Katori_Bussei_SS09_HP1.dvi
|
|
|
- みがね あくや
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SLE (18 May 2009 (version 1)) SLE Bessel [13] N Hermite N 2 Hermite N N N N N [7] Riemann Brown 2000 Schramm-Loewner Evolution (SLE) [10] [14] SLE [5, 17] 2006 Werner SLE [22] [16] : katori@phys.chuo-u.ac.jp HP 1
2 Brown Bessel Itô Karlin-McGregor Brown Schur Selberg Hermite Bru Markov Schramm-Loewner Evolution (SLE) Riemann Loewner SLE κ : Brown Bessel Itô Schramm-Loewner evolution (SLE) Virasoro 2
3 Part I : Brown Bessel (Ω, F, P) 1 Brown {B(t, ω)} t [0, ) 2 1. B(0,ω)= ω Ω ω B(t, ω) t 3. t 0 0 <t 1 < <t M,M=1, 2,..., {B(t j+1 ) B(t j )} j=0,1,...,m 1 0 t j+1 t j Gauss p(t, y x) = 1 } (y x)2 exp {, t > 0, x,y R (1.1) 2πt 2t R Brown t j, 1 j M [a j,b j ] ( ) b1 bm M 1 P B(t j ) [a j,b j ],j =1,...,M = dx 1 dx M p(t j+1 t j,x j+1 x j ) a 1 a M p(t s, y x) Brown 3 s 0 Brown B(s) Brown B(u),u<s Brown B(t),t>s 1 Ω Ω A Ω F σ (i) Ω F, (ii) A F A A c F, (iii) A 1,A 2,..., F n A n F, 3 2 filtration, {F t } t 0 (i) F s F t F, 0 s<t, (ii) t F t σ (Ω, F, P; {F t } t 0 ) 3 (1.1) t p(t, y x) =1 p(t, y x) p(0,y x) = 2 x2 δ(y x) heat kernel) Green propagator, 3 j=0 2
4 Markov τ Markov τ u u Markov Brown Markov s Markov τ Markov Markov s x t (> 0) y g(s, x; t, y) Brown g(s, x; t, y) t s g(s, x; t, y) y x d d N {1, 2, } d Brown B(t) =(B 1 (t),...,b d (t)) X (d) (t) = B(t) = B 1 (t) 2 + B 2 (t) B d (t) 2 (1.2) d Bessel d Bessel X (d) (t),d N p (d) (t, y x) ν = d 2 2 d =2(ν + 1) (1.3) p (d) (t, y x) = yν+1 1 ( x ν t exp x2 + y 2 2t p (d) (t, y 0) = y 2ν+1 exp 2 ν Γ(ν +1)tν+1 ) ( xy I ν t ( y2 2t ), t > 0, x > 0, y 0 ), t > 0, y 0 (1.4) I ν (z) Bessel Γ(z) : Γ(z) = I ν (z) = 0 n=0 e u u z 1 du Re u>0, (1.5) (z/2) 2n+ν Γ(n + 1)Γ(ν + n +1). (1.6) Bessel X (d) (t) Bessel (1.3) d =1, 2, 3, 4,... ν = 1/2, 0, 1/2, 1,... 4
5 (1.4) ν (1.4) (1.3) d 1 d Bessel Bessel (d 2) (1 d<2) [3] 1.2 Itô s>0 B(s) Brown B(u),u<s B(t) B(s) t 4 Brown X(s)dB(s) Z(t) (quadratic variation) Z t : Z t = P- lim n n (Z(t j+1 ) Z(t j )) 2 j=0 P- lim [0,t] 0 t 0 <t 1 < <t n t n 5 Z(t) Z t =0 Z(t), Ẑ(t) Z, Ẑ t 1 4 { } Z + Ẑ t Z Ẑ t 0 dz(t)dẑ(t) =d Z, Ẑ t Brown db(t)db(t) =dt dt Brown B 1 (t) B 2 (t) Brown db 1 (t)db 2 (t) =0 4 ) 5 {X n } n=1 X (Ω, F, P) n {X n } X ε>0 lim n P( X n X >ε)=0 P- lim n 5
6 d Brown B(t) =(B 1 (t),b 2 (t),...,b d (t)) db j (t)db k (t) =δ jk dt dm j (t)dm k (t), 1 j, k d M(t) =(M 1 (t),m 2 (t),...,m d (t)) Z(t) = (Z 1 (t),z 2 (t),...,z d (t)) M(t) A(t) =(A 1 (t),a 2 (t),...,a d (t)) d F R d F (Z(t)) df (Z(t)) = d j=1 F x j (Z(t)) (dm j (t)+da j (t)) 15j,k5d Itô [12, 3] F (x) = d j=1 x2 j 2 F x j x k (Z(t))dM j (t)dm k (t) (1.7) (1.2) d Bessel dx (d) (t) =db(t)+ d 1 dt (1.8) 2X (d) (t) d >1 d Bessel Brown d 1 t ds 2 0 X (d) (s) 6. (1.8) t u(t, x) =1 2 1 u(t, x)+d u(t, x). (1.9) 2 x2 2x x Kolmogorov [12, 3] (1.4) d Bessel p (d) (t, y x) t =0 δ(x y) 1.3 Karlin-McGregor X 1,X 2 X 1 (τ) =X 2 (τ) τ x = X 1 (τ) =X 2 (τ) 2 N 6 (1.4) d =1 ν = 1/2 I 1/2 (z) = 2/(πz) cosh z p (1) (t, y x) = p(t, y x)+p(t, y x) p (1.1) Brown X (1) (t) = B(t) (1.2) d =1 6
7 [7] Karlin-McGregor Lindström-Gessel-Viennot Fermi Slater [4, 7, 20] 1.1 (Karlin-McGregor ) g(s, x; t, y) N x j, j =1, 2,...,N N y j, j =1, 2,...,N x 1 <x 2 < <x N y 1 <y 2 < <y N N [ ] [s, t] det g(s, x j ; t, y k ) [ ] det g(s, x j ; t, y k ) = N sgn(σ) g(s, x j ; t, y σ(j) ). (1.10) σ S N j=1 S N {1, 2,...,N} (s, x) (t, y) Ω(s, x; t, y) π j Ω(s, x j ; t, y σ(j) ),j =1, 2,...,N (1.10) σ N (σ, π 1,...,π N ) (σ, π 1,...,π N ) { } τ = sup s<u<t: π 1,...,π N u 7 v R τ π l1,π l2 1 π l1 = π l1 ( v)π l1 (v ), π l2 = π l2 ( v)π l2 (v ) 2 v π l 1 = π l1 ( v)π l2 (v ), π l 2 = π l2 ( v)π l1 (v ) j l 1,l 2 π j = π j σ (l 1,l 2 ) σ (σ, π 1,...,π N ) (σ,π 1,...,π N) (1.11) 7 sup (supremum) inf (infimum) 7
8 y σ(4) y σ(3) y σ(1) y σ(2) y σ(5) y π (k) y π (j) y π (k) y π (j) π ' 1 π ' 2 υ υ υ π 1 π 2 π 2 π 1 x j x k x j x k x 1 x 2 x 3 x 4 x 5 (a) (b) 1: (π 1,...,π N ) 2: (a) π l1 π l2 (b) π l v π l1 1 π l π l sgn(σ )= sgn(σ) (σ, π 1,...,π N ) (1.10) (1.11) (1.10) σ sgn(σ) =1 (1.10) 1.4 Brown R N W A N = {x RN : x 1 <x 2 < <x N } A N 1 Weyl W A N Brown 8 0 W A N x =(x 1,...,x N ) Brown W A N t WA N y =(y 1,...,y N ) 1.1 Karlin-McGregor [ ] f N (t, y x) = p(t, y j x k ) det (1.12) 8 (0, ) Brown p (1.1) g abs (s, x; t, y) =p(t s, y x) p(t s, y x), 0 <s<t,x,y 0 Brown [7] (1.4) d =3 ν =1/2 I 1/2 (z) = 2/(πz) sinh z p (3) (t s, y x) =(y/x)g abs (s, x; t, y) (1.12) (1.14) N 8
9 0 x Brown t W A N N N (t, x) = f N (t, y x)dy (1.13) dy = W A N N dy j j=1 T>0 (0,T] Brown Z(t) =(Z 1 (t),z 2 (t),...,z N (t)) gn T (s, x; t, y) T s x W A N N Brown t y W A N g T N (s, x; t, y) = N N(T t, y) N N (T s, x) f N(t s, y x), 0 s<t T, x, y W A N (1.14) Schur [4, 20] N N (t, x) C 2(N) C 1 (N) h N [6, 8] h N (x) ( h N (x) = det x j 1 k ( x t ), ) = 1 j<k N C 1 (N),C 2 (N) (1.6) C 1 (N) =(2π) N/2 N j=1 x t 0 (1.15) (x k x j ) (1.16) N Γ(j), C 2 (N) =2 N/2 Γ(j/2) (1.17) x =(x 1,x 2,...,x N ) x = N x 2 j (1.15) Brown Z(t) T p N (t, y x) = h N(y) h N (x) f N(t, x, y), t > 0, x, y W A N (1.18) j=1 j=1 9
10 X(t) =(X 1 (t),x 2 (t),...,x N (t)) N 2 h N (x) =0 x 2 j=1 j p N (t, y x) t p N(t, y x) = 1 2 N 2 x 2 j=1 j p N (t, y x)+ 1 k N k j 1 x j x k x j p N (t, y x). (1.19) (1.9) d =3 Bessel Kolmogorov N (1.9) Bessel (1.8) (1.19) Brown X(t) =(X 1 (t),...,x N (t)) dx j (t) =db j (t)+ β 2 1 k N k j 1 dt, 1 j N (1.20) X j (t) X k (t) β =2 β (1.20) Dyson [7] 1.5 Schur Selberg μ 1 μ 2 μ N 0,μ j N 0 N {0} = {0, 1, 2,...} μ =(μ 1,...,μ N ) N μ μ j {μ j } j=1 l(μ) 1 j N μ j =0 (0, 0,...,0) = μ N x =(x 1,...,x N ) s μ (x) = det [ det x μ k+n k j [ x N k j ] ] (1.21) [4, 20] Vandermonde (1.16) [ ] = (x j x k )=( 1) N(N 1)/2 h N (x). (1.22) det x N k j 1 j<k N 10
11 s μ (x) x 1,...,x N μ Schur μ = s (x) =1 s μ (x) N Z[x 1,...,x N ] Taylor 1.1 ρ ψ(x) x =0 ψ(x) = x =(x 1,...,x N ), y =(y 1,...,y N ) [ ] det ψ(x j y k ) = h N (x)h N (y) N (x j y j ) ρ j=1 x 0 y 0 μ:l(μ) N c n x n+ρ n=0 s μ (x)s μ (y) N c μj +N j. (1.23) j=1 [ ] det ψ(x j y k ) = h N (x)h N (y) N N (x j y j ) ρ c j 1 j=1 j=1 { } 1+O( x, y ) (1.24) [ ] det ψ(x j y k ) = det = [ ] (x j y k ) ρ c n (x j y k ) n n=0 N (x j y j ) ρ j=1 n=(n 1,...,n N ) N N 0 N j=1 c nj [ ] det (x j y k ) n j. n =(n 1,...,n N ) σ S N σ(n) = (n σ(1),...,n σ(n) ) f(n) n f(σ(n)) = f(n), σ S N n N N 0 f(n) det [ ] (x j y k ) n j = 1 N! = n N N 0 f(n) [ ] det (x j y k ) n σ(j) σ S N [ ] det (x j y k ) n σ(j) f(n) 0 n 1 < <n N σ S N σ S N [ ] [ det (x j y k ) n σ(j) = det x n k j ] det 1 l,m N [ y nm l ] 11
12 N j=1 c nj n [ ] det ψ(x j y k ) = N (x j y j ) ρ j=1 N 0 n 1 < <n N j=1 c nj [ det x n k j ] det 1 l,m N μ j = n j N + j, 1 j N Schur (1.21) (1.23) s μ (x) x 1,...,x N μ s (x) =1 x 0 y 0 (1.24) [ y nm l ]. [ ] 1 f N (t, y x) = det e (x j y k ) 2 /(2t) 2πt = (2πt) N/2 e ( x 2 + y 2 )/(2t) det [ ] e x jy k /t ψ(x) =e x/t = x n /(n!t n ) 1.1 (1.24) x=0 x / t 0 y / t 0 f N (t, y x) = t N 2 /2 C 1 (N) e ( x 2 + y 2 )/(2t) h N (x)h N (y) { ( x 1+O, y )} t t (1.25) C 1 (N) (1.17) N N (t, x) = f N (t, y x)dy = W A N 1 C 1 (N) h N ( x t ) { ( )} x C 2 (N) 1+O, t x t 0 C 2 (N) = W A N e x 2 /2 h N (x)dx (1.26) Selberg [11] N h N (x) 2γ =(2π) N/2 (2a) N(γ(N 1)+1)/2 R N e a x 2 j=1 Γ(1 + jγ) Γ(1 + γ) (1.27) a =1/2,γ =1/2 (1.17) (1.15) 12
13 2 Hermite 2.1 Bru N N Hermite H(N) N N S(N) A t A A A t A Bru H(N) Wishart ξ jk (t), 1 j, k N [6, 7] Bru 9 λ(t) =(λ 1 (t),λ 2 (t),...,λ N (t)) H(N) Ξ(t) =(ξ jk (t)) 15j,k5N λ 1 (t) λ 2 (t) λ N (t) U(t) =(u jk (t)) ( ) U(t) Ξ(t)U(t) =Λ(t) = diag λ 1 (t),λ 2 (t),,λ N (t) Ξ(t) ( ) ( ) Γ jk,lm (t)dt = U(t) dξ(t)u(t) U(t) dξ(t)u(t) (U(t) dξ(t)u(t)) jj dυ j (t) (λ 1 (t),λ 2 (t),...,λ N (t)) τ : { } τ = inf t>0:λ j (t) =λ k (t) 1 j k N jk lm 2.1 [ Bru ] ξ jk (t), 1 j, k N Ξ(t) λ(t) dλ j (t) =dm j (t)+dj j (t), t (0,τ), j =1, 2,...,N. (2.1) M(t) =(M 1 (t),m 2 (t),...,m N (t)) dm j (t)dm k (t) =Γ jj,kk (t)dt J(t) =(J 1 (t),j 2 (t),...,j N (t)) dj j (t) = 15k5N k j 1 λ j (t) λ k (t) 1 {λ j (t) λ k (t)}γ jk,kj (t)dt + dυ j (t) 1 {ω} ω ω Itô (1.7) M M N N d(m M) =(dm) M + M (d M)+(dM) (d M) 13
14 2.2 Bjk R (t), BI jk (t), 1 j, k N 2N 2 Brown 1 j, k N 1 Bjk R (t), j < k 1 Bjk 2 I (t), j < k 2 s jk (t) = Bjj(t), R j = k a jk(t) = 0, j = k 1 Bkj R (t), j > k 1 Bkj I (t), j > k 2 2 (i) GUE Ξ GUE (t) = ( s jk (t)+ ) 1a jk (t), t [0, ) (2.2) 15j,k5N H(N) t [0, ), Ξ GUE (t) H(N) H(N) U(dH) μ GUE (H, t) = t N 2 /2 ( c 1 (N) exp 12t ) TrH2, H H(N) Tr c 1 (N) =2 N/2 π N 2 /2 N N U(N) U U(N) μ GUE (H, t)u(dh) H U HU H(N) Gauss (Gaussian unitary ensemble, GUE) [11, 13] GUE x 1 <x 2 < <x N x =(x 1,x 2,,x N ) g GUE (x,t)= t N 2 /2 C 1 (N) exp ) ( x 2 h N (x) 2 (2.3) 2t [11, 13] h N (x) N N Vandermonde (1.22) C 1 (N) (1.17) Bru Ξ GUE (t) dξ jk (t)dξ lm (t) dξ jj (t)dξ jj (t) =dbjj R(t)dBR jj (t) =dt j<k dξ jk (t) =dbjk R (t)/ 2+ 1dBjk I (t)/ 2=dξ kj (t) dξ jk (t)dξ jk (t) =dt/2 dt/2 =0,dξ jk (t)dξ kj (t) =dt/2 +dt/2 =dt (j, k) (l, m), (m, l) dbjk R (t)dbr lm (t) = dbjk I (t)dbi lm (t) =0 dξ jk(t)dξ lm (t) =0 14
15 dξ jk (t)dξ lm (t) =δ jm δ kl dt, 1 j, k, l, m N dm j (t)dm k (t) ( ) ( ) Γ jj,kk (t)dt = U(t) dξ(t)u(t) U(t) dξ(t)u(t) jj kk = u lj dξ lm u mj u pk dξ pq u qk l,m p,q = l,m u lj u lk u mj u mk dt = δ jk dt U(t) U(t) U(t) =U(t)U(t) = I N N Brown Γ jk,kj (t) =1, 1 j, k N (U(t) dξ(t)u(t)) jj (dυ j (t) =0) Bru λ(t) dλ j (t) =db j (t)+ 15k5N k j 1 dt, 1 j N (2.4) λ j (t) λ k (t) τ = (2.4) Dyson (1.20) β =2 (ii) GOE ( ) Ξ GOE (t) = s jk (t), t [0, ) (2.5) 15j,k5N S(N) t [0, ) Ξ GOE (t) S(N) V(dS) μ GOE (S, t) = t N(N+1)/4 c 2 (N) exp ( 12t ) TrS2, S S(N) S(N) c 2 (N) = 2 N/2 π N(N+1)/4 N N O(N) V O(N) μ GOE (S, t)v(ds) S t VSV S(N) Gauss (Gaussian orthogonal ensemble, GOE) GOE x 1 < x 2 < < x N x =(x 1,x 2,,x N ) g GOE (x,t)= t N(N+1)/4 C 2 (N) 15 exp ) ( x 2 h N (x) (2.6) 2t
16 C 2 (N) (1.17) [11, 13] GUE λ(t) dλ j (t) =db j (t) k5N k j 1 λ j (t) λ k (t) dt, 1 j N τ = Dyson (1.20) β = (i) GUE λ(t) =(λ 1 (t),...,λ N ) Brown X(t) =(X 1 (t),...,x N (t)) β =2 Dyson 3.1 Brown X(t) =(X 1 (t),...,x N (t)) GUE λ(t) =(λ 1 (t),...,λ N (t)) Dyson (1.20) N Brown β =2 Dyson (1.20) log log- Dyson 1 Coulomb (1.20) β β =1/k B T T =1/(2k B ) β 2 2 N 16
17 Part II : Schramm-Loewner Evolution (SLE) C S S = Z 1Z, Z S { z S n } Wn z = ω =(ω(0),...,ω(n)) : ω(0) = z, ω(j) S, ω(j) ω(j 1) =1, 1 j n (RW) Wn z =4n { ω Wn z 4 n C D 0 = x + } 1y : 1 <x<1, 0 <y<2, D 0 2 O =0 P =2 1 N N N NO =0 NP =2N 1 RW ND 0 Ω N (D 0 ; O, P) Z N (D 0 ; O, P) = 4 ω. (4.1) ω Ω N (D 0 ;O,P ) ω ω N Z N (D 0 ; O, P) C(D 0 ; O, P)N 2 0. f(n) g(n),n f(n)/g(n) 1,N C(D 0 ; O, P) D 0 Poisson H D0 (,P) O D 0 (loop-erased RW: LERW) Ω N (D 0 ; O, P) ω =(ω(0),ω(1),...) ω(j) =ω(k),j < k ω ω ω =( ω(0), ω(1),...) t 0 =0, ω(0) = ω(t 0 )=0 m 1 t m = max { } l>t m 1 : ω(l) = ω(t m 1 +1), ω(m) = ω(t m )= ω(t m 1 +1) Schramm-Loewner Evolution 17
18 ND 0 0 NP Ω 0 N (D 0; O, P) RW Ω 0 N (D 0; O, P) RW ω 4 w (LERW) LERW LERW ω =(ω(0),...,ω( ω )) ν>0 ( ) j ω 1/N = 1 ω(j), 0 j ω (4.2) N 1/ν N ω 1/N O ω /N 1/ν P =2 1 D 0 1/N ν N P γ P t γ = lim N ω /N 1/ν : γ :(0,t γ ) D 0, lim t 0 γ(t) =O, lim γ(t) =P, t γ (0, ). (4.3) t tγ γ d LERW =1/ν γ γ(t 1 ) γ(t 2 ), 0 t 1 <t 2 t γ LERW (4.3) K LERW (D 0 ; O, P) K LERW (D 0 ; O, P) μ LERW (D 0 ;O,P ) C(D 0; O, P) μ LERW (D 0 ;O,P ) ( )=C(D 0; O, P)μ LERW (D 0 ;O,P ) ( ) (4.4) μ LERW (D 0 ;O,P ) (self-avoiding walk : SAW) Wn z { Wn,0 z = ω Wn }. z : 0 j<k n ω(j) ω(k) 2 <e β < 3 Wn,0 z e βn,n 11 f(n) g(n),n log f(n) log g(n),n ω e β ω (SAW) (4.1) SAW ZN SAW (D 0 ; O, P) = e β ω ω Ω 0 N (D 0;O,P ) 11 e β SAW connective constant S
19 b SAW > 0 Z SAW N (D 0 ; O, P) C SAW (D 0 ; O, P)N 2b SAW, N (4.5) LERW b LERW =1 SAW γ d SAW LERW d LERW (4.4) SAW μ SAW (D 0 ;O,P ) ( )=CSAW (D 0 ; O, P)μ SAW (D 0 ;O,P ) ( ) (critical percolation model) NP _ Λ Ν + Λ Ν 0 3: T H 1 0 C τ = exp(2π { 1/3) T = z 0 +(j+kτ) 3a : } j, k Z. a =2/3 z 0 = a 1 T a H O NP =2N 1,N N z T η(z) {0, 1} Bernoulli ν p, 0 p 1 ν p (η(z) = 1) = p, ν p (η(z) =0)=1 p. T 1 0 p 1/2 19
20 1 p >1/2 p c =1/2 p c T p c =1/2 Bernoulli N 1 b per =0 N N T ND 0 =Λ N 3 N =6 Λ N z T O NP Λ + N Λ N η(z) =1, z Λ + N, η(z) =0, z Λ N Dobrushin Λ N ν p η {0, 1} T ND 0 H ND 0 O ω 0 1 ν>0 (4.2) N d per =1/ν (4.3) γ γ μ per (D 0 ;O,P ) ( ) Ising (critical Ising model) Λ N =Λ N Λ + N Λ N z Λ N σ(z) { 1, 1} z Λ ± N σ(z) =±1 Dobrushin o Λ N =Λ N ( Λ + N )c ( Λ N )c σ { 1, 1} Λ N E(σ) = 1 2 z,z Λ N : z z = 3a σ(z)σ(z ) k B β =1/(k B T ) β>0 Gibbs π N,β (σ) = e βe(σ) Z N,β, Z N,β = σ { 1,1} o Λ N e βe(σ) T 0 Ising ω 1 +1 H ND 0 β T Ising β c = (log 3)/4 = d Ising (4.3) γ μ Ising (D 0 ;O,P ) ( ) 20
21 4.2 Markov f D 0 C f (z) 0, z D 0 f : D 0 f(d 0 ) (4.6) f D 0 O, P f(d 0 ) f(o),f(p ) 4.1 γ μ (D0 ;O,P )( )=C(D 0 ; O, P)μ (D0 ;O,P )( ) (4.7) (conformal covariance) (conformal invariance) (4.6) f μ (D0 ;O,P )( )= f (O) b f (P ) b μ (f(d0 );f(o),f(p ))( ) (4.8) b 4.1 N (4.8) (boundary scaling exponent) (4.8) 12 C(D 0 ; O, P) = f (O) b f (P ) b C(f(D 0 ); f(o),f(p )), (4.9) μ (D0 ;O,P )( ) = μ (f(d0 );f(o),f(p ))( ). (4.10) Markov (domain Markov property) μ (D0 ;O,P ) γ γ(0,t],t (0,t γ ) D 0 γ(0,t] γ(t) γ(t γ )=P ( ) γ(0,t] = μ (D0 \γ(0,t];γ(t),p )( ). μ (D0 ;O,P ) Markov γ (4.3) t [0,t γ ] (4.6) (4.2) f(z) =z/n,n N f (z) =1/N f (O) b = f (P ) b = N b (4.9) (4.5) 21
22 (4.2) f γ f(γ[t 1,t 2 ]), 0 <t 1 <t 2 <t γ, t2 t 1 f (γ(s)) d ds d γ θ :[0,t γ ] [0,t γ ] γ(t) γ(θ(t)) 4.3 (4.7) / Markov (restriction property) D 0 D 1 D 0 O, P D LERW μ LERW (D 1 ;O,P ) O P RW RW LERW LERW Radon-Nikodym dμ LERW (D 1 ;O,P ) dμ LERW (D 0 ;O,P ) < 1, D 1 D 0, D 1 D 0 SAW dμ SAW (D 1 ;O,P ) dμ SAW (D 0 ;O,P ) = 1{γ(0,t γ ) D 1 }, D 1 D 0 (4.11) 1{ω} ω (4.11) η Bernoulli η μ per μ Ising (locality property) D 1 D 0 O, P D 1 μ per (D 1 ;O,P )(γ(0,t]) = μper (D 0 ;O,P ) (γ(0,t])1{γ(0,t) D 1}, t (0,t γ ). (4.12) (4.11) γ(0,t γ ) (4.12) γ(0,t],t (0,t γ ) 22
23 5 Schramm-Loewner Evolution (SLE) 5.1 Riemann D, D C D, D C, z, w D, z,w D Riemann f : D D, f(z) =z, f(w) =w f (w) =1 H = {z C :Imz>0} μ (H;0, ) D C,D C, z, w D μ (D;z,w) H \ D D H w = f(w) = f (w) =1 w f(w ) w f μ (D;z, ) ( )= f (z) b μ (f(d);f(z), ) ( ), z D. (5.1) 5.2 Loewner γ :(0, ) H lim γ(t) =U 0 R lim γ(t) = t 0 t H t γ(0,t] H \ γ(0,t] t (0, ) H \ γ(0,t] H f lim f (z) =1 g t z a(t) > 0 g t (z) =z + a(t) + O( z 2 ), z z a(t) γ(0,t] (half-plane capacity) g t (z) (chordal) Loewner d dt g t(z) = da(t)/dt g t (z) U t, g 0 (z) =z. (5.2) U t = g t (γ(t)) R t U t U t a(t) Loewner (5.2) g t : H t H,t (0, ) H t H H t pioneer point H pion = H s 0 s<t γ(0) R γ :(0, ) H H pion t = R γ(0,t] g t γ 23
24 5.3 SLE κ γ a(t) =at, a > 0 U t Loewner (5.2) g t γ μ (H;0, ) / Markov U t γ U t U t 1.1 Brown B(t) Loewner d dt g t(z) = a g t (z) U t, g 0 (z) =z, U t = B(t) (5.3) Schramm Schramm-Loewner evolution [15] 13 Schramm κ (0, ) a = 2 κ SLE κ SLE κ g t SLE κ γ SLE κ μ κ (H;0, ) SLE κ lim γ(t) =B(0) = 0 lim γ(t) = t 0 t 5.1 (Lawler-Schramm-Werner [9]) 14 Markov SLE κ, κ (0, ) (5.3) h t (z) =g t (z) U t = g t (z) B(t) z H x dh t (x) =db(t)+ (1.8) a h t (x) dt, h 0(x) =x>0 (5.4) a = d 1 2 d =2a +1 d = 4 κ +1 κ = 4 d 1 (5.5) 13 Oded Schramm (ICM 2006) Wendelin Werner [16] John Charles Fields 1998 Andrew Wiles Fermat ICM 2006 Gauss 24
25 0 0 0 (a) (b) (c) 4: (a) 0 <κ 4 SLE (b) H H 4 <κ<8 SLE (c) H κ 8 SLE h t (x) x>0 (2a +1)=(4/κ +1) Bessel Bessel (Bessel flow) 15 SLE κ κ (phase) 4 (5.5) d =2 κ =4,d =3/2 κ =8 5.2 (Lawler-Schramm-Werner [9]) (a) 0 <κ 4 SLE κ γ γ(0, ) H (b) κ>4 γ γ(0, ) R (c) κ 8 γ H γ[0, ) =H. 5.3 (Beffara[1]) κ 8 SLE κ γ(0, ) Hausdorff 16 d(κ) =1+ κ x>0 d Bessel T x (i) d 2 P(T x = ) =1, x >0. (ii) 1 d<2 P(T x < ) =1, x >0. (iii) 3/2 <d<2 0 <x<y P(T x = T y ) > 0. (iv) 1 d 3/2 0 <x<y P(T x <T y )=1. 16 d R d V ε >0 ε U 1,U 2,... diam(u n ) sup{ x y : x, y U n } <ε,n 1, V U n. α>0 n 1 25
26 5.4 H { } D = D H :, H \ D, 0 D D D D H Φ D Φ D (z) =z + o(1),z. SLE κ γ { } τ D = inf t : γ H \ D t <τ D γ D SLE γ(0,τ D ) Φ D Φ D (γ(0,τ D )) H = H R γ Φ D (γ(0,τ D )) gt (z) Loewner (5.3) Φ D Itô gt (z) U t (5.3) du t = b Φ t (U t ) dt + db(t). (5.6) Φ t(u t ) b(κ) = 3a 1 2 = 6 κ 2κ. (5.7) κ =6 b =0 D D g t (z) g t (z) t<τ D, U t = B(t) Brown SLE, (5.3) 5.4 SLE κ μ κ (H ;0, ) κ =6 κ 6 (5.6) U t Girsanov [12, 3] M t 17 f Schwarz H α ε (V ) = inf n 1(diam(U n )) α inf ε H α (V ) = lim ε 0 H α ε (V ) Hausdorff α V Hausdorff dim H (V ) = inf{α : H α (V )=0} = sup{α : H α (V )= }. 17 j τ j τ 1 <τ 2 < j Z(t τ j ) a b = min{a, b} Z(t) 26
27 Sf(z) = f (z) f (z) 3f (z) 2 2f (z) 2 c = 2b(3 4a) a = (3κ 8)(6 κ) 2κ (5.8) { t } a M t = exp c 0 12 SΦ s(u s )ds Φ t(u t ) b (5.9) dμ (H ;0, ) dm t = b Φ t (U t) Φ t(u t ) M tdb(t) 18 κ = 2 4,D D a { dμ } (D;0, ) a (γ) =M = 1{γ(0, ) D} exp c 0 12 SΦ s(u s )ds (5.10) (5.8) κ 4 κ =8/3 c =0 (5.10) 1{γ(0, ) D} (4.11) 5.5 SLE κ μ κ (H ;0, ) κ = μ per (D 0 ;0,P ) μsaw (D 0 ;O,P ) μ6 (H;0, ), μ 8/3 (H;0, ) H D 0 Smirnov [18, 21] μ LERW (D 0 ;0,P ) = μ2 (H;0, ) [15, 9] μising (D 0 ;0,P ) = μ3 (H ;0, ) [19] = 5.3 (5.7) 19 d LERW = d(2) = 5 4, d SAW = d(8/3) = 4 3, d Ising = d(3) = 11 8, d per = d(6) = 7 4, b LERW = b(2) = 1, b SAW = b(8/3) = 5 8, b Ising = b(3) = 1 2, b per = b(6) = (i) t γ(t) γ(0, ) D Φ t (U t) 1,t (ii) SΦ t (U t ) 0 κ 4 (i) [9] 19 t γ(t) (5.1) (5.9) (5.1) (5.7) b 27
28 a (a 0 =0) 0 a [a, a ]=1 L n (n =1, 2, 3, ) L n (n = 1, 2, 3, ), L 0 [L n,l m ]=(n m)l n+m + c n(n2 1) δ n+m,0, n,m Z (6.1) 12 c Virasoro [22] (L n b =0,n 1) b L n,n 1 L 0 b = b b b b n k,...,n 1 ; b = L nk L n1 b, 0 <n 1 n 1 n k Verma L 0 L 0 n k,...,n 1 ; b =(b + n n k ) n k,...,n 1 ; b. L 0 b k j=1 n j 2 L 1 L 1 b L 2 b ( ) ( b L 2 L 2 b b L 2 L 1 L 1 b 4b + c/2 6b det = det b L 1 L 1 L 2 b b L 1 L 1 L 1 L 1 b 6b 4b(1 + 2b) ) =0 (6.2) Kac ( ) 1 χ 2,1 = 2 L 2b +1 1L 1 L 2 b (6.3) 3 2 null vector L n,n 1 2 b 0 (6.2) c = 2b(5 8b) 1+2b 28 (6.4)
29 (5.7) (5.8) κ b c (6.4) L 1 x, L 2 1 x x 20 (6.3) b x + a 2 x x, a = 2 2b +1 = κ 3 (2a+1) Bessel (5.4) (generator) G (2a+1) Kolmogorov (1.9) t u = G(d) u. SLE κ (5.8) Virasoro (5.7) 2 [2] : [1] V. Beffara : The dimension of the SLE curves, Ann. Probab. 36, (2008); [2] R. Friedrich and W. Werner : Conformal restriction, highest-weight representations and SLE, Commun. Math. Phys. 243, (2003); [3] I. S. E. (2001). [4] : 13, No.4, ([296]-[307]) (2003). [5] SLE, 62, No.7, (2007). [6] M. Katori and H. Tanemura : Symmetry of matrix-valued stochastic processes and noncolliding diffusion particle systems, J. Math. Phys. 45, (2004); { } (n 1)Δ 20 L n L n = (x z) n 1 (x z) n 1 x z =0, Δ=0 29
30 [7] 6 ), (2006) [8] M. Katori and H. Tanemura : Noncolliding Brownian motion and determinantal processes, J. Stat. Phys., 129, (2007); [9] G. F. Lawler : Conformally Invariant Processes in the Plane, (American Mathematical Society, 2005). [10] I, II (2004). [11] M. L. Mehta : Random Matrices, 3rd ed. (Elsevier Academic Press, London, 2004). [12] (1999). [13] (2005). [14] 2005). [15] O. Schramm : Scaling limits of loop-erased random walks and uniform spanning trees, Israel J. Math. 118, (2000); [16],, No.545 ( ), pp.46-51,. [17] SLE Schramm-Loewner Evolution,, No.546 ( ), pp.7-12, [18] S. Smirnov : Critical percolation in the plane: Conformal invariance, Cardy s formula, scaling limits, C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris, Sér. I Math. 333, (2001); Smirnov web page pdf file smirnov/papers/index.html. [19] S. Smirnov : Conformal invariance in random cluster models. I. Holomorphic fermions in the Ising model, [20] :,,, [21],, No.546 ( ), pp [22] 2006). 30
統計力学模型とSLE 中央大学理工学部 香取眞理
 1 Loewner 0. 1. 1.1 (loop erased RW : LERW) (self avoiding walk : SAW) (critical percolation model) Ising (critical Ising model) 1.2 Markov (conformal cov./inv.) Markov (domain Markov property) 1.3 LERW
1 Loewner 0. 1. 1.1 (loop erased RW : LERW) (self avoiding walk : SAW) (critical percolation model) Ising (critical Ising model) 1.2 Markov (conformal cov./inv.) Markov (domain Markov property) 1.3 LERW
Katori_SLE_Feb2010_s1.dvi
 Schramm-Loewner Evolution H H H H H. H γ H t t U t U t g t (z) t = g t (z) U t, g 0 (z) =z, t 0 t g t (z) t 0 g t (z) H t γ(0,t] B t κ >0 Schramm 000 U t = κb t H U t = κb t κ Schramm- Loewner Evolution
Schramm-Loewner Evolution H H H H H. H γ H t t U t U t g t (z) t = g t (z) U t, g 0 (z) =z, t 0 t g t (z) t 0 g t (z) H t γ(0,t] B t κ >0 Schramm 000 U t = κb t H U t = κb t κ Schramm- Loewner Evolution
( ) Loewner SLE 13 February
 ( ) Loewner SLE 3 February 00 G. F. Lawler, Conformally Invariant Processes in the Plane, (American Mathematical Society, 005)., Summer School 009 (009 8 7-9 ) . d- (BES d ) d B t = (Bt, B t,, Bd t ) (d
( ) Loewner SLE 3 February 00 G. F. Lawler, Conformally Invariant Processes in the Plane, (American Mathematical Society, 005)., Summer School 009 (009 8 7-9 ) . d- (BES d ) d B t = (Bt, B t,, Bd t ) (d
Katori_SLE_Sep07_v2c.dvi
 Schramm-Loewner Evolution (SLE) and Conformal Restriction 4 September 007 (version c) SLE [6] Lawler ( [7]), 3 Werner ( []), 4 Friedrich and Werner ( [3]) 3........................ 3. d-.................................
Schramm-Loewner Evolution (SLE) and Conformal Restriction 4 September 007 (version c) SLE [6] Lawler ( [7]), 3 Werner ( []), 4 Friedrich and Werner ( [3]) 3........................ 3. d-.................................
 n ξ n,i, i = 1,, n S n ξ n,i n 0 R 1,.. σ 1 σ i .10.14.15 0 1 0 1 1 3.14 3.18 3.19 3.14 3.14,. ii 1 1 1.1..................................... 1 1............................... 3 1.3.........................
n ξ n,i, i = 1,, n S n ξ n,i n 0 R 1,.. σ 1 σ i .10.14.15 0 1 0 1 1 3.14 3.18 3.19 3.14 3.14,. ii 1 1 1.1..................................... 1 1............................... 3 1.3.........................
(Bessel) (Legendre).. (Hankel). (Laplace) V = (x, y, z) n (r, θ, ϕ) r n f n (θ, ϕ). f n (θ, ϕ) n f n (θ, ϕ) z = cos θ z θ ϕ n ν. P ν (z), Q ν (z) (Fou
 (Bessel) (Legendre).. (Hankel). (Laplace) V = (x, y, z) n (r, θ, ϕ) r n f n (θ, ϕ). f n (θ, ϕ) n f n (θ, ϕ) z = cos θ z θ ϕ n ν. P ν (z), Q ν (z) (Fourier) (Fourier Bessel).. V ρ(x, y, z) V = 4πGρ G :.
(Bessel) (Legendre).. (Hankel). (Laplace) V = (x, y, z) n (r, θ, ϕ) r n f n (θ, ϕ). f n (θ, ϕ) n f n (θ, ϕ) z = cos θ z θ ϕ n ν. P ν (z), Q ν (z) (Fourier) (Fourier Bessel).. V ρ(x, y, z) V = 4πGρ G :.
II No.01 [n/2] [1]H n (x) H n (x) = ( 1) r n! r!(n 2r)! (2x)n 2r. r=0 [2]H n (x) n,, H n ( x) = ( 1) n H n (x). [3] H n (x) = ( 1) n dn x2 e dx n e x2
![II No.01 [n/2] [1]H n (x) H n (x) = ( 1) r n! r!(n 2r)! (2x)n 2r. r=0 [2]H n (x) n,, H n ( x) = ( 1) n H n (x). [3] H n (x) = ( 1) n dn x2 e dx n e x2 II No.01 [n/2] [1]H n (x) H n (x) = ( 1) r n! r!(n 2r)! (2x)n 2r. r=0 [2]H n (x) n,, H n ( x) = ( 1) n H n (x). [3] H n (x) = ( 1) n dn x2 e dx n e x2](/thumbs/101/149159646.jpg) II No.1 [n/] [1]H n x) H n x) = 1) r n! r!n r)! x)n r r= []H n x) n,, H n x) = 1) n H n x) [3] H n x) = 1) n dn x e dx n e x [4] H n+1 x) = xh n x) nh n 1 x) ) d dx x H n x) = H n+1 x) d dx H nx) = nh
II No.1 [n/] [1]H n x) H n x) = 1) r n! r!n r)! x)n r r= []H n x) n,, H n x) = 1) n H n x) [3] H n x) = 1) n dn x e dx n e x [4] H n+1 x) = xh n x) nh n 1 x) ) d dx x H n x) = H n+1 x) d dx H nx) = nh
Part () () Γ Part ,
 Contents a 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 7 7. 8.. 8.. 8.3. 8 Part. 9. 9.. 9.. 3. 3.. 3.. 3 4. 5 4.. 5 4.. 9 4.3. 3 Part. 6 5. () 6 5.. () 7 5.. 9 5.3. Γ 3 6. 3 6.. 3 6.. 3 6.3. 33 Part 3. 34 7. 34 7.. 34 7.. 34 8. 35
Contents a 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 7 7. 8.. 8.. 8.3. 8 Part. 9. 9.. 9.. 3. 3.. 3.. 3 4. 5 4.. 5 4.. 9 4.3. 3 Part. 6 5. () 6 5.. () 7 5.. 9 5.3. Γ 3 6. 3 6.. 3 6.. 3 6.3. 33 Part 3. 34 7. 34 7.. 34 7.. 34 8. 35
Grushin 2MA16039T
 Grushin 2MA1639T 3 2 2 R d Borel α i k (x, bi (x, 1 i d, 1 k N d N α R d b α = α(x := (αk(x i 1 i d, 1 k N b = b(x := (b i (x 1 i d X = (X t t x R d dx t = α(x t db t + b(x t dt ( 3 u t = Au + V u, u(,
Grushin 2MA1639T 3 2 2 R d Borel α i k (x, bi (x, 1 i d, 1 k N d N α R d b α = α(x := (αk(x i 1 i d, 1 k N b = b(x := (b i (x 1 i d X = (X t t x R d dx t = α(x t db t + b(x t dt ( 3 u t = Au + V u, u(,
II Brown Brown
 II 16 12 5 1 Brown 3 1.1..................................... 3 1.2 Brown............................... 5 1.3................................... 8 1.4 Markov.................................... 1 1.5
II 16 12 5 1 Brown 3 1.1..................................... 3 1.2 Brown............................... 5 1.3................................... 8 1.4 Markov.................................... 1 1.5
,. Black-Scholes u t t, x c u 0 t, x x u t t, x c u t, x x u t t, x + σ x u t, x + rx ut, x rux, t 0 x x,,.,. Step 3, 7,,, Step 6., Step 4,. Step 5,,.
 9 α ν β Ξ ξ Γ γ o δ Π π ε ρ ζ Σ σ η τ Θ θ Υ υ ι Φ φ κ χ Λ λ Ψ ψ µ Ω ω Def, Prop, Th, Lem, Note, Remark, Ex,, Proof, R, N, Q, C [a, b {x R : a x b} : a, b {x R : a < x < b} : [a, b {x R : a x < b} : a,
9 α ν β Ξ ξ Γ γ o δ Π π ε ρ ζ Σ σ η τ Θ θ Υ υ ι Φ φ κ χ Λ λ Ψ ψ µ Ω ω Def, Prop, Th, Lem, Note, Remark, Ex,, Proof, R, N, Q, C [a, b {x R : a x b} : a, b {x R : a < x < b} : [a, b {x R : a x < b} : a,
No δs δs = r + δr r = δr (3) δs δs = r r = δr + u(r + δr, t) u(r, t) (4) δr = (δx, δy, δz) u i (r + δr, t) u i (r, t) = u i x j δx j (5) δs 2
 No.2 1 2 2 δs δs = r + δr r = δr (3) δs δs = r r = δr + u(r + δr, t) u(r, t) (4) δr = (δx, δy, δz) u i (r + δr, t) u i (r, t) = u i δx j (5) δs 2 = δx i δx i + 2 u i δx i δx j = δs 2 + 2s ij δx i δx j
No.2 1 2 2 δs δs = r + δr r = δr (3) δs δs = r r = δr + u(r + δr, t) u(r, t) (4) δr = (δx, δy, δz) u i (r + δr, t) u i (r, t) = u i δx j (5) δs 2 = δx i δx i + 2 u i δx i δx j = δs 2 + 2s ij δx i δx j
構造と連続体の力学基礎
 II 37 Wabash Avenue Bridge, Illinois 州 Winnipeg にある歩道橋 Esplanade Riel 橋6 6 斜張橋である必要は多分無いと思われる すぐ横に道路用桁橋有り しかも塔基部のレストランは 8 年には営業していなかった 9 9. 9.. () 97 [3] [5] k 9. m w(t) f (t) = f (t) + mg k w(t) Newton
II 37 Wabash Avenue Bridge, Illinois 州 Winnipeg にある歩道橋 Esplanade Riel 橋6 6 斜張橋である必要は多分無いと思われる すぐ横に道路用桁橋有り しかも塔基部のレストランは 8 年には営業していなかった 9 9. 9.. () 97 [3] [5] k 9. m w(t) f (t) = f (t) + mg k w(t) Newton
 43433 8 3 . Stochastic exponentials...................................... 3. Girsanov s theorem......................................... 4 On the martingale property of stochastic exponentials 5. Gronwall
43433 8 3 . Stochastic exponentials...................................... 3. Girsanov s theorem......................................... 4 On the martingale property of stochastic exponentials 5. Gronwall
x (x, ) x y (, y) iy x y z = x + iy (x, y) (r, θ) r = x + y, θ = tan ( y ), π < θ π x r = z, θ = arg z z = x + iy = r cos θ + ir sin θ = r(cos θ + i s
 ... x, y z = x + iy x z y z x = Rez, y = Imz z = x + iy x iy z z () z + z = (z + z )() z z = (z z )(3) z z = ( z z )(4)z z = z z = x + y z = x + iy ()Rez = (z + z), Imz = (z z) i () z z z + z z + z.. z
... x, y z = x + iy x z y z x = Rez, y = Imz z = x + iy x iy z z () z + z = (z + z )() z z = (z z )(3) z z = ( z z )(4)z z = z z = x + y z = x + iy ()Rez = (z + z), Imz = (z z) i () z z z + z z + z.. z
I A A441 : April 21, 2014 Version : Kawahira, Tomoki TA (Kondo, Hirotaka ) Google
 I4 - : April, 4 Version :. Kwhir, Tomoki TA (Kondo, Hirotk) Google http://www.mth.ngoy-u.c.jp/~kwhir/courses/4s-biseki.html pdf 4 4 4 4 8 e 5 5 9 etc. 5 6 6 6 9 n etc. 6 6 6 3 6 3 7 7 etc 7 4 7 7 8 5 59
I4 - : April, 4 Version :. Kwhir, Tomoki TA (Kondo, Hirotk) Google http://www.mth.ngoy-u.c.jp/~kwhir/courses/4s-biseki.html pdf 4 4 4 4 8 e 5 5 9 etc. 5 6 6 6 9 n etc. 6 6 6 3 6 3 7 7 etc 7 4 7 7 8 5 59
meiji_resume_1.PDF
 β β β (q 1,q,..., q n ; p 1, p,..., p n ) H(q 1,q,..., q n ; p 1, p,..., p n ) Hψ = εψ ε k = k +1/ ε k = k(k 1) (x, y, z; p x, p y, p z ) (r; p r ), (θ; p θ ), (ϕ; p ϕ ) ε k = 1/ k p i dq i E total = E
β β β (q 1,q,..., q n ; p 1, p,..., p n ) H(q 1,q,..., q n ; p 1, p,..., p n ) Hψ = εψ ε k = k +1/ ε k = k(k 1) (x, y, z; p x, p y, p z ) (r; p r ), (θ; p θ ), (ϕ; p ϕ ) ε k = 1/ k p i dq i E total = E
Feynman Encounter with Mathematics 52, [1] N. Kumano-go, Feynman path integrals as analysis on path space by time slicing approximation. Bull
![Feynman Encounter with Mathematics 52, [1] N. Kumano-go, Feynman path integrals as analysis on path space by time slicing approximation. Bull Feynman Encounter with Mathematics 52, [1] N. Kumano-go, Feynman path integrals as analysis on path space by time slicing approximation. Bull](/thumbs/94/118365979.jpg) Feynman Encounter with Mathematics 52, 200 9 [] N. Kumano-go, Feynman path integrals as analysis on path space by time slicing approximation. Bull. Sci. Math. vol. 28 (2004) 97 25. [2] D. Fujiwara and
Feynman Encounter with Mathematics 52, 200 9 [] N. Kumano-go, Feynman path integrals as analysis on path space by time slicing approximation. Bull. Sci. Math. vol. 28 (2004) 97 25. [2] D. Fujiwara and
Z: Q: R: C: sin 6 5 ζ a, b
 Z: Q: R: C: 3 3 7 4 sin 6 5 ζ 9 6 6............................... 6............................... 6.3......................... 4 7 6 8 8 9 3 33 a, b a bc c b a a b 5 3 5 3 5 5 3 a a a a p > p p p, 3,
Z: Q: R: C: 3 3 7 4 sin 6 5 ζ 9 6 6............................... 6............................... 6.3......................... 4 7 6 8 8 9 3 33 a, b a bc c b a a b 5 3 5 3 5 5 3 a a a a p > p p p, 3,
D = [a, b] [c, d] D ij P ij (ξ ij, η ij ) f S(f,, {P ij }) S(f,, {P ij }) = = k m i=1 j=1 m n f(ξ ij, η ij )(x i x i 1 )(y j y j 1 ) = i=1 j
![D = [a, b] [c, d] D ij P ij (ξ ij, η ij ) f S(f,, {P ij }) S(f,, {P ij }) = = k m i=1 j=1 m n f(ξ ij, η ij )(x i x i 1 )(y j y j 1 ) = i=1 j D = [a, b] [c, d] D ij P ij (ξ ij, η ij ) f S(f,, {P ij }) S(f,, {P ij }) = = k m i=1 j=1 m n f(ξ ij, η ij )(x i x i 1 )(y j y j 1 ) = i=1 j](/thumbs/103/158001152.jpg) 6 6.. [, b] [, d] ij P ij ξ ij, η ij f Sf,, {P ij } Sf,, {P ij } k m i j m fξ ij, η ij i i j j i j i m i j k i i j j m i i j j k i i j j kb d {P ij } lim Sf,, {P ij} kb d f, k [, b] [, d] f, d kb d 6..
6 6.. [, b] [, d] ij P ij ξ ij, η ij f Sf,, {P ij } Sf,, {P ij } k m i j m fξ ij, η ij i i j j i j i m i j k i i j j m i i j j k i i j j kb d {P ij } lim Sf,, {P ij} kb d f, k [, b] [, d] f, d kb d 6..
数学Ⅱ演習(足助・09夏)
 II I 9/4/4 9/4/2 z C z z z z, z 2 z, w C zw z w 3 z, w C z + w z + w 4 t R t C t t t t t z z z 2 z C re z z + z z z, im z 2 2 3 z C e z + z + 2 z2 + 3! z3 + z!, I 4 x R e x cos x + sin x 2 z, w C e z+w
II I 9/4/4 9/4/2 z C z z z z, z 2 z, w C zw z w 3 z, w C z + w z + w 4 t R t C t t t t t z z z 2 z C re z z + z z z, im z 2 2 3 z C e z + z + 2 z2 + 3! z3 + z!, I 4 x R e x cos x + sin x 2 z, w C e z+w
December 28, 2018
 e-mail : kigami@i.kyoto-u.ac.jp December 28, 28 Contents 2............................. 3.2......................... 7.3..................... 9.4................ 4.5............. 2.6.... 22 2 36 2..........................
e-mail : kigami@i.kyoto-u.ac.jp December 28, 28 Contents 2............................. 3.2......................... 7.3..................... 9.4................ 4.5............. 2.6.... 22 2 36 2..........................
 http://www.ike-dyn.ritsumei.ac.jp/ hyoo/wave.html 1 1, 5 3 1.1 1..................................... 3 1.2 5.1................................... 4 1.3.......................... 5 1.4 5.2, 5.3....................
http://www.ike-dyn.ritsumei.ac.jp/ hyoo/wave.html 1 1, 5 3 1.1 1..................................... 3 1.2 5.1................................... 4 1.3.......................... 5 1.4 5.2, 5.3....................
II A A441 : October 02, 2014 Version : Kawahira, Tomoki TA (Kondo, Hirotaka )
 II 214-1 : October 2, 214 Version : 1.1 Kawahira, Tomoki TA (Kondo, Hirotaka ) http://www.math.nagoya-u.ac.jp/~kawahira/courses/14w-biseki.html pdf 1 2 1 9 1 16 1 23 1 3 11 6 11 13 11 2 11 27 12 4 12 11
II 214-1 : October 2, 214 Version : 1.1 Kawahira, Tomoki TA (Kondo, Hirotaka ) http://www.math.nagoya-u.ac.jp/~kawahira/courses/14w-biseki.html pdf 1 2 1 9 1 16 1 23 1 3 11 6 11 13 11 2 11 27 12 4 12 11
 4................................. 4................................. 4 6................................. 6................................. 9.................................................... 3..3..........................
4................................. 4................................. 4 6................................. 6................................. 9.................................................... 3..3..........................
18 I ( ) (1) I-1,I-2,I-3 (2) (3) I-1 ( ) (100 ) θ ϕ θ ϕ m m l l θ ϕ θ ϕ 2 g (1) (2) 0 (3) θ ϕ (4) (3) θ(t) = A 1 cos(ω 1 t + α 1 ) + A 2 cos(ω 2 t + α
 18 I ( ) (1) I-1,I-2,I-3 (2) (3) I-1 ( ) (100 ) θ ϕ θ ϕ m m l l θ ϕ θ ϕ 2 g (1) (2) 0 (3) θ ϕ (4) (3) θ(t) = A 1 cos(ω 1 t + α 1 ) + A 2 cos(ω 2 t + α 2 ), ϕ(t) = B 1 cos(ω 1 t + α 1 ) + B 2 cos(ω 2 t
18 I ( ) (1) I-1,I-2,I-3 (2) (3) I-1 ( ) (100 ) θ ϕ θ ϕ m m l l θ ϕ θ ϕ 2 g (1) (2) 0 (3) θ ϕ (4) (3) θ(t) = A 1 cos(ω 1 t + α 1 ) + A 2 cos(ω 2 t + α 2 ), ϕ(t) = B 1 cos(ω 1 t + α 1 ) + B 2 cos(ω 2 t
II 1 II 2012 II Gauss-Bonnet II
 II 1 II 212 II Gauss-Bonnet II 1 1 1.1......................................... 1 1.2............................................ 2 1.3.................................. 3 1.4.............................................
II 1 II 212 II Gauss-Bonnet II 1 1 1.1......................................... 1 1.2............................................ 2 1.3.................................. 3 1.4.............................................
医系の統計入門第 2 版 サンプルページ この本の定価 判型などは, 以下の URL からご覧いただけます. このサンプルページの内容は, 第 2 版 1 刷発行時のものです.
 医系の統計入門第 2 版 サンプルページ この本の定価 判型などは, 以下の URL からご覧いただけます. http://www.morikita.co.jp/books/mid/009192 このサンプルページの内容は, 第 2 版 1 刷発行時のものです. i 2 t 1. 2. 3 2 3. 6 4. 7 5. n 2 ν 6. 2 7. 2003 ii 2 2013 10 iii 1987
医系の統計入門第 2 版 サンプルページ この本の定価 判型などは, 以下の URL からご覧いただけます. http://www.morikita.co.jp/books/mid/009192 このサンプルページの内容は, 第 2 版 1 刷発行時のものです. i 2 t 1. 2. 3 2 3. 6 4. 7 5. n 2 ν 6. 2 7. 2003 ii 2 2013 10 iii 1987
,,,17,,, ( ),, E Q [S T F t ] < S t, t [, T ],,,,,,,,
![,,,17,,, ( ),, E Q [S T F t ] < S t, t [, T ],,,,,,,, ,,,17,,, ( ),, E Q [S T F t ] < S t, t [, T ],,,,,,,,](/thumbs/91/105754403.jpg) 14 5 1 ,,,17,,,194 1 4 ( ),, E Q [S T F t ] < S t, t [, T ],,,,,,,, 1 4 1.1........................................ 4 5.1........................................ 5.........................................
14 5 1 ,,,17,,,194 1 4 ( ),, E Q [S T F t ] < S t, t [, T ],,,,,,,, 1 4 1.1........................................ 4 5.1........................................ 5.........................................
S I. dy fx x fx y fx + C 3 C dy fx 4 x, y dy v C xt y C v e kt k > xt yt gt [ v dt dt v e kt xt v e kt + C k x v + C C k xt v k 3 r r + dr e kt S dt d
 S I.. http://ayapin.film.s.dendai.ac.jp/~matuda /TeX/lecture.html PDF PS.................................... 3.3.................... 9.4................5.............. 3 5. Laplace................. 5....
S I.. http://ayapin.film.s.dendai.ac.jp/~matuda /TeX/lecture.html PDF PS.................................... 3.3.................... 9.4................5.............. 3 5. Laplace................. 5....
( ) ) ) ) 5) 1 J = σe 2 6) ) 9) 1955 Statistical-Mechanical Theory of Irreversible Processes )
 ( 3 7 4 ) 2 2 ) 8 2 954 2) 955 3) 5) J = σe 2 6) 955 7) 9) 955 Statistical-Mechanical Theory of Irreversible Processes 957 ) 3 4 2 A B H (t) = Ae iωt B(t) = B(ω)e iωt B(ω) = [ Φ R (ω) Φ R () ] iω Φ R (t)
( 3 7 4 ) 2 2 ) 8 2 954 2) 955 3) 5) J = σe 2 6) 955 7) 9) 955 Statistical-Mechanical Theory of Irreversible Processes 957 ) 3 4 2 A B H (t) = Ae iωt B(t) = B(ω)e iωt B(ω) = [ Φ R (ω) Φ R () ] iω Φ R (t)
 X G P G (X) G BG [X, BG] S 2 2 2 S 2 2 S 2 = { (x 1, x 2, x 3 ) R 3 x 2 1 + x 2 2 + x 2 3 = 1 } R 3 S 2 S 2 v x S 2 x x v(x) T x S 2 T x S 2 S 2 x T x S 2 = { ξ R 3 x ξ } R 3 T x S 2 S 2 x x T x S 2
X G P G (X) G BG [X, BG] S 2 2 2 S 2 2 S 2 = { (x 1, x 2, x 3 ) R 3 x 2 1 + x 2 2 + x 2 3 = 1 } R 3 S 2 S 2 v x S 2 x x v(x) T x S 2 T x S 2 S 2 x T x S 2 = { ξ R 3 x ξ } R 3 T x S 2 S 2 x x T x S 2
24 I ( ) 1. R 3 (i) C : x 2 + y 2 1 = 0 (ii) C : y = ± 1 x 2 ( 1 x 1) (iii) C : x = cos t, y = sin t (0 t 2π) 1.1. γ : [a, b] R n ; t γ(t) = (x
![24 I ( ) 1. R 3 (i) C : x 2 + y 2 1 = 0 (ii) C : y = ± 1 x 2 ( 1 x 1) (iii) C : x = cos t, y = sin t (0 t 2π) 1.1. γ : [a, b] R n ; t γ(t) = (x 24 I ( ) 1. R 3 (i) C : x 2 + y 2 1 = 0 (ii) C : y = ± 1 x 2 ( 1 x 1) (iii) C : x = cos t, y = sin t (0 t 2π) 1.1. γ : [a, b] R n ; t γ(t) = (x](/thumbs/94/118744578.jpg) 24 I 1.1.. ( ) 1. R 3 (i) C : x 2 + y 2 1 = 0 (ii) C : y = ± 1 x 2 ( 1 x 1) (iii) C : x = cos t, y = sin t (0 t 2π) 1.1. γ : [a, b] R n ; t γ(t) = (x 1 (t), x 2 (t),, x n (t)) ( ) ( ), γ : (i) x 1 (t),
24 I 1.1.. ( ) 1. R 3 (i) C : x 2 + y 2 1 = 0 (ii) C : y = ± 1 x 2 ( 1 x 1) (iii) C : x = cos t, y = sin t (0 t 2π) 1.1. γ : [a, b] R n ; t γ(t) = (x 1 (t), x 2 (t),, x n (t)) ( ) ( ), γ : (i) x 1 (t),
S I. dy fx x fx y fx + C 3 C vt dy fx 4 x, y dy yt gt + Ct + C dt v e kt xt v e kt + C k x v k + C C xt v k 3 r r + dr e kt S Sr πr dt d v } dt k e kt
 S I. x yx y y, y,. F x, y, y, y,, y n http://ayapin.film.s.dendai.ac.jp/~matuda n /TeX/lecture.html PDF PS yx.................................... 3.3.................... 9.4................5..............
S I. x yx y y, y,. F x, y, y, y,, y n http://ayapin.film.s.dendai.ac.jp/~matuda n /TeX/lecture.html PDF PS yx.................................... 3.3.................... 9.4................5..............
 211 kotaro@math.titech.ac.jp 1 R *1 n n R n *2 R n = {(x 1,..., x n ) x 1,..., x n R}. R R 2 R 3 R n R n R n D D R n *3 ) (x 1,..., x n ) f(x 1,..., x n ) f D *4 n 2 n = 1 ( ) 1 f D R n f : D R 1.1. (x,
211 kotaro@math.titech.ac.jp 1 R *1 n n R n *2 R n = {(x 1,..., x n ) x 1,..., x n R}. R R 2 R 3 R n R n R n D D R n *3 ) (x 1,..., x n ) f(x 1,..., x n ) f D *4 n 2 n = 1 ( ) 1 f D R n f : D R 1.1. (x,
7 π L int = gψ(x)ψ(x)φ(x) + (7.4) [ ] p ψ N = n (7.5) π (π +,π 0,π ) ψ (σ, σ, σ )ψ ( A) σ τ ( L int = gψψφ g N τ ) N π * ) (7.6) π π = (π, π, π ) π ±
![7 π L int = gψ(x)ψ(x)φ(x) + (7.4) [ ] p ψ N = n (7.5) π (π +,π 0,π ) ψ (σ, σ, σ )ψ ( A) σ τ ( L int = gψψφ g N τ ) N π * ) (7.6) π π = (π, π, π ) π ± 7 π L int = gψ(x)ψ(x)φ(x) + (7.4) [ ] p ψ N = n (7.5) π (π +,π 0,π ) ψ (σ, σ, σ )ψ ( A) σ τ ( L int = gψψφ g N τ ) N π * ) (7.6) π π = (π, π, π ) π ±](/thumbs/91/106462075.jpg) 7 7. ( ) SU() SU() 9 ( MeV) p 98.8 π + π 0 n 99.57 9.57 97.4 497.70 δm m 0.4%.% 0.% 0.8% π 9.57 4.96 Σ + Σ 0 Σ 89.6 9.46 K + K 0 49.67 (7.) p p = αp + βn, n n = γp + δn (7.a) [ ] p ψ ψ = Uψ, U = n [ α
7 7. ( ) SU() SU() 9 ( MeV) p 98.8 π + π 0 n 99.57 9.57 97.4 497.70 δm m 0.4%.% 0.% 0.8% π 9.57 4.96 Σ + Σ 0 Σ 89.6 9.46 K + K 0 49.67 (7.) p p = αp + βn, n n = γp + δn (7.a) [ ] p ψ ψ = Uψ, U = n [ α
n (1.6) i j=1 1 n a ij x j = b i (1.7) (1.7) (1.4) (1.5) (1.4) (1.7) u, v, w ε x, ε y, ε x, γ yz, γ zx, γ xy (1.8) ε x = u x ε y = v y ε z = w z γ yz
 1 2 (a 1, a 2, a n ) (b 1, b 2, b n ) A (1.1) A = a 1 b 1 + a 2 b 2 + + a n b n (1.1) n A = a i b i (1.2) i=1 n i 1 n i=1 a i b i n i=1 A = a i b i (1.3) (1.3) (1.3) (1.1) (ummation convention) a 11 x
1 2 (a 1, a 2, a n ) (b 1, b 2, b n ) A (1.1) A = a 1 b 1 + a 2 b 2 + + a n b n (1.1) n A = a i b i (1.2) i=1 n i 1 n i=1 a i b i n i=1 A = a i b i (1.3) (1.3) (1.3) (1.1) (ummation convention) a 11 x
 IA hara@math.kyushu-u.ac.jp Last updated: January,......................................................................................................................................................................................
IA hara@math.kyushu-u.ac.jp Last updated: January,......................................................................................................................................................................................
201711grade1ouyou.pdf
 2017 11 26 1 2 52 3 12 13 22 23 32 33 42 3 5 3 4 90 5 6 A 1 2 Web Web 3 4 1 2... 5 6 7 7 44 8 9 1 2 3 1 p p >2 2 A 1 2 0.6 0.4 0.52... (a) 0.6 0.4...... B 1 2 0.8-0.2 0.52..... (b) 0.6 0.52.... 1 A B 2
2017 11 26 1 2 52 3 12 13 22 23 32 33 42 3 5 3 4 90 5 6 A 1 2 Web Web 3 4 1 2... 5 6 7 7 44 8 9 1 2 3 1 p p >2 2 A 1 2 0.6 0.4 0.52... (a) 0.6 0.4...... B 1 2 0.8-0.2 0.52..... (b) 0.6 0.52.... 1 A B 2
Note.tex 2008/09/19( )
 1 20 9 19 2 1 5 1.1........................ 5 1.2............................. 8 2 9 2.1............................. 9 2.2.............................. 10 3 13 3.1.............................. 13 3.2..................................
1 20 9 19 2 1 5 1.1........................ 5 1.2............................. 8 2 9 2.1............................. 9 2.2.............................. 10 3 13 3.1.............................. 13 3.2..................................
() n C + n C + n C + + n C n n (3) n C + n C + n C 4 + n C + n C 3 + n C 5 + (5) (6 ) n C + nc + 3 nc n nc n (7 ) n C + nc + 3 nc n nc n (
 3 n nc k+ k + 3 () n C r n C n r nc r C r + C r ( r n ) () n C + n C + n C + + n C n n (3) n C + n C + n C 4 + n C + n C 3 + n C 5 + (4) n C n n C + n C + n C + + n C n (5) k k n C k n C k (6) n C + nc
3 n nc k+ k + 3 () n C r n C n r nc r C r + C r ( r n ) () n C + n C + n C + + n C n n (3) n C + n C + n C 4 + n C + n C 3 + n C 5 + (4) n C n n C + n C + n C + + n C n (5) k k n C k n C k (6) n C + nc
) ] [ h m x + y + + V x) φ = Eφ 1) z E = i h t 13) x << 1) N n n= = N N + 1) 14) N n n= = N N + 1)N + 1) 6 15) N n 3 n= = 1 4 N N + 1) 16) N n 4
![) ] [ h m x + y + + V x) φ = Eφ 1) z E = i h t 13) x << 1) N n n= = N N + 1) 14) N n n= = N N + 1)N + 1) 6 15) N n 3 n= = 1 4 N N + 1) 16) N n 4 ) ] [ h m x + y + + V x) φ = Eφ 1) z E = i h t 13) x << 1) N n n= = N N + 1) 14) N n n= = N N + 1)N + 1) 6 15) N n 3 n= = 1 4 N N + 1) 16) N n 4](/thumbs/92/107866707.jpg) 1. k λ ν ω T v p v g k = π λ ω = πν = π T v p = λν = ω k v g = dω dk 1) ) 3) 4). p = hk = h λ 5) E = hν = hω 6) h = h π 7) h =6.6618 1 34 J sec) hc=197.3 MeV fm = 197.3 kev pm= 197.3 ev nm = 1.97 1 3 ev
1. k λ ν ω T v p v g k = π λ ω = πν = π T v p = λν = ω k v g = dω dk 1) ) 3) 4). p = hk = h λ 5) E = hν = hω 6) h = h π 7) h =6.6618 1 34 J sec) hc=197.3 MeV fm = 197.3 kev pm= 197.3 ev nm = 1.97 1 3 ev
[ ] (Ising model) 2 i S i S i = 1 (up spin : ) = 1 (down spin : ) (4.38) s z = ±1 4 H 0 = J zn/2 i,j S i S j (4.39) i, j z 5 2 z = 4 z = 6 3
![[ ] (Ising model) 2 i S i S i = 1 (up spin : ) = 1 (down spin : ) (4.38) s z = ±1 4 H 0 = J zn/2 i,j S i S j (4.39) i, j z 5 2 z = 4 z = 6 3 [ ] (Ising model) 2 i S i S i = 1 (up spin : ) = 1 (down spin : ) (4.38) s z = ±1 4 H 0 = J zn/2 i,j S i S j (4.39) i, j z 5 2 z = 4 z = 6 3](/thumbs/103/161261933.jpg) 4.2 4.2.1 [ ] (Ising model) 2 i S i S i = 1 (up spin : ) = 1 (down spin : ) (4.38) s z = ±1 4 H 0 = J zn/2 S i S j (4.39) i, j z 5 2 z = 4 z = 6 3 z = 6 z = 8 zn/2 1 2 N i z nearest neighbors of i j=1
4.2 4.2.1 [ ] (Ising model) 2 i S i S i = 1 (up spin : ) = 1 (down spin : ) (4.38) s z = ±1 4 H 0 = J zn/2 S i S j (4.39) i, j z 5 2 z = 4 z = 6 3 z = 6 z = 8 zn/2 1 2 N i z nearest neighbors of i j=1
III Kepler ( )
 III 9 8 3....................................... 3.2 Kepler ( ).......................... 0 2 3 2.................................. 3 2.2......................................... 7 3 9 3..........................................
III 9 8 3....................................... 3.2 Kepler ( ).......................... 0 2 3 2.................................. 3 2.2......................................... 7 3 9 3..........................................
2 1 κ c(t) = (x(t), y(t)) ( ) det(c (t), c x (t)) = det (t) x (t) y (t) y = x (t)y (t) x (t)y (t), (t) c (t) = (x (t)) 2 + (y (t)) 2. c (t) =
 1 1 1.1 I R 1.1.1 c : I R 2 (i) c C (ii) t I c (t) (0, 0) c (t) c(i) c c(t) 1.1.2 (1) (2) (3) (1) r > 0 c : R R 2 : t (r cos t, r sin t) (2) C f : I R c : I R 2 : t (t, f(t)) (3) y = x c : R R 2 : t (t,
1 1 1.1 I R 1.1.1 c : I R 2 (i) c C (ii) t I c (t) (0, 0) c (t) c(i) c c(t) 1.1.2 (1) (2) (3) (1) r > 0 c : R R 2 : t (r cos t, r sin t) (2) C f : I R c : I R 2 : t (t, f(t)) (3) y = x c : R R 2 : t (t,
I A A441 : April 15, 2013 Version : 1.1 I Kawahira, Tomoki TA (Shigehiro, Yoshida )
 I013 00-1 : April 15, 013 Version : 1.1 I Kawahira, Tomoki TA (Shigehiro, Yoshida) http://www.math.nagoya-u.ac.jp/~kawahira/courses/13s-tenbou.html pdf * 4 15 4 5 13 e πi = 1 5 0 5 7 3 4 6 3 6 10 6 17
I013 00-1 : April 15, 013 Version : 1.1 I Kawahira, Tomoki TA (Shigehiro, Yoshida) http://www.math.nagoya-u.ac.jp/~kawahira/courses/13s-tenbou.html pdf * 4 15 4 5 13 e πi = 1 5 0 5 7 3 4 6 3 6 10 6 17
微分積分 サンプルページ この本の定価 判型などは, 以下の URL からご覧いただけます. このサンプルページの内容は, 初版 1 刷発行時のものです.
 微分積分 サンプルページ この本の定価 判型などは, 以下の URL からご覧いただけます. ttp://www.morikita.co.jp/books/mid/00571 このサンプルページの内容は, 初版 1 刷発行時のものです. i ii 014 10 iii [note] 1 3 iv 4 5 3 6 4 x 0 sin x x 1 5 6 z = f(x, y) 1 y = f(x)
微分積分 サンプルページ この本の定価 判型などは, 以下の URL からご覧いただけます. ttp://www.morikita.co.jp/books/mid/00571 このサンプルページの内容は, 初版 1 刷発行時のものです. i ii 014 10 iii [note] 1 3 iv 4 5 3 6 4 x 0 sin x x 1 5 6 z = f(x, y) 1 y = f(x)
TOP URL 1
 TOP URL http://amonphys.web.fc.com/ 3.............................. 3.............................. 4.3 4................... 5.4........................ 6.5........................ 8.6...........................7
TOP URL http://amonphys.web.fc.com/ 3.............................. 3.............................. 4.3 4................... 5.4........................ 6.5........................ 8.6...........................7
30
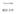 3 ............................................2 2...........................................2....................................2.2...................................2.3..............................
3 ............................................2 2...........................................2....................................2.2...................................2.3..............................
all.dvi
 I 1 Density Matrix 1.1 ( (Observable) Ô :ensemble ensemble average) Ô en =Tr ˆρ en Ô ˆρ en Tr  n, n =, 1,, Tr  = n n  n Tr  I w j j ( j =, 1,, ) ˆρ en j w j j ˆρ en = j w j j j Ô en = j w j j Ô j emsemble
I 1 Density Matrix 1.1 ( (Observable) Ô :ensemble ensemble average) Ô en =Tr ˆρ en Ô ˆρ en Tr  n, n =, 1,, Tr  = n n  n Tr  I w j j ( j =, 1,, ) ˆρ en j w j j ˆρ en = j w j j j Ô en = j w j j Ô j emsemble
prime number theorem
 For Tutor MeBio ζ Eite by kamei MeBio 7.8.3 : Bernoulli Bernoulli 4 Bernoulli....................................................................................... 4 Bernoulli............................................................................
For Tutor MeBio ζ Eite by kamei MeBio 7.8.3 : Bernoulli Bernoulli 4 Bernoulli....................................................................................... 4 Bernoulli............................................................................
untitled
 3 3. (stochastic differential equations) { dx(t) =f(t, X)dt + G(t, X)dW (t), t [,T], (3.) X( )=X X(t) : [,T] R d (d ) f(t, X) : [,T] R d R d (drift term) G(t, X) : [,T] R d R d m (diffusion term) W (t)
3 3. (stochastic differential equations) { dx(t) =f(t, X)dt + G(t, X)dW (t), t [,T], (3.) X( )=X X(t) : [,T] R d (d ) f(t, X) : [,T] R d R d (drift term) G(t, X) : [,T] R d R d m (diffusion term) W (t)
i 18 2H 2 + O 2 2H 2 + ( ) 3K
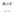 i 18 2H 2 + O 2 2H 2 + ( ) 3K ii 1 1 1.1.................................. 1 1.2........................................ 3 1.3......................................... 3 1.4....................................
i 18 2H 2 + O 2 2H 2 + ( ) 3K ii 1 1 1.1.................................. 1 1.2........................................ 3 1.3......................................... 3 1.4....................................
chap9.dvi
 9 AR (i) (ii) MA (iii) (iv) (v) 9.1 2 1 AR 1 9.1.1 S S y j = (α i + β i j) D ij + η j, η j = ρ S η j S + ε j (j =1,,T) (1) i=1 {ε j } i.i.d(,σ 2 ) η j (j ) D ij j i S 1 S =1 D ij =1 S>1 S =4 (1) y j =
9 AR (i) (ii) MA (iii) (iv) (v) 9.1 2 1 AR 1 9.1.1 S S y j = (α i + β i j) D ij + η j, η j = ρ S η j S + ε j (j =1,,T) (1) i=1 {ε j } i.i.d(,σ 2 ) η j (j ) D ij j i S 1 S =1 D ij =1 S>1 S =4 (1) y j =
I, II 1, A = A 4 : 6 = max{ A, } A A 10 10%
 1 2006.4.17. A 3-312 tel: 092-726-4774, e-mail: hara@math.kyushu-u.ac.jp, http://www.math.kyushu-u.ac.jp/ hara/lectures/lectures-j.html Office hours: B A I ɛ-δ ɛ-δ 1. 2. A 1. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 2. ɛ-δ 1. ɛ-n
1 2006.4.17. A 3-312 tel: 092-726-4774, e-mail: hara@math.kyushu-u.ac.jp, http://www.math.kyushu-u.ac.jp/ hara/lectures/lectures-j.html Office hours: B A I ɛ-δ ɛ-δ 1. 2. A 1. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 2. ɛ-δ 1. ɛ-n
B ver B
 B ver. 2017.02.24 B Contents 1 11 1.1....................... 11 1.1.1............. 11 1.1.2.......................... 12 1.2............................. 14 1.2.1................ 14 1.2.2.......................
B ver. 2017.02.24 B Contents 1 11 1.1....................... 11 1.1.1............. 11 1.1.2.......................... 12 1.2............................. 14 1.2.1................ 14 1.2.2.......................
A B P (A B) = P (A)P (B) (3) A B A B P (B A) A B A B P (A B) = P (B A)P (A) (4) P (B A) = P (A B) P (A) (5) P (A B) P (B A) P (A B) A B P
 1 1.1 (population) (sample) (event) (trial) Ω () 1 1 Ω 1.2 P 1. A A P (A) 0 1 0 P (A) 1 (1) 2. P 1 P 0 1 6 1 1 6 0 3. A B P (A B) = P (A) + P (B) (2) A B A B A 1 B 2 A B 1 2 1 2 1 1 2 2 3 1.3 A B P (A
1 1.1 (population) (sample) (event) (trial) Ω () 1 1 Ω 1.2 P 1. A A P (A) 0 1 0 P (A) 1 (1) 2. P 1 P 0 1 6 1 1 6 0 3. A B P (A B) = P (A) + P (B) (2) A B A B A 1 B 2 A B 1 2 1 2 1 1 2 2 3 1.3 A B P (A
2011de.dvi
 211 ( 4 2 1. 3 1.1............................... 3 1.2 1- -......................... 13 1.3 2-1 -................... 19 1.4 3- -......................... 29 2. 37 2.1................................ 37
211 ( 4 2 1. 3 1.1............................... 3 1.2 1- -......................... 13 1.3 2-1 -................... 19 1.4 3- -......................... 29 2. 37 2.1................................ 37
4. ϵ(ν, T ) = c 4 u(ν, T ) ϵ(ν, T ) T ν π4 Planck dx = 0 e x 1 15 U(T ) x 3 U(T ) = σt 4 Stefan-Boltzmann σ 2π5 k 4 15c 2 h 3 = W m 2 K 4 5.
 A 1. Boltzmann Planck u(ν, T )dν = 8πh ν 3 c 3 kt 1 dν h 6.63 10 34 J s Planck k 1.38 10 23 J K 1 Boltzmann u(ν, T ) T ν e hν c = 3 10 8 m s 1 2. Planck λ = c/ν Rayleigh-Jeans u(ν, T )dν = 8πν2 kt dν c
A 1. Boltzmann Planck u(ν, T )dν = 8πh ν 3 c 3 kt 1 dν h 6.63 10 34 J s Planck k 1.38 10 23 J K 1 Boltzmann u(ν, T ) T ν e hν c = 3 10 8 m s 1 2. Planck λ = c/ν Rayleigh-Jeans u(ν, T )dν = 8πν2 kt dν c
III 1 (X, d) d U d X (X, d). 1. (X, d).. (i) d(x, y) d(z, y) d(x, z) (ii) d(x, y) d(z, w) d(x, z) + d(y, w) 2. (X, d). F X.. (1), X F, (2) F 1, F 2 F
 III 1 (X, d) d U d X (X, d). 1. (X, d).. (i) d(x, y) d(z, y) d(x, z) (ii) d(x, y) d(z, w) d(x, z) + d(y, w) 2. (X, d). F X.. (1), X F, (2) F 1, F 2 F F 1 F 2 F, (3) F λ F λ F λ F. 3., A λ λ A λ. B λ λ
III 1 (X, d) d U d X (X, d). 1. (X, d).. (i) d(x, y) d(z, y) d(x, z) (ii) d(x, y) d(z, w) d(x, z) + d(y, w) 2. (X, d). F X.. (1), X F, (2) F 1, F 2 F F 1 F 2 F, (3) F λ F λ F λ F. 3., A λ λ A λ. B λ λ
IA 2013 : :10722 : 2 : :2 :761 :1 (23-27) : : ( / ) (1 /, ) / e.g. (Taylar ) e x = 1 + x + x xn n! +... sin x = x x3 6 + x5 x2n+1 + (
 IA 2013 : :10722 : 2 : :2 :761 :1 23-27) : : 1 1.1 / ) 1 /, ) / e.g. Taylar ) e x = 1 + x + x2 2 +... + xn n! +... sin x = x x3 6 + x5 x2n+1 + 1)n 5! 2n + 1)! 2 2.1 = 1 e.g. 0 = 0.00..., π = 3.14..., 1
IA 2013 : :10722 : 2 : :2 :761 :1 23-27) : : 1 1.1 / ) 1 /, ) / e.g. Taylar ) e x = 1 + x + x2 2 +... + xn n! +... sin x = x x3 6 + x5 x2n+1 + 1)n 5! 2n + 1)! 2 2.1 = 1 e.g. 0 = 0.00..., π = 3.14..., 1
量子力学 問題
 3 : 203 : 0. H = 0 0 2 6 0 () = 6, 2 = 2, 3 = 3 3 H 6 2 3 ϵ,2,3 (2) ψ = (, 2, 3 ) ψ Hψ H (3) P i = i i P P 2 = P 2 P 3 = P 3 P = O, P 2 i = P i (4) P + P 2 + P 3 = E 3 (5) i ϵ ip i H 0 0 (6) R = 0 0 [H,
3 : 203 : 0. H = 0 0 2 6 0 () = 6, 2 = 2, 3 = 3 3 H 6 2 3 ϵ,2,3 (2) ψ = (, 2, 3 ) ψ Hψ H (3) P i = i i P P 2 = P 2 P 3 = P 3 P = O, P 2 i = P i (4) P + P 2 + P 3 = E 3 (5) i ϵ ip i H 0 0 (6) R = 0 0 [H,
τ τ
 1 1 1.1 1.1.1 τ τ 2 1 1.1.2 1.1 1.1 µ ν M φ ν end ξ µ ν end ψ ψ = µ + ν end φ ν = 1 2 (µφ + ν end) ξ = ν (µ + ν end ) + 1 1.1 3 6.18 a b 1.2 a b 1.1.3 1.1.3.1 f R{A f } A f 1 B R{AB f 1 } COOH A OH B 1.3
1 1 1.1 1.1.1 τ τ 2 1 1.1.2 1.1 1.1 µ ν M φ ν end ξ µ ν end ψ ψ = µ + ν end φ ν = 1 2 (µφ + ν end) ξ = ν (µ + ν end ) + 1 1.1 3 6.18 a b 1.2 a b 1.1.3 1.1.3.1 f R{A f } A f 1 B R{AB f 1 } COOH A OH B 1.3
Microsoft Word - 信号処理3.doc
 Junji OHTSUBO 2012 FFT FFT SN sin cos x v ψ(x,t) = f (x vt) (1.1) t=0 (1.1) ψ(x,t) = A 0 cos{k(x vt) + φ} = A 0 cos(kx ωt + φ) (1.2) A 0 v=ω/k φ ω k 1.3 (1.2) (1.2) (1.2) (1.1) 1.1 c c = a + ib, a = Re[c],
Junji OHTSUBO 2012 FFT FFT SN sin cos x v ψ(x,t) = f (x vt) (1.1) t=0 (1.1) ψ(x,t) = A 0 cos{k(x vt) + φ} = A 0 cos(kx ωt + φ) (1.2) A 0 v=ω/k φ ω k 1.3 (1.2) (1.2) (1.2) (1.1) 1.1 c c = a + ib, a = Re[c],
(2 X Poisso P (λ ϕ X (t = E[e itx ] = k= itk λk e k! e λ = (e it λ k e λ = e eitλ e λ = e λ(eit 1. k! k= 6.7 X N(, 1 ϕ X (t = e 1 2 t2 : Cauchy ϕ X (t
![(2 X Poisso P (λ ϕ X (t = E[e itx ] = k= itk λk e k! e λ = (e it λ k e λ = e eitλ e λ = e λ(eit 1. k! k= 6.7 X N(, 1 ϕ X (t = e 1 2 t2 : Cauchy ϕ X (t (2 X Poisso P (λ ϕ X (t = E[e itx ] = k= itk λk e k! e λ = (e it λ k e λ = e eitλ e λ = e λ(eit 1. k! k= 6.7 X N(, 1 ϕ X (t = e 1 2 t2 : Cauchy ϕ X (t](/thumbs/67/56612994.jpg) 6 6.1 6.1 (1 Z ( X = e Z, Y = Im Z ( Z = X + iy, i = 1 (2 Z E[ e Z ] < E[ Im Z ] < Z E[Z] = E[e Z] + ie[im Z] 6.2 Z E[Z] E[ Z ] : E[ Z ] < e Z Z, Im Z Z E[Z] α = E[Z], Z = Z Z 1 {Z } E[Z] = α = α [ α ]
6 6.1 6.1 (1 Z ( X = e Z, Y = Im Z ( Z = X + iy, i = 1 (2 Z E[ e Z ] < E[ Im Z ] < Z E[Z] = E[e Z] + ie[im Z] 6.2 Z E[Z] E[ Z ] : E[ Z ] < e Z Z, Im Z Z E[Z] α = E[Z], Z = Z Z 1 {Z } E[Z] = α = α [ α ]
untitled
 1 25/5/3-6/3 1 1 1.1.................................. 1 1.2.................................. 4 2 5 2.1.............................. 5 2.2.............................. 6 3 Black Scholes 7 3.1 BS............................
1 25/5/3-6/3 1 1 1.1.................................. 1 1.2.................................. 4 2 5 2.1.............................. 5 2.2.............................. 6 3 Black Scholes 7 3.1 BS............................
 K E N Z U 2012 7 16 HP M. 1 1 4 1.1 3.......................... 4 1.2................................... 4 1.2.1..................................... 4 1.2.2.................................... 5................................
K E N Z U 2012 7 16 HP M. 1 1 4 1.1 3.......................... 4 1.2................................... 4 1.2.1..................................... 4 1.2.2.................................... 5................................
 20 9 19 1 3 11 1 3 111 3 112 1 4 12 6 121 6 122 7 13 7 131 8 132 10 133 10 134 12 14 13 141 13 142 13 143 15 144 16 145 17 15 19 151 1 19 152 20 2 21 21 21 211 21 212 1 23 213 1 23 214 25 215 31 22 33
20 9 19 1 3 11 1 3 111 3 112 1 4 12 6 121 6 122 7 13 7 131 8 132 10 133 10 134 12 14 13 141 13 142 13 143 15 144 16 145 17 15 19 151 1 19 152 20 2 21 21 21 211 21 212 1 23 213 1 23 214 25 215 31 22 33
(1.2) T D = 0 T = D = 30 kn 1.2 (1.4) 2F W = 0 F = W/2 = 300 kn/2 = 150 kn 1.3 (1.9) R = W 1 + W 2 = = 1100 N. (1.9) W 2 b W 1 a = 0
 1 1 1.1 1.) T D = T = D = kn 1. 1.4) F W = F = W/ = kn/ = 15 kn 1. 1.9) R = W 1 + W = 6 + 5 = 11 N. 1.9) W b W 1 a = a = W /W 1 )b = 5/6) = 5 cm 1.4 AB AC P 1, P x, y x, y y x 1.4.) P sin 6 + P 1 sin 45
1 1 1.1 1.) T D = T = D = kn 1. 1.4) F W = F = W/ = kn/ = 15 kn 1. 1.9) R = W 1 + W = 6 + 5 = 11 N. 1.9) W b W 1 a = a = W /W 1 )b = 5/6) = 5 cm 1.4 AB AC P 1, P x, y x, y y x 1.4.) P sin 6 + P 1 sin 45
A 2 3. m S m = {x R m+1 x = 1} U + k = {x S m x k > 0}, U k = {x S m x k < 0}, ϕ ± k (x) = (x 0,..., ˆx k,... x m ) 1. {(U ± k, ϕ± k ) 0 k m} S m 1.2.
 A A 1 A 5 A 6 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1 1.1 1.1 (). Hausdorff M R m M M {U α } U α R m E α ϕ α : U α E α U α U β = ϕ α (ϕ β ϕβ (U α U β )) 1 : ϕ β (U α U β ) ϕ α (U α U β ) C M a m dim M a U α ϕ α {x i, 1 i m} {U,
A A 1 A 5 A 6 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1 1.1 1.1 (). Hausdorff M R m M M {U α } U α R m E α ϕ α : U α E α U α U β = ϕ α (ϕ β ϕβ (U α U β )) 1 : ϕ β (U α U β ) ϕ α (U α U β ) C M a m dim M a U α ϕ α {x i, 1 i m} {U,
2 1 x 2 x 2 = RT 3πηaN A t (1.2) R/N A N A N A = N A m n(z) = n exp ( ) m gz k B T (1.3) z n z = m = m ρgv k B = erg K 1 R =
 1 1 1.1 1827 *1 195 *2 x 2 t x 2 = 2Dt D RT D = RT N A 1 6πaη (1.1) D N A a η 198 *3 ( a =.212µ) *1 Robert Brown (1773-1858. *2 Albert Einstein (1879-1955 *3 Jean Baptiste Perrin (187-1942 2 1 x 2 x 2
1 1 1.1 1827 *1 195 *2 x 2 t x 2 = 2Dt D RT D = RT N A 1 6πaη (1.1) D N A a η 198 *3 ( a =.212µ) *1 Robert Brown (1773-1858. *2 Albert Einstein (1879-1955 *3 Jean Baptiste Perrin (187-1942 2 1 x 2 x 2
V(x) m e V 0 cos x π x π V(x) = x < π, x > π V 0 (i) x = 0 (V(x) V 0 (1 x 2 /2)) n n d 2 f dξ 2ξ d f 2 dξ + 2n f = 0 H n (ξ) (ii) H
 199 1 1 199 1 1. Vx) m e V cos x π x π Vx) = x < π, x > π V i) x = Vx) V 1 x /)) n n d f dξ ξ d f dξ + n f = H n ξ) ii) H n ξ) = 1) n expξ ) dn dξ n exp ξ )) H n ξ)h m ξ) exp ξ )dξ = π n n!δ n,m x = Vx)
199 1 1 199 1 1. Vx) m e V cos x π x π Vx) = x < π, x > π V i) x = Vx) V 1 x /)) n n d f dξ ξ d f dξ + n f = H n ξ) ii) H n ξ) = 1) n expξ ) dn dξ n exp ξ )) H n ξ)h m ξ) exp ξ )dξ = π n n!δ n,m x = Vx)
untitled
 1 kaiseki1.lec(tex) 19951228 19960131;0204 14;16 26;0329; 0410;0506;22;0603-05;08;20;0707;09;11-22;24-28;30;0807;12-24;27;28; 19970104(σ,F = µ);0212( ); 0429(σ- A n ); 1221( ); 20000529;30(L p ); 20050323(
1 kaiseki1.lec(tex) 19951228 19960131;0204 14;16 26;0329; 0410;0506;22;0603-05;08;20;0707;09;11-22;24-28;30;0807;12-24;27;28; 19970104(σ,F = µ);0212( ); 0429(σ- A n ); 1221( ); 20000529;30(L p ); 20050323(
chap10.dvi
 . q {y j } I( ( L y j =Δy j = u j = C l ε j l = C(L ε j, {ε j } i.i.d.(,i q ( l= y O p ( {u j } q {C l } A l C l
. q {y j } I( ( L y j =Δy j = u j = C l ε j l = C(L ε j, {ε j } i.i.d.(,i q ( l= y O p ( {u j } q {C l } A l C l
H.Haken Synergetics 2nd (1978)
 27 3 27 ) Ising Landau Synergetics Fokker-Planck F-P Landau F-P Gizburg-Landau G-L G-L Bénard/ Hopfield H.Haken Synergetics 2nd (1978) (1) Ising m T T C 1: m h Hamiltonian H = J ij S i S j h i S
27 3 27 ) Ising Landau Synergetics Fokker-Planck F-P Landau F-P Gizburg-Landau G-L G-L Bénard/ Hopfield H.Haken Synergetics 2nd (1978) (1) Ising m T T C 1: m h Hamiltonian H = J ij S i S j h i S
July 28, H H 0 H int = H H 0 H int = H int (x)d 3 x Schrödinger Picture Ψ(t) S =e iht Ψ H O S Heisenberg Picture Ψ H O H (t) =e iht O S e i
 July 8, 4. H H H int H H H int H int (x)d 3 x Schrödinger Picture Ψ(t) S e iht Ψ H O S Heisenberg Picture Ψ H O H (t) e iht O S e iht Interaction Picture Ψ(t) D e iht Ψ(t) S O D (t) e iht O S e ih t (Dirac
July 8, 4. H H H int H H H int H int (x)d 3 x Schrödinger Picture Ψ(t) S e iht Ψ H O S Heisenberg Picture Ψ H O H (t) e iht O S e iht Interaction Picture Ψ(t) D e iht Ψ(t) S O D (t) e iht O S e ih t (Dirac
z f(z) f(z) x, y, u, v, r, θ r > 0 z = x + iy, f = u + iv C γ D f(z) f(z) D f(z) f(z) z, Rm z, z 1.1 z = x + iy = re iθ = r (cos θ + i sin θ) z = x iy
 z fz fz x, y, u, v, r, θ r > z = x + iy, f = u + iv γ D fz fz D fz fz z, Rm z, z. z = x + iy = re iθ = r cos θ + i sin θ z = x iy = re iθ = r cos θ i sin θ x = z + z = Re z, y = z z = Im z i r = z = z
z fz fz x, y, u, v, r, θ r > z = x + iy, f = u + iv γ D fz fz D fz fz z, Rm z, z. z = x + iy = re iθ = r cos θ + i sin θ z = x iy = re iθ = r cos θ i sin θ x = z + z = Re z, y = z z = Im z i r = z = z
Macdonald, ,,, Macdonald. Macdonald,,,,,.,, Gauss,,.,, Lauricella A, B, C, D, Gelfand, A,., Heckman Opdam.,,,.,,., intersection,. Macdona
 Macdonald, 2015.9.1 9.2.,,, Macdonald. Macdonald,,,,,.,, Gauss,,.,, Lauricella A, B, C, D, Gelfand, A,., Heckman Opdam.,,,.,,., intersection,. Macdonald,, q., Heckman Opdam q,, Macdonald., 1 ,,. Macdonald,
Macdonald, 2015.9.1 9.2.,,, Macdonald. Macdonald,,,,,.,, Gauss,,.,, Lauricella A, B, C, D, Gelfand, A,., Heckman Opdam.,,,.,,., intersection,. Macdonald,, q., Heckman Opdam q,, Macdonald., 1 ,,. Macdonald,
grad φ(p ) φ P grad φ(p ) p P p φ P p l t φ l t = 0 g (0) g (0) (31) grad φ(p ) p grad φ φ (P, φ(p )) xy (x, y) = (ξ(t), η(t)) ( )
 2 9 2 5 2.2.3 grad φ(p ) φ P grad φ(p ) p P p φ P p l t φ l t = g () g () (3) grad φ(p ) p grad φ φ (P, φ(p )) y (, y) = (ξ(t), η(t)) ( ) ξ (t) (t) := η (t) grad f(ξ(t), η(t)) (t) g(t) := f(ξ(t), η(t))
2 9 2 5 2.2.3 grad φ(p ) φ P grad φ(p ) p P p φ P p l t φ l t = g () g () (3) grad φ(p ) p grad φ φ (P, φ(p )) y (, y) = (ξ(t), η(t)) ( ) ξ (t) (t) := η (t) grad f(ξ(t), η(t)) (t) g(t) := f(ξ(t), η(t))
数学の基礎訓練I
 I 9 6 13 1 1 1.1............... 1 1................ 1 1.3.................... 1.4............... 1.4.1.............. 1.4................. 3 1.4.3........... 3 1.4.4.. 3 1.5.......... 3 1.5.1..............
I 9 6 13 1 1 1.1............... 1 1................ 1 1.3.................... 1.4............... 1.4.1.............. 1.4................. 3 1.4.3........... 3 1.4.4.. 3 1.5.......... 3 1.5.1..............
 006 11 8 0 3 1 5 1.1..................... 5 1......................... 6 1.3.................... 6 1.4.................. 8 1.5................... 8 1.6................... 10 1.6.1......................
006 11 8 0 3 1 5 1.1..................... 5 1......................... 6 1.3.................... 6 1.4.................. 8 1.5................... 8 1.6................... 10 1.6.1......................
I
 I 6 4 10 1 1 1.1............... 1 1................ 1 1.3.................... 1.4............... 1.4.1.............. 1.4................. 1.4.3........... 3 1.4.4.. 3 1.5.......... 3 1.5.1..............
I 6 4 10 1 1 1.1............... 1 1................ 1 1.3.................... 1.4............... 1.4.1.............. 1.4................. 1.4.3........... 3 1.4.4.. 3 1.5.......... 3 1.5.1..............
Z: Q: R: C:
 0 Z: Q: R: C: 3 4 4 4................................ 4 4.................................. 7 5 3 5...................... 3 5......................... 40 5.3 snz) z)........................... 4 6 46 x
0 Z: Q: R: C: 3 4 4 4................................ 4 4.................................. 7 5 3 5...................... 3 5......................... 40 5.3 snz) z)........................... 4 6 46 x
Radiation from moving charges#1 Liénard-Wiechert potential Yuji Chinone 1 Maxwell Maxwell MKS E (x, t) + B (x, t) t = 0 (1) B (x, t) = 0 (2) B (x, t)
 Radiation from moving harges# Liénard-Wiehert potential Yuji Chinone Maxwell Maxwell MKS E x, t + B x, t = B x, t = B x, t E x, t = µ j x, t 3 E x, t = ε ρ x, t 4 ε µ ε µ = E B ρ j A x, t φ x, t A x, t
Radiation from moving harges# Liénard-Wiehert potential Yuji Chinone Maxwell Maxwell MKS E x, t + B x, t = B x, t = B x, t E x, t = µ j x, t 3 E x, t = ε ρ x, t 4 ε µ ε µ = E B ρ j A x, t φ x, t A x, t
 http://www.ns.kogakuin.ac.jp/~ft13389/lecture/physics1a2b/ pdf I 1 1 1.1 ( ) 1. 30 m µm 2. 20 cm km 3. 10 m 2 cm 2 4. 5 cm 3 km 3 5. 1 6. 1 7. 1 1.2 ( ) 1. 1 m + 10 cm 2. 1 hr + 6400 sec 3. 3.0 10 5 kg
http://www.ns.kogakuin.ac.jp/~ft13389/lecture/physics1a2b/ pdf I 1 1 1.1 ( ) 1. 30 m µm 2. 20 cm km 3. 10 m 2 cm 2 4. 5 cm 3 km 3 5. 1 6. 1 7. 1 1.2 ( ) 1. 1 m + 10 cm 2. 1 hr + 6400 sec 3. 3.0 10 5 kg
(3) (2),,. ( 20) ( s200103) 0.7 x C,, x 2 + y 2 + ax = 0 a.. D,. D, y C, C (x, y) (y 0) C m. (2) D y = y(x) (x ± y 0), (x, y) D, m, m = 1., D. (x 2 y
 [ ] 7 0.1 2 2 + y = t sin t IC ( 9) ( s090101) 0.2 y = d2 y 2, y = x 3 y + y 2 = 0 (2) y + 2y 3y = e 2x 0.3 1 ( y ) = f x C u = y x ( 15) ( s150102) [ ] y/x du x = Cexp f(u) u (2) x y = xey/x ( 16) ( s160101)
[ ] 7 0.1 2 2 + y = t sin t IC ( 9) ( s090101) 0.2 y = d2 y 2, y = x 3 y + y 2 = 0 (2) y + 2y 3y = e 2x 0.3 1 ( y ) = f x C u = y x ( 15) ( s150102) [ ] y/x du x = Cexp f(u) u (2) x y = xey/x ( 16) ( s160101)
1: 3.3 1/8000 1/ m m/s v = 2kT/m = 2RT/M k R 8.31 J/(K mole) M 18 g 1 5 a v t πa 2 vt kg (
 1905 1 1.1 0.05 mm 1 µm 2 1 1 2004 21 2004 7 21 2005 web 2 [1, 2] 1 1: 3.3 1/8000 1/30 3 10 10 m 3 500 m/s 4 1 10 19 5 6 7 1.2 3 4 v = 2kT/m = 2RT/M k R 8.31 J/(K mole) M 18 g 1 5 a v t πa 2 vt 6 6 10
1905 1 1.1 0.05 mm 1 µm 2 1 1 2004 21 2004 7 21 2005 web 2 [1, 2] 1 1: 3.3 1/8000 1/30 3 10 10 m 3 500 m/s 4 1 10 19 5 6 7 1.2 3 4 v = 2kT/m = 2RT/M k R 8.31 J/(K mole) M 18 g 1 5 a v t πa 2 vt 6 6 10
III III 2010 PART I 1 Definition 1.1 (, σ-),,,, Borel( ),, (σ-) (M, F, µ), (R, B(R)), (C, B(C)) Borel Definition 1.2 (µ-a.e.), (in µ), (in L 1 (µ)). T
 III III 2010 PART I 1 Definition 1.1 (, σ-),,,, Borel( ),, (σ-) (M, F, µ), (R, B(R)), (C, B(C)) Borel Definition 1.2 (µ-a.e.), (in µ), (in L 1 (µ)). Theorem 1.3 (Lebesgue ) lim n f n = f µ-a.e. g L 1 (µ)
III III 2010 PART I 1 Definition 1.1 (, σ-),,,, Borel( ),, (σ-) (M, F, µ), (R, B(R)), (C, B(C)) Borel Definition 1.2 (µ-a.e.), (in µ), (in L 1 (µ)). Theorem 1.3 (Lebesgue ) lim n f n = f µ-a.e. g L 1 (µ)
III Kepler ( )
 III 20 6 24 3....................................... 3.2 Kepler ( ).......................... 2 2 4 2.................................. 4 2.2......................................... 8 3 20 3..........................................
III 20 6 24 3....................................... 3.2 Kepler ( ).......................... 2 2 4 2.................................. 4 2.2......................................... 8 3 20 3..........................................
( )
 7..-8..8.......................................................................... 4.................................... 3...................................... 3..3.................................. 4.3....................................
7..-8..8.......................................................................... 4.................................... 3...................................... 3..3.................................. 4.3....................................
 2019 1 5 0 3 1 4 1.1.................... 4 1.1.1......................... 4 1.1.2........................ 5 1.1.3................... 5 1.1.4........................ 6 1.1.5......................... 6 1.2..........................
2019 1 5 0 3 1 4 1.1.................... 4 1.1.1......................... 4 1.1.2........................ 5 1.1.3................... 5 1.1.4........................ 6 1.1.5......................... 6 1.2..........................
RIMS98R2.dvi
 RIMS Kokyuroku, vol.084, (999), 45 59. Euler Fourier Euler Fourier S = ( ) n f(n) = e in f(n) (.) I = 0 e ix f(x) dx (.2) Euler Fourier Fourier Euler Euler Fourier Euler Euler Fourier Fourier [5], [6]
RIMS Kokyuroku, vol.084, (999), 45 59. Euler Fourier Euler Fourier S = ( ) n f(n) = e in f(n) (.) I = 0 e ix f(x) dx (.2) Euler Fourier Fourier Euler Euler Fourier Euler Euler Fourier Fourier [5], [6]
6kg 1.1m 1.m.1m.1 l λ ϵ λ l + λ l l l dl dl + dλ ϵ dλ dl dl + dλ dl dl 3 1. JIS 1 6kg 1% 66kg 1 13 σ a1 σ m σ a1 σ m σ m σ a1 f f σ a1 σ a1 σ m f 4
 35-8585 7 8 1 I I 1 1.1 6kg 1m P σ σ P 1 l l λ λ l 1.m 1 6kg 1.1m 1.m.1m.1 l λ ϵ λ l + λ l l l dl dl + dλ ϵ dλ dl dl + dλ dl dl 3 1. JIS 1 6kg 1% 66kg 1 13 σ a1 σ m σ a1 σ m σ m σ a1 f f σ a1 σ a1 σ m
35-8585 7 8 1 I I 1 1.1 6kg 1m P σ σ P 1 l l λ λ l 1.m 1 6kg 1.1m 1.m.1m.1 l λ ϵ λ l + λ l l l dl dl + dλ ϵ dλ dl dl + dλ dl dl 3 1. JIS 1 6kg 1% 66kg 1 13 σ a1 σ m σ a1 σ m σ m σ a1 f f σ a1 σ a1 σ m
(5) 75 (a) (b) ( 1 ) v ( 1 ) E E 1 v (a) ( 1 ) x E E (b) (a) (b)
 (5) 74 Re, bondar laer (Prandtl) Re z ω z = x (5) 75 (a) (b) ( 1 ) v ( 1 ) E E 1 v (a) ( 1 ) x E E (b) (a) (b) (5) 76 l V x ) 1/ 1 ( 1 1 1 δ δ = x Re x p V x t V l l (1-1) 1/ 1 δ δ δ δ = x Re p V x t V
(5) 74 Re, bondar laer (Prandtl) Re z ω z = x (5) 75 (a) (b) ( 1 ) v ( 1 ) E E 1 v (a) ( 1 ) x E E (b) (a) (b) (5) 76 l V x ) 1/ 1 ( 1 1 1 δ δ = x Re x p V x t V l l (1-1) 1/ 1 δ δ δ δ = x Re p V x t V
: 2005 ( ρ t +dv j =0 r m m r = e E( r +e r B( r T 208 T = d E j 207 ρ t = = = e t δ( r r (t e r r δ( r r (t e r ( r δ( r r (t dv j =
 72 Maxwell. Maxwell e r ( =,,N Maxwell rot E + B t = 0 rot H D t = j dv D = ρ dv B = 0 D = ɛ 0 E H = μ 0 B ρ( r = j( r = N e δ( r r = N e r δ( r r = : 2005 ( 2006.8.22 73 207 ρ t +dv j =0 r m m r = e E(
72 Maxwell. Maxwell e r ( =,,N Maxwell rot E + B t = 0 rot H D t = j dv D = ρ dv B = 0 D = ɛ 0 E H = μ 0 B ρ( r = j( r = N e δ( r r = N e r δ( r r = : 2005 ( 2006.8.22 73 207 ρ t +dv j =0 r m m r = e E(
2
 III 22 7 4 3....................................... 3.2 Kepler ( ).......................... 2 2 4 2.................................. 4 2.2......................................... 8 3 20 3..........................................
III 22 7 4 3....................................... 3.2 Kepler ( ).......................... 2 2 4 2.................................. 4 2.2......................................... 8 3 20 3..........................................
I-2 (100 ) (1) y(x) y dy dx y d2 y dx 2 (a) y + 2y 3y = 9e 2x (b) x 2 y 6y = 5x 4 (2) Bernoulli B n (n = 0, 1, 2,...) x e x 1 = n=0 B 0 B 1 B 2 (3) co
 16 I ( ) (1) I-1 I-2 I-3 (2) I-1 ( ) (100 ) 2l x x = 0 y t y(x, t) y(±l, t) = 0 m T g y(x, t) l y(x, t) c = 2 y(x, t) c 2 2 y(x, t) = g (A) t 2 x 2 T/m (1) y 0 (x) y 0 (x) = g c 2 (l2 x 2 ) (B) (2) (1)
16 I ( ) (1) I-1 I-2 I-3 (2) I-1 ( ) (100 ) 2l x x = 0 y t y(x, t) y(±l, t) = 0 m T g y(x, t) l y(x, t) c = 2 y(x, t) c 2 2 y(x, t) = g (A) t 2 x 2 T/m (1) y 0 (x) y 0 (x) = g c 2 (l2 x 2 ) (B) (2) (1)
: , 2.0, 3.0, 2.0, (%) ( 2.
 2017 1 2 1.1...................................... 2 1.2......................................... 4 1.3........................................... 10 1.4................................. 14 1.5..........................................
2017 1 2 1.1...................................... 2 1.2......................................... 4 1.3........................................... 10 1.4................................. 14 1.5..........................................
II (Percolation) ( 3-4 ) 1. [ ],,,,,,,. 2. [ ],.. 3. [ ],. 4. [ ] [ ] G. Grimmett Percolation Springer-Verlag New-York [ ] 3
![II (Percolation) ( 3-4 ) 1. [ ],,,,,,,. 2. [ ],.. 3. [ ],. 4. [ ] [ ] G. Grimmett Percolation Springer-Verlag New-York [ ] 3 II (Percolation) ( 3-4 ) 1. [ ],,,,,,,. 2. [ ],.. 3. [ ],. 4. [ ] [ ] G. Grimmett Percolation Springer-Verlag New-York [ ] 3](/thumbs/94/121840826.jpg) II (Percolation) 12 9 27 ( 3-4 ) 1 [ ] 2 [ ] 3 [ ] 4 [ ] 1992 5 [ ] G Grimmett Percolation Springer-Verlag New-York 1989 6 [ ] 3 1 3 p H 2 3 2 FKG BK Russo 2 p H = p T (=: p c ) 3 2 Kesten p c =1/2 ( )
II (Percolation) 12 9 27 ( 3-4 ) 1 [ ] 2 [ ] 3 [ ] 4 [ ] 1992 5 [ ] G Grimmett Percolation Springer-Verlag New-York 1989 6 [ ] 3 1 3 p H 2 3 2 FKG BK Russo 2 p H = p T (=: p c ) 3 2 Kesten p c =1/2 ( )
1 No.1 5 C 1 I III F 1 F 2 F 1 F 2 2 Φ 2 (t) = Φ 1 (t) Φ 1 (t t). = Φ 1(t) t = ( 1.5e 0.5t 2.4e 4t 2e 10t ) τ < 0 t > τ Φ 2 (t) < 0 lim t Φ 2 (t) = 0
 1 No.1 5 C 1 I III F 1 F 2 F 1 F 2 2 Φ 2 (t) = Φ 1 (t) Φ 1 (t t). = Φ 1(t) t = ( 1.5e 0.5t 2.4e 4t 2e 10t ) τ < 0 t > τ Φ 2 (t) < 0 lim t Φ 2 (t) = 0 0 < t < τ I II 0 No.2 2 C x y x y > 0 x 0 x > b a dx
1 No.1 5 C 1 I III F 1 F 2 F 1 F 2 2 Φ 2 (t) = Φ 1 (t) Φ 1 (t t). = Φ 1(t) t = ( 1.5e 0.5t 2.4e 4t 2e 10t ) τ < 0 t > τ Φ 2 (t) < 0 lim t Φ 2 (t) = 0 0 < t < τ I II 0 No.2 2 C x y x y > 0 x 0 x > b a dx
