ R
 R John Fox 2006 8 26 2008 8 28 1 R R R Console library(rcmdr) Rcmdr R GUI Windows R R SDI *1 R Console R 1 2 Windows XP Windows * 2 R R Console R ˆ R GUI R R R Console > ˆ 2 ˆ Fox(2005) jfox@mcmaster.ca
R John Fox 2006 8 26 2008 8 28 1 R R R Console library(rcmdr) Rcmdr R GUI Windows R R SDI *1 R Console R 1 2 Windows XP Windows * 2 R R Console R ˆ R GUI R R R Console > ˆ 2 ˆ Fox(2005) jfox@mcmaster.ca
( )/2 hara/lectures/lectures-j.html 2, {H} {T } S = {H, T } {(H, H), (H, T )} {(H, T ), (T, T )} {(H, H), (T, T )} {1
 ( )/2 http://www2.math.kyushu-u.ac.jp/ hara/lectures/lectures-j.html 1 2011 ( )/2 2 2011 4 1 2 1.1 1 2 1 2 3 4 5 1.1.1 sample space S S = {H, T } H T T H S = {(H, H), (H, T ), (T, H), (T, T )} (T, H) S
( )/2 http://www2.math.kyushu-u.ac.jp/ hara/lectures/lectures-j.html 1 2011 ( )/2 2 2011 4 1 2 1.1 1 2 1 2 3 4 5 1.1.1 sample space S S = {H, T } H T T H S = {(H, H), (H, T ), (T, H), (T, T )} (T, H) S
α β *2 α α β β α = α 1 β = 1 β 2.2 α 0 β *3 2.3 * *2 *3 *4 (µ A ) (µ P ) (µ A > µ P ) 10 (µ A = µ P + 10) 15 (µ A = µ P +
 Armitage 1 1.1 2 t *1 α β 1.2 µ x µ 2 2 2 α β 2.1 1 α β α ( ) β *1 t t 1 α β *2 α α β β α = α 1 β = 1 β 2.2 α 0 β 1 0 0 1 1 5 2.5 *3 2.3 *4 3 3.1 1 1 1 *2 *3 *4 (µ A ) (µ P ) (µ A > µ P ) 10 (µ A = µ P
Armitage 1 1.1 2 t *1 α β 1.2 µ x µ 2 2 2 α β 2.1 1 α β α ( ) β *1 t t 1 α β *2 α α β β α = α 1 β = 1 β 2.2 α 0 β 1 0 0 1 1 5 2.5 *3 2.3 *4 3 3.1 1 1 1 *2 *3 *4 (µ A ) (µ P ) (µ A > µ P ) 10 (µ A = µ P
dvi
 2017 65 2 217 234 2017 Covariate Balancing Propensity Score 1 2 2017 1 15 4 30 8 28 Covariate Balancing Propensity Score CBPS, Imai and Ratkovic, 2014 1 0 1 2 Covariate Balancing Propensity Score CBPS
2017 65 2 217 234 2017 Covariate Balancing Propensity Score 1 2 2017 1 15 4 30 8 28 Covariate Balancing Propensity Score CBPS, Imai and Ratkovic, 2014 1 0 1 2 Covariate Balancing Propensity Score CBPS
5 Armitage x 1,, x n y i = 10x i + 3 y i = log x i {x i } {y i } 1.2 n i i x ij i j y ij, z ij i j 2 1 y = a x + b ( cm) x ij (i j )
 5 Armitage. x,, x n y i = 0x i + 3 y i = log x i x i y i.2 n i i x ij i j y ij, z ij i j 2 y = a x + b 2 2. ( cm) x ij (i j ) (i) x, x 2 σ 2 x,, σ 2 x,2 σ x,, σ x,2 t t x * (ii) (i) m y ij = x ij /00 y
5 Armitage. x,, x n y i = 0x i + 3 y i = log x i x i y i.2 n i i x ij i j y ij, z ij i j 2 y = a x + b 2 2. ( cm) x ij (i j ) (i) x, x 2 σ 2 x,, σ 2 x,2 σ x,, σ x,2 t t x * (ii) (i) m y ij = x ij /00 y
統計学のポイント整理
 .. September 17, 2012 1 / 55 n! = n (n 1) (n 2) 1 0! = 1 10! = 10 9 8 1 = 3628800 n k np k np k = n! (n k)! (1) 5 3 5 P 3 = 5! = 5 4 3 = 60 (5 3)! n k n C k nc k = npk k! = n! k!(n k)! (2) 5 3 5C 3 = 5!
.. September 17, 2012 1 / 55 n! = n (n 1) (n 2) 1 0! = 1 10! = 10 9 8 1 = 3628800 n k np k np k = n! (n k)! (1) 5 3 5 P 3 = 5! = 5 4 3 = 60 (5 3)! n k n C k nc k = npk k! = n! k!(n k)! (2) 5 3 5C 3 = 5!
kubostat2017e p.1 I 2017 (e) GLM logistic regression : : :02 1 N y count data or
 kubostat207e p. I 207 (e) GLM kubo@ees.hokudai.ac.jp https://goo.gl/z9ycjy 207 4 207 6:02 N y 2 binomial distribution logit link function 3 4! offset kubostat207e (https://goo.gl/z9ycjy) 207 (e) 207 4
kubostat207e p. I 207 (e) GLM kubo@ees.hokudai.ac.jp https://goo.gl/z9ycjy 207 4 207 6:02 N y 2 binomial distribution logit link function 3 4! offset kubostat207e (https://goo.gl/z9ycjy) 207 (e) 207 4
II (2011 ) ( ) α β û i R
 II 3 9 9 α β 3 û i 4 R 3 5 4 4 3 6 3 6 3 6 4 6 5 3 6 F 5 7 F 6 8 GLS 8 8 heil and Goldberger Model 9 MLE 9 9 I 3 93 II 3 94 AR 4 95 5 96 6 6 8 3 3 3 3 3 i 3 33 3 Wald, LM, LR 33 3 34 4 38 5 39 6 43 7 44
II 3 9 9 α β 3 û i 4 R 3 5 4 4 3 6 3 6 3 6 4 6 5 3 6 F 5 7 F 6 8 GLS 8 8 heil and Goldberger Model 9 MLE 9 9 I 3 93 II 3 94 AR 4 95 5 96 6 6 8 3 3 3 3 3 i 3 33 3 Wald, LM, LR 33 3 34 4 38 5 39 6 43 7 44
chap10.dvi
 . q {y j } I( ( L y j =Δy j = u j = C l ε j l = C(L ε j, {ε j } i.i.d.(,i q ( l= y O p ( {u j } q {C l } A l C l
. q {y j } I( ( L y j =Δy j = u j = C l ε j l = C(L ε j, {ε j } i.i.d.(,i q ( l= y O p ( {u j } q {C l } A l C l
kubostat2015e p.2 how to specify Poisson regression model, a GLM GLM how to specify model, a GLM GLM logistic probability distribution Poisson distrib
 kubostat2015e p.1 I 2015 (e) GLM kubo@ees.hokudai.ac.jp http://goo.gl/76c4i 2015 07 22 2015 07 21 16:26 kubostat2015e (http://goo.gl/76c4i) 2015 (e) 2015 07 22 1 / 42 1 N k 2 binomial distribution logit
kubostat2015e p.1 I 2015 (e) GLM kubo@ees.hokudai.ac.jp http://goo.gl/76c4i 2015 07 22 2015 07 21 16:26 kubostat2015e (http://goo.gl/76c4i) 2015 (e) 2015 07 22 1 / 42 1 N k 2 binomial distribution logit
untitled
 IT (1, horiike@ml.me.titech.ac.jp) (1, jun-jun@ms.kagu.tus.ac.jp) 1. 1-1 19802000 2000ITIT IT IT TOPIX (%) 1TOPIX 2 1-2. 80 80 ( ) 2004/11/26 S-PLUS 2 1-3. IT IT IT IT 2. 2-1. a. b. (Size) c. B/M(Book
IT (1, horiike@ml.me.titech.ac.jp) (1, jun-jun@ms.kagu.tus.ac.jp) 1. 1-1 19802000 2000ITIT IT IT TOPIX (%) 1TOPIX 2 1-2. 80 80 ( ) 2004/11/26 S-PLUS 2 1-3. IT IT IT IT 2. 2-1. a. b. (Size) c. B/M(Book
!!! 2!
 2016/5/17 (Tue) SPSS (mugiyama@l.u-tokyo.ac.jp)! !!! 2! 3! 4! !!! 5! (Population)! (Sample) 6! case, observation, individual! variable!!! 1 1 4 2 5 2 1 5 3 4 3 2 3 3 1 4 2 1 4 8 7! (1) (2) (3) (4) categorical
2016/5/17 (Tue) SPSS (mugiyama@l.u-tokyo.ac.jp)! !!! 2! 3! 4! !!! 5! (Population)! (Sample) 6! case, observation, individual! variable!!! 1 1 4 2 5 2 1 5 3 4 3 2 3 3 1 4 2 1 4 8 7! (1) (2) (3) (4) categorical
ii
 NLAS 7 2 Excel Excel 2013 7 2 1 3 7 Excel 2012 1 78 2012 125 2008 10 28 6994.9 6 2 6 7 2015 8 i 2008 10 10 9 679 8579 9 29 778 8 29 1 1500 1 3000 10 881 8276 8 29 1 3007 4700 8 109 100 162 135 200 171
NLAS 7 2 Excel Excel 2013 7 2 1 3 7 Excel 2012 1 78 2012 125 2008 10 28 6994.9 6 2 6 7 2015 8 i 2008 10 10 9 679 8579 9 29 778 8 29 1 1500 1 3000 10 881 8276 8 29 1 3007 4700 8 109 100 162 135 200 171
分布
 (normal distribution) 30 2 Skewed graph 1 2 (variance) s 2 = 1/(n-1) (xi x) 2 x = mean, s = variance (variance) (standard deviation) SD = SQR (var) or 8 8 0.3 0.2 0.1 0.0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 8 0 1 8 (probability
(normal distribution) 30 2 Skewed graph 1 2 (variance) s 2 = 1/(n-1) (xi x) 2 x = mean, s = variance (variance) (standard deviation) SD = SQR (var) or 8 8 0.3 0.2 0.1 0.0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 8 0 1 8 (probability
2004 2 µ i ν it IN(0, σ 2 ) 1 i ȳ i = β x i + µ i + ν i (2) 12 y it ȳ i = β(x it x i ) + (ν it ν i ) (3) 3 β 1 µ i µ i = ȳ i β x i (4) (least square d
 2004 1 3 3.1 1 5 1 2 3.2 1 α = 0, λ t = 0 y it = βx it + µ i + ν it (1) 1 (1995)1998Fujiki and Kitamura (1995). 2004 2 µ i ν it IN(0, σ 2 ) 1 i ȳ i = β x i + µ i + ν i (2) 12 y it ȳ i = β(x it x i ) +
2004 1 3 3.1 1 5 1 2 3.2 1 α = 0, λ t = 0 y it = βx it + µ i + ν it (1) 1 (1995)1998Fujiki and Kitamura (1995). 2004 2 µ i ν it IN(0, σ 2 ) 1 i ȳ i = β x i + µ i + ν i (2) 12 y it ȳ i = β(x it x i ) +
2 Tobin (1958) 2 limited dependent variables: LDV 2 corner solution 2 truncated censored x top coding censor from above censor from below 2 Heck
 10 2 1 2007 4 6 25-44 57% 2017 71% 2 Heckit 6 1 2 Tobin (1958) 2 limited dependent variables: LDV 2 corner solution 2 truncated 50 50 censored x top coding censor from above censor from below 2 Heckit
10 2 1 2007 4 6 25-44 57% 2017 71% 2 Heckit 6 1 2 Tobin (1958) 2 limited dependent variables: LDV 2 corner solution 2 truncated 50 50 censored x top coding censor from above censor from below 2 Heckit
X X X Y R Y R Y R MCAR MAR MNAR Figure 1: MCAR, MAR, MNAR Y R X 1.2 Missing At Random (MAR) MAR MCAR MCAR Y X X Y MCAR 2 1 R X Y Table 1 3 IQ MCAR Y I
 (missing data analysis) - - 1/16/2011 (missing data, missing value) (list-wise deletion) (pair-wise deletion) (full information maximum likelihood method, FIML) (multiple imputation method) 1 missing completely
(missing data analysis) - - 1/16/2011 (missing data, missing value) (list-wise deletion) (pair-wise deletion) (full information maximum likelihood method, FIML) (multiple imputation method) 1 missing completely
populatio sample II, B II? [1] I. [2] 1 [3] David J. Had [4] 2 [5] 3 2
![populatio sample II, B II? [1] I. [2] 1 [3] David J. Had [4] 2 [5] 3 2 populatio sample II, B II? [1] I. [2] 1 [3] David J. Had [4] 2 [5] 3 2](/thumbs/49/25550404.jpg) (2015 ) 1 NHK 2012 5 28 2013 7 3 2014 9 17 2015 4 8!? New York Times 2009 8 5 For Today s Graduate, Just Oe Word: Statistics Google Hal Varia I keep sayig that the sexy job i the ext 10 years will be statisticias.
(2015 ) 1 NHK 2012 5 28 2013 7 3 2014 9 17 2015 4 8!? New York Times 2009 8 5 For Today s Graduate, Just Oe Word: Statistics Google Hal Varia I keep sayig that the sexy job i the ext 10 years will be statisticias.
と入力する すると最初の 25 行が表示される 1 行目は変数の名前であり 2 列目は企業番号 (1,,10),3 列目は西暦 (1935,,1954) を表している ( 他のパネルデータを分析する際もデ ータをこのように並べておかなくてはならない つまりまず i=1 を固定し i=1 の t に関
 R によるパネルデータモデルの推定 R を用いて 静学的パネルデータモデルに対して Pooled OLS, LSDV (Least Squares Dummy Variable) 推定 F 検定 ( 個別効果なしの F 検定 ) GLS(Generalized Least Square : 一般化最小二乗 ) 法による推定 およびハウスマン検定を行うやり方を 動学的パネルデータモデルに対して 1 階階差
R によるパネルデータモデルの推定 R を用いて 静学的パネルデータモデルに対して Pooled OLS, LSDV (Least Squares Dummy Variable) 推定 F 検定 ( 個別効果なしの F 検定 ) GLS(Generalized Least Square : 一般化最小二乗 ) 法による推定 およびハウスマン検定を行うやり方を 動学的パネルデータモデルに対して 1 階階差
,, Poisson 3 3. t t y,, y n Nµ, σ 2 y i µ + ɛ i ɛ i N0, σ 2 E[y i ] µ * i y i x i y i α + βx i + ɛ i ɛ i N0, σ 2, α, β *3 y i E[y i ] α + βx i
![,, Poisson 3 3. t t y,, y n Nµ, σ 2 y i µ + ɛ i ɛ i N0, σ 2 E[y i ] µ * i y i x i y i α + βx i + ɛ i ɛ i N0, σ 2, α, β *3 y i E[y i ] α + βx i ,, Poisson 3 3. t t y,, y n Nµ, σ 2 y i µ + ɛ i ɛ i N0, σ 2 E[y i ] µ * i y i x i y i α + βx i + ɛ i ɛ i N0, σ 2, α, β *3 y i E[y i ] α + βx i](/thumbs/87/95421301.jpg) Armitage.? SAS.2 µ, µ 2, µ 3 a, a 2, a 3 a µ + a 2 µ 2 + a 3 µ 3 µ, µ 2, µ 3 µ, µ 2, µ 3 log a, a 2, a 3 a µ + a 2 µ 2 + a 3 µ 3 µ, µ 2, µ 3 * 2 2. y t y y y Poisson y * ,, Poisson 3 3. t t y,, y n Nµ,
Armitage.? SAS.2 µ, µ 2, µ 3 a, a 2, a 3 a µ + a 2 µ 2 + a 3 µ 3 µ, µ 2, µ 3 µ, µ 2, µ 3 log a, a 2, a 3 a µ + a 2 µ 2 + a 3 µ 3 µ, µ 2, µ 3 * 2 2. y t y y y Poisson y * ,, Poisson 3 3. t t y,, y n Nµ,
こんにちは由美子です
 1 2 . sum Variable Obs Mean Std. Dev. Min Max ---------+----------------------------------------------------- var1 13.4923077.3545926.05 1.1 3 3 3 0.71 3 x 3 C 3 = 0.3579 2 1 0.71 2 x 0.29 x 3 C 2 = 0.4386
1 2 . sum Variable Obs Mean Std. Dev. Min Max ---------+----------------------------------------------------- var1 13.4923077.3545926.05 1.1 3 3 3 0.71 3 x 3 C 3 = 0.3579 2 1 0.71 2 x 0.29 x 3 C 2 = 0.4386


